
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material such as coal,oil,and natural gas,formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. Fossil fuels may be burned to provide heat for use directly,to power engines,or to generate electricity. Some fossil fuels are refined into derivatives such as kerosene,gasoline and propane before burning. The origin of fossil fuels is the anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms,containing organic molecules created by photosynthesis. The conversion from these materials to high-carbon fossil fuels typically require a geological process of millions of years.

A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel,such as coal or natural gas,to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy,which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine,a gas turbine or,in small plants,a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas,either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist,all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.

Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly due to emissions from burning fossil fuels such as coal,oil,and natural gas. Mitigation can reduce emissions by transitioning to sustainable energy sources,conserving energy,and increasing efficiency. It is possible to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by enlarging forests,restoring wetlands and using other natural and technical processes. Experts call these processes carbon sequestration. Governments and companies have pledged to reduce emissions to prevent dangerous climate change in line with international negotiations to limit warming by reducing emissions.

Coal pollution mitigation,sometimes called clean coal,is a series of systems and technologies that seek to mitigate the health and environmental impact of coal;in particular air pollution from coal-fired power stations,and from coal burnt by heavy industry. Primary focus is on removing sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides,the most important gases which caused acid rain;and particulates which cause visible air pollution,illness,and premature deaths. Reducing fly ash reduces emissions of radioactive materials. Mercury emissions can be reduced up to 95%. Capturing carbon dioxide emissions from coal is also being pursued.
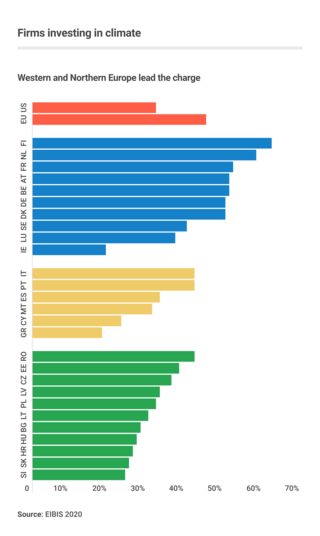
Business action on climate change includes a range of activities relating to climate change,and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation,such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change,especially in the United States,through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change,through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.

The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal,state,and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production,distribution,consumption,and modes of use,such as building codes,mileage standards,and commuting policies. Energy policy may be addressed via legislation,regulation,court decisions,public participation,and other techniques.

Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect,contributing to climate change. Carbon dioxide,from burning fossil fuels such as coal,oil,and natural gas,is one of the most important factors in causing climate change. The largest emitters are China followed by the US,although the United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Human-caused emissions have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied,but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year,higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2017 were 425±20 GtC from fossil fuels and industry,and 180±60 GtC from land use change. Land-use change,such as deforestation,caused about 31% of cumulative emissions over 1870–2017,coal 32%,oil 25%,and gas 10%.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020,the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG,followed by the United States with 11%,then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG,more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and,amongst the top eight emitters,is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person. However,the IEA estimates that the richest decile in the US emits over 55 tonnes of CO2 per capita each year. Because coal-fired power stations are gradually shutting down,in the 2010s emissions from electricity generation fell to second place behind transportation which is now the largest single source. In 2020,27% of the GHG emissions of the United States were from transportation,25% from electricity,24% from industry,13% from commercial and residential buildings and 11% from agriculture. In 2021,the electric power sector was the second largest source of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions,accounting for 25% of the U.S. total. These greenhouse gas emissions are contributing to climate change in the United States,as well as worldwide.

Fossil fuel phase-out is the gradual reduction of the use and production of fossil fuels to zero,to reduce deaths and illness from air pollution,limit climate change,and strengthen energy independence. It is part of the ongoing renewable energy transition,but is being hindered by fossil fuel subsidies.
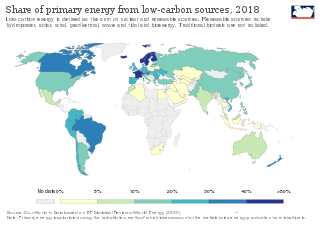
Low-carbon power is electricity produced with substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions over the entire lifecycle than power generation using fossil fuels. The energy transition to low-carbon power is one of the most important actions required to limit climate change. Power sector emissions may have peaked in 2018. During the first six months of 2020,scientists observed an 8.8% decrease in global CO2 emissions relative to 2019 due to COVID-19 lockdown measures. The two main sources of the decrease in emissions included ground transportation (40%) and the power sector (22%). This event is the largest absolute decrease in CO2 emissions in history,but emphasizes that low-carbon power "must be based on structural and transformational changes in energy-production systems".
Greenhouse gas emissions by Australia totalled 533 million tonnes CO2-equivalent based on greenhouse gas national inventory report data for 2019;representing per capita CO2e emissions of 21 tons,three times the global average. Coal was responsible for 30% of emissions. The national Greenhouse Gas Inventory estimates for the year to March 2021 were 494.2 million tonnes,which is 27.8 million tonnes,or 5.3%,lower than the previous year. It is 20.8% lower than in 2005. According to the government,the result reflects the decrease in transport emissions due to COVID-19 pandemic restrictions,reduced fugitive emissions,and reductions in emissions from electricity;however,there were increased greenhouse gas emissions from the land and agriculture sectors.
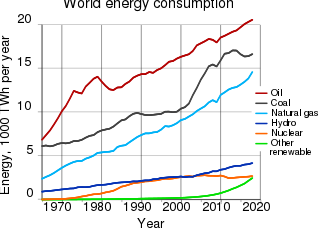
The environmental impact of the energy industry is significant,as energy and natural resource consumption are closely related. Producing,transporting,or consuming energy all have an environmental impact. Energy has been harnessed by human beings for millennia. Initially it was with the use of fire for light,heat,cooking and for safety,and its use can be traced back at least 1.9 million years. In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources. Scientific consensus on some of the main human activities that contribute to global warming are considered to be increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases,causing a warming effect,global changes to land surface,such as deforestation,for a warming effect,increasing concentrations of aerosols,mainly for a cooling effect.

The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China,and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. In total,the United States has emitted over 400 billion metric tons of greenhouse gasses,more than any country in the world.
The Climate Action Plan is an environmental plan by Barack Obama,the 44th President of the United States,that proposed a reduction in carbon dioxide emissions. It included preserving forests,encouraging alternate fuels,and increasing the study of climate change. The plan was first prepared in 2008 and was then updated every two years.

The Clean Power Plan was an Obama administration policy aimed at combating anthropogenic climate change that was first proposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in June 2014. The final version of the plan was unveiled by President Obama on August 3,2015. Each state was assigned an individual goal for reducing carbon emissions,which could be accomplished how they saw fit,but with the possibility of the EPA stepping in if the state refused to submit a plan. If every state met its target,the plan was projected to reduce carbon emissions from electricity generation 32% by 2030,relative to 2005 levels,as well as achieving various health benefits due to reduced air pollution.

The environmental policy of the Donald Trump administration represented a shift from the policy priorities and goals of the preceding Barack Obama administration. Where President Obama's environmental agenda prioritized the reduction of carbon emissions through the use of renewable energy with the goal of conserving the environment for future generations,the Trump administration policy was for the US to attain energy independence based on fossil fuel use and to rescind many environmental regulations. By the end of Trump's term,his administration had rolled back 98 environmental rules and regulations,leaving an additional 14 rollbacks still in progress. As of early 2021,the Biden administration was making a public accounting of regulatory decisions under the Trump administration that had been influenced by politics rather than science.
Fossil fuel regulations are part of the energy policy in the United States and have gained major significance with the nation's strong dependence on fossil fuel-based energy. Regulatory processes are established at the federal and state level due to the immense economic,socio-political and environmental impact of fossil fuel extraction and production. Over 80% of the United States' energy comes from fossil fuels such as coal,natural gas,and oil. The Bush administration was marked by the Energy Policy Act of 2005,which provided a monetary incentive for renewable energy adoption and addressed the issue of climate change. The Obama administration was made up of advocates for renewable energy and natural gas,while Donald Trump built his campaign on promises to revive the coal industry.

The 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference,more commonly referred to as COP26,was the 26th United Nations Climate Change conference,held at the SEC Centre in Glasgow,Scotland,United Kingdom,from 31 October to 13 November 2021. The president of the conference was UK cabinet minister Alok Sharma. Delayed for a year due to the COVID-19 pandemic,it was the 26th Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC),the third meeting of the parties to the 2015 Paris Agreement,and the 16th meeting of the parties to the Kyoto Protocol (CMP16).
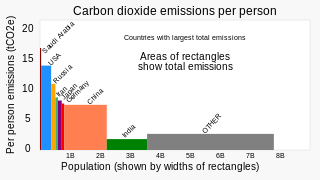
Greenhouse gas emissions by China are the largest of any country in the world both in production and consumption terms,and stem mainly from coal burning in China,including coal-fired power stations,coal mining,and blast furnaces producing iron and steel. When measuring production-based emissions,China emitted over 14 gigatonnes (Gt) CO2eq of greenhouse gases in 2019,27% of the world total. When measuring in consumption-based terms,which adds emissions associated with imported goods and extracts those associated with exported goods,China accounts for 13 gigatonnes (Gt) or 25% of global emissions.

Greenhouse gas emissionsbyRussia are mostly from fossil gas,oil and coal. Russia emits 2 or 3 billion tonnes CO2eq of greenhouse gases each year;about 4% of world emissions. Annual carbon dioxide emissions alone are about 12 tons per person,more than double the world average. Cutting greenhouse gas emissions,and therefore air pollution in Russia,would have health benefits greater than the cost. The country is the world's biggest methane emitter,and 4 billion dollars worth of methane was estimated to leak in 2019/20.

















