
A glacier is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water.

Granite is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers.

Magma is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and gas bubbles.
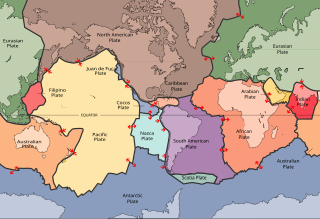
A lithosphere is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy.
Petroleum geology is the study of origin, occurrence, movement, accumulation, and exploration of hydrocarbon fuels. It refers to the specific set of geological disciplines that are applied to the search for hydrocarbons.

In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rifts, which eventually become rift valleys. Most active divergent plate boundaries occur between oceanic plates and exist as mid-oceanic ridges.

Andesite is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende.

Hydrocarbon exploration is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology.

Scree is a collection of broken rock fragments at the base of a cliff or other steep rocky mass that has accumulated through periodic rockfall. Landforms associated with these materials are often called talus deposits. Talus deposits typically have a concave upwards form, where the maximum inclination corresponds to the angle of repose of the mean debris particle size. The exact definition of scree in the primary literature is somewhat relaxed, and it often overlaps with both talus and colluvium.

Reginald Aldworth Daly was a Canadian geologist.

In geology, a dike or dyke is a sheet of rock that is formed in a fracture of a pre-existing rock body. Dikes can be either magmatic or sedimentary in origin. Magmatic dikes form when magma flows into a crack then solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. Clastic dikes are formed when sediment fills a pre-existing crack.
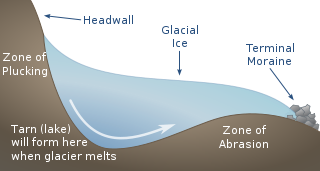
Plucking, also referred to as quarrying, is a glacial phenomenon that is responsible for the weathering and erosion of pieces of bedrock, especially large "joint blocks". This occurs in a type of glacier called a "valley glacier". As a glacier moves down a valley, friction causes the basal ice of the glacier to melt and infiltrate joints (cracks) in the bedrock. The freezing and thawing action of the ice enlarges, widens, or causes further cracks in the bedrock as it changes volume across the ice/water phase transition, gradually loosening the rock between the joints. This produces large pieces of rock called joint blocks. Eventually these joint blocks come loose and become trapped in the glacier.

Exfoliation joints or sheet joints are surface-parallel fracture systems in rock, and often leading to erosion of concentric slabs. (See Joint ).
In geology, igneous differentiation, or magmatic differentiation, is an umbrella term for the various processes by which magmas undergo bulk chemical change during the partial melting process, cooling, emplacement, or eruption. The sequence of magmas produced by igneous differentiation is known as a magma series.
A petroleum geologist is an earth scientist who works in the field of petroleum geology, which involves all aspects of oil discovery and production. Petroleum geologists are usually linked to the actual discovery of oil and the identification of possible oil deposits, gas caps, or leads. It can be a very labor-intensive task involving several different fields of science and elaborate equipment. Petroleum geologists look at the structural and sedimentary aspects of the stratum/strata to identify possible oil traps or tight shale plays.

Geodynamics is a subfield of geophysics dealing with dynamics of the Earth. It applies physics, chemistry and mathematics to the understanding of how mantle convection leads to plate tectonics and geologic phenomena such as seafloor spreading, mountain building, volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting. It also attempts to probe the internal activity by measuring magnetic fields, gravity, and seismic waves, as well as the mineralogy of rocks and their isotopic composition. Methods of geodynamics are also applied to exploration of other planets.
The methods of pluton emplacement are the ways magma is accommodated in a host rock where the final result is a pluton. The methods of pluton emplacement are not yet fully understood, but there are many different proposed pluton emplacement mechanisms. Stoping, diapirism and ballooning are the widely accepted mechanisms. There is now evidence of incremental emplacement of plutons.

Magmatic underplating occurs when basaltic magmas are trapped during their rise to the surface at the Mohorovičić discontinuity or within the crust. Entrapment of magmas within the crust occurs due to the difference in relative densities between the rising magma and the surrounding rock. Magmatic underplating can be responsible for thickening of the crust when the magma cools. Geophysical seismic studies utilize the differences in densities to identify underplating that occurs at depth.
Mountains are widely distributed across the surface of Io, the innermost large moon of Jupiter. There are about 115 named mountains; the average length is 157 km (98 mi) and the average height is 6,300 m (20,700 ft). The longest is 570 km (350 mi), and the highest is Boösaule Montes, at 17,500 metres (57,400 ft), taller than any mountain on Earth. Ionian mountains often appear as large, isolated structures; no global tectonic pattern is evident, unlike on Earth, where plate tectonics is dominant.

Volcanic and igneous plumbing systems (VIPS) consist of interconnected magma channels and chambers through which magma flows and is stored within Earth's crust. Volcanic plumbing systems can be found in all active tectonic settings, such as mid-oceanic ridges, subduction zones, and mantle plumes, when magmas generated in continental lithosphere, oceanic lithosphere, and in the sub-lithospheric mantle are transported. Magma is first generated by partial melting, followed by segregation and extraction from the source rock to separate the melt from the solid. As magma propagates upwards, a self-organised network of magma channels develops, transporting the melt from lower crust to upper regions. Channelled ascent mechanisms include the formation of dykes and ductile fractures that transport the melt in conduits. For bulk transportation, diapirs carry a large volume of melt and ascent through the crust. When magma stops ascending, or when magma supply stops, magma emplacement occurs. Different mechanisms of emplacement result in different structures, including plutons, sills, laccoliths and lopoliths.















