The Jakarta Messaging API is a Java application programming interface (API) for message-oriented middleware. It provides generic messaging models, able to handle the producer–consumer problem, that can be used to facilitate the sending and receiving of messages between software systems. Jakarta Messaging is a part of Jakarta EE and was originally defined by a specification developed at Sun Microsystems before being guided by the Java Community Process.
Middleware in the context of distributed applications is software that provides services beyond those provided by the operating system to enable the various components of a distributed system to communicate and manage data. Middleware supports and simplifies complex distributed applications. It includes web servers, application servers, messaging and similar tools that support application development and delivery. Middleware is especially integral to modern information technology based on XML, SOAP, Web services, and service-oriented architecture.

Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol is an open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML, it enables the near-real-time exchange of structured data between two or more network entities. Designed to be extensible, the protocol offers a multitude of applications beyond traditional IM in the broader realm of message-oriented middleware, including signalling for VoIP, video, file transfer, gaming and other uses.
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components typically used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter-thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the passing of control or of content. Group communication systems provide similar kinds of functionality.
Message-oriented middleware (MOM) is software or hardware infrastructure supporting sending and receiving messages between distributed systems. MOM allows application modules to be distributed over heterogeneous platforms and reduces the complexity of developing applications that span multiple operating systems and network protocols. The middleware creates a distributed communications layer that insulates the application developer from the details of the various operating systems and network interfaces. APIs that extend across diverse platforms and networks are typically provided by MOM.
Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) is a message queue implementation developed by Microsoft and deployed in its Windows Server operating systems since Windows NT 4 and Windows 95. Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 also includes this component. In addition to its mainstream server platform support, MSMQ has been incorporated into Microsoft Embedded platforms since 1999 and the release of Windows CE 3.0.
IBM MQ is a family of message-oriented middleware products that IBM launched in December 1993. It was originally called MQSeries, and was renamed WebSphere MQ in 2002 to join the suite of WebSphere products. In April 2014, it was renamed IBM MQ. The products that are included in the MQ family are IBM MQ, IBM MQ Advanced, IBM MQ Appliance, IBM MQ for z/OS, and IBM MQ on IBM Cloud. IBM MQ also has containerised deployment options.
Mule is a lightweight enterprise service bus (ESB) and integration framework provided by MuleSoft. The platform is Java-based but can broker interactions between other platforms such as .NET using web services or sockets.
The Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) is an open standard application layer protocol for message-oriented middleware. The defining features of AMQP are message orientation, queuing, routing, reliability and security.
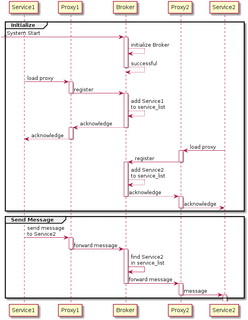
A message broker is an intermediary computer program module that translates a message from the formal messaging protocol of the sender to the formal messaging protocol of the receiver. Message brokers are elements in telecommunication or computer networks where software applications communicate by exchanging formally-defined messages. Message brokers are a building block of message-oriented middleware (MOM) but are typically not a replacement for traditional middleware like MOM and remote procedure call (RPC).
A message queueing service is a message-oriented middleware or MOM deployed in a compute cloud using software as a service model. Service subscribers access queues and or topics to exchange data using point-to-point or publish and subscribe patterns.

Apache Qpid is an open-source messaging system which implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP). It provides transaction management, queuing, distribution, security, management, clustering, federation and heterogeneous multi-platform support. The Apache Qpid API supports multiple programming languages and comes with both C++ and Java brokers.
Middleware analysts are computer software engineers with a specialization in products that connect two different computer systems together. These products can be open-source or proprietary. As the term implies, the software, tools, and technologies used by Middleware analysts sit "in-the-middle", between two or more systems; the purpose being to enable two systems to communicate and share information.
HornetQ is an open-source asynchronous messaging project from JBoss. It is an example of Message-oriented middleware. HornetQ is an open source project to build a multi-protocol, embeddable, very high performance, clustered, asynchronous messaging system. During much of its development, the HornetQ code base was developed under the name JBoss Messaging 2.0.
RabbitMQ is an open-source message-broker software that originally implemented the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) and has since been extended with a plug-in architecture to support Streaming Text Oriented Messaging Protocol (STOMP), MQ Telemetry Transport (MQTT), and other protocols.
ZeroMQ is an asynchronous messaging library, aimed at use in distributed or concurrent applications. It provides a message queue, but unlike message-oriented middleware, a ZeroMQ system can run without a dedicated message broker; the zero in the name is for zero broker. The library's API is designed to resemble Berkeley sockets.

Apache ActiveMQ is an open source message broker written in Java together with a full Java Message Service (JMS) client. It provides "Enterprise Features" which in this case means fostering the communication from more than one client or server. Supported clients include Java via JMS 1.1 as well as several other "cross language" clients. The communication is managed with features such as computer clustering and ability to use any database as a JMS persistence provider besides virtual memory, cache, and journal persistency.
MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe, machine to machine network protocol for Message queue/Message queuing service. It is designed for connections with remote locations that have devices with resource constraints or limited network bandwidth. It must run over a transport protocol that provides ordered, lossless, bi-directional connections—typically, TCP/IP. It is an open OASIS standard and an ISO recommendation.
Apache Kafka is a distributed event store and stream-processing platform. It is an open-source system developed by the Apache Software Foundation written in Java and Scala. The project aims to provide a unified, high-throughput, low-latency platform for handling real-time data feeds. Kafka can connect to external systems via Kafka Connect, and provides the Kafka Streams libraries for stream processing applications. Kafka uses a binary TCP-based protocol that is optimized for efficiency and relies on a "message set" abstraction that naturally groups messages together to reduce the overhead of the network roundtrip. This "leads to larger network packets, larger sequential disk operations, contiguous memory blocks [...] which allows Kafka to turn a bursty stream of random message writes into linear writes."

RocketMQ is a distributed messaging and streaming platform with low latency, high performance and reliability, trillion-level capacity and flexible scalability. It is the third generation distributed messaging middleware open sourced by Alibaba in 2012. On November 21, 2016, Alibaba donated RocketMQ to the Apache Software Foundation. Next year, on February 20, the Apache Software Foundation announced Apache RocketMQ as a Top-Level Project.




