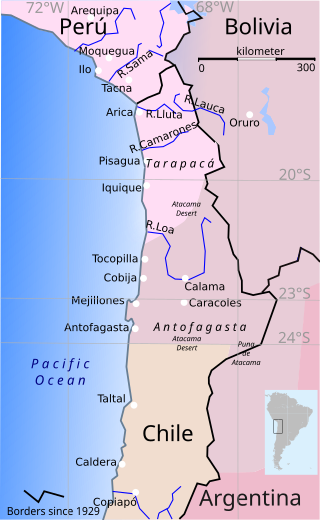
The War of the Pacific, also known by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Chilean claims on coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia.

Huáscar is an ironclad turret ship owned by the Chilean Navy built in 1865 for the Peruvian government. It is named after the 16th-century Inca emperor, Huáscar. She was the flagship of the Peruvian Navy and participated in the Battle of Pacocha and the War of the Pacific of 1879–1883. At the Battle of Angamos, Huáscar, captained by renowned Peruvian naval officer Miguel Grau Seminario, was captured by the Chilean fleet and commissioned into the Chilean Navy.

The Battle of Angamos was a naval encounter of the War of the Pacific fought between the navies of Chile and Perú at Punta Angamos, on 8 October 1879. The battle was the culminating point of a naval campaign that lasted about five months in which the Chilean Navy had the sole mission of eliminating its Peruvian counterpart. In the struggle, two armored frigates, led by Commodore Galvarino Riveros Cárdenas and Navy Captain Juan José Latorre battered and later captured the Peruvian monitor Huáscar, under Rear Admiral Miguel Grau Seminario.

The Chincha Islands War, also known as Spanish–South American War, was a series of coastal and naval battles between Spain and its former colonies of Peru, Chile, Ecuador, and Bolivia from 1865 to 1879. The conflict began with Spain's seizure of the guano-rich Chincha Islands in one of a series of attempts by Spain, under Isabella II, to reassert its influence over its former South American colonies. The war saw the use of ironclads, including the Spanish armoured frigate Numancia, the first ironclad to circumnavigate the world.

The Battle of Arica, also known as Assault and Capture of Cape Arica, was a battle in the War of the Pacific. It was fought on 7 June 1880, between the forces of Chile and Peru.

The Battle of Pisagua, was a landing operation of the War of the Pacific, fought on November 2, 1879, between Chile and the combined forces of Bolivia and Peru. The Chilean army commanded by Erasmo Escala, supported by the Chilean Fleet, launched an amphibious assault on the port of Pisagua and successfully drove the defending Bolivian-Peruvian forces, led by Gen. Juan Buendia, back from the shore. They established a beachhead that allowed an initial force of about 1,000 Chilean soldiers in two assault waves to disembark onto Peruvian territory at Pisagua in Tarapacá Department. This region was the principal territory in dispute.

The Battle of Punta Gruesa was a naval action that took place on May 21, 1879, during the War of the Pacific between Chile and Peru. This may be labelled as the second part of the Naval Battle of Iquique, although it is described in many sources as a separate battle.
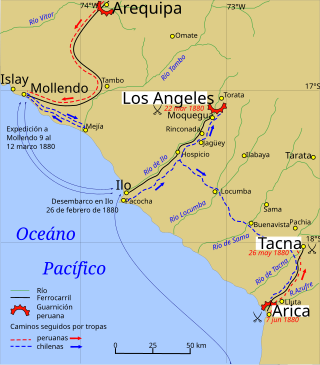
The Tacna and Arica campaign is known as the stage of the War of the Pacific after the Chilean conquest of the Peruvian department of Tarapacá, ending with Chilean domination of the Moquegua department in southern Peru. During this campaign Bolivia retired from the war after the Battle of Tacna, and Peru lost the port of Arica. Also, Manuel Baquedano assumed command as the new Commander in Chief of the Chilean Army, and the Allied Presidents were thrown out of office and replaced by Nicolas de Pierola in Peru and General Narciso Campero in Bolivia.

The Naval campaign of the War of the Pacific or Saltpeter war, was a naval campaign that took place from 1879 to 1884, involving Peru, and Chile, undertaken in order to support land forces in the Atacama Desert. Although the conflict lasted until 1884, the primary naval engagements occurred between 1879 and 1880. Due to the rough terrain and few transport methods it was imperative to have control of the ports in order to have a good supply source in the region. It resulted in a successful campaign by Chile, and the success of their land campaigns eventually led to a Chilean victory, which cut off Bolivia's access to the coast.

After the naval campaign of the War of the Pacific was resolved, the Chilean terrestrial invasion began.

The Chilean occupation of Peru began on November 2, 1879, with the beginning of the Tarapacá campaign during the War of the Pacific. The Chilean Army successfully defeated the Peruvian Army and occupied the southern Peruvian territories of Tarapacá, Arica and Tacna. By January 1881, the Chilean army had reached Lima, and on January 17 of the same year, the occupation of Lima began.

The Maritime history of Chile started when Chile gained independence, but traces it origin in the colonial era and has ultimately origin in the seafaring tradition of the Iberian Peninsula, Europe and the Mediterranean as well as from indigenous peoples of Chile.

The Battle of Iquique was a naval engagement on 21 May 1879, during the War of the Pacific, where a Chilean corvette commanded by Arturo Prat Chacón faced a Peruvian ironclad under Miguel Grau Seminario. The battle occurred off the port of Iquique, Peru, and ended with the sinking of the Chilean wooden corvette Esmeralda by the Peruvian ironclad Huáscar after four hours of combat, marking a victory for Peru.

The Tarapacá campaign was a short stage of the War of the Pacific in the last months of 1879, after the Chileans won definitive naval superiority at Angamos. It took its name from the region where it was fought.

Juan Bravo (1865–?) was a Chilean Navy sailor of Mapuche origin, hero of the naval Battle of Punta Gruesa during the War of the Pacific. Juan Bravo distinguished himself in the Battle of Punta Gruesa where he, while on board the schooner Covadonga, sniped down numerous Peruvians on board the ironclad Independencia.

The Naval Battle of Arica was a naval battle which took place on 27 February 1880 during the Blockade of Arica as part of the War of the Pacific.

BAP Unión was a corvette of the Peruvian Navy, originally ordered by the government of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. Built in France it was bought by the Peruvian Navy and during its service participated in the Chincha Islands War and in the War of the Pacific in which it was scuttled following the Blockade of Callao to prevent it falling into Chilean hands. The current Peruvian training ship; BAP Unión, is named after this vessel.

The Raids of the Huáscar were a series of raids that occurred by the Peruvian ironclad Huáscar under the command of Miguel Grau Seminario during the War of the Pacific. The actions kept the Chilean government in check for nearly five months which ended after the Battle of Angamos.

The First Battle of Antofagasta or the Bombardment of Antofagasta took place during the War of the Pacific. It was the first nightly raid of the War as well as the first raid of the Huáscar in a campaign to destroy and capture Chilean ports and ships.

The Rupture of the Blockade of Arica was a naval battle of the War of the Pacific during the Blockade of Arica. The rupture was carried out by Manuel Villavicencio who commanded the BAP Unión of the Peruvian Navy. The Unión broke the Chilean blockade of the port twice in less than 8 hours on March 17, 1880.



















