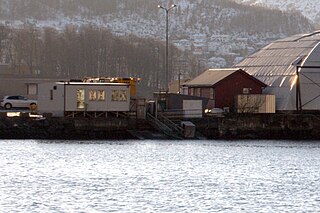Stordø Kisgruber was a Norwegian mining company which operated the pyrite mines in Litlabø at Stord in Hordaland, Norway. [1]

The mineral pyrite, or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula FeS2 (iron(II) disulfide). Pyrite is considered the most common of the sulfide minerals.

Litlabø is a village and former mining community in the municipality of Stord in Hordaland county, Norway. It is located at the northern side of the lake of Storavatnet, just northeast of the village of Sagvåg. The village had about 450 inhabitants as of 2001. Litlabø was the location for the pyrite mines of Stordø Kisgruber, which operated from 1907 to 1968.

Stord is a municipality in Hordaland county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Sunnhordland. Stord is sometimes called "Norway in miniature" since it has such a variety of landscapes: coastline, fjords, forests, agricultural land, and mountain areas. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Leirvik, which is also the largest town in the municipality and the whole region of Sunnhordland. Leirvik was declared a town in 1997. Other population centres in the municipality include the large village of Sagvåg and the smaller villages of Litlabø and Grov.
Mining for pyrite at Litlabø had first been estgablished in 1865. Stordø Kisgruber A/S was established in 1907 and maintained mining operations which ended in 1968. A total of about eight million tons of ore was won during the operation of the mine. Under the elevator tower is the main mine shaft which went straight down about 750 meters deep. Altogether there are 80 km of shafts into the mountain. A railway line operated between Litlabø and the quays at Sagvåg. [2] [3]

Sagvåg is a village in Stord municipality in Hordaland county, Norway. The village is located on the southwest coast of the island of Stord, about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) west of the town of Leirvik. The Stord Airport, Sørstokken lies about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) northwest of Sagvåg. Nysæter Church was built here in 1991 to serve the population of the village. The small mining village of Litlabø lies just northeast of Sagvåg.
During the Nazi occupation of Norway, the mines delivered pyrite to Germany for use by the country's war industry. During 1941, this amounted to 9,000 tons per month. In January 1943 the mines were targeted by the British Commando raid Operation Cartoon. Several dynamite charges were set off in various buildings at Litlabø. The hoist machine, the compressor house and the locomotive engine shed, among others, were blown up. [4]
Operation Cartoon was a British Commando raid on the island of Stord near Leirvik in Hordaland, Norway on the night of 23/24 January 1943. The operation was carried out by 53 men of No. 12 Commando supported by ten men from the Norwegian 10 (IA) Commando. RAF Coastal Command co-operated with the Commandos, with aircraft from 18 Group.
The Mining Museum at Litlabø (Norwegian : Gruvemuseet på Litlabø) was later established to commemorate the mines and the accompanying society. [5] [6]
Norwegian is a North Germanic language spoken mainly in Norway, where it is the official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties, and some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are hardly mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Era.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stordø Kisgruber . |
Coordinates: 59°47′30″N5°24′00″E / 59.79167°N 5.40000°E

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.