Related Research Articles

Uintah County is a county in the U.S. state of Utah. As of the 2020 United States Census the population was 35,620. Its county seat and largest city is Vernal. The county was named for the portion of the Ute Indian tribe that lived in the basin.

Duchesne is a city in and the county seat of Duchesne County, Utah, United States. The population was 1,588 at the 2020 census.

The Colorado River is one of the principal rivers in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The 1,450-mile-long (2,330 km) river, the 5th longest in the United States, drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. states and two Mexican states. The name Colorado derives from the Spanish language for "colored reddish" due to its heavy silt load. Starting in the central Rocky Mountains of Colorado, it flows generally southwest across the Colorado Plateau and through the Grand Canyon before reaching Lake Mead on the Arizona–Nevada border, where it turns south toward the international border. After entering Mexico, the Colorado approaches the mostly dry Colorado River Delta at the tip of the Gulf of California between Baja California and Sonora.

The Green River, located in the western United States, is the chief tributary of the Colorado River. The watershed of the river, known as the Green River Basin, covers parts of the U.S. states of Wyoming, Utah, and Colorado. The Green River is 730 miles (1,170 km) long, beginning in the Wind River Mountains of Wyoming and flowing through Wyoming and Utah for most of its course, except for a short segment of 40 miles (64 km) in western Colorado. Much of the route traverses the arid Colorado Plateau, where the river has carved some of the most spectacular canyons in the United States. The Green is slightly smaller than Colorado when the two rivers merge but typically carries a larger load of silt. The average yearly mean flow of the river at Green River, Utah is 6,121 cubic feet (173.3 m3) per second.

The Bear River is the largest tributary of the Great Salt Lake, draining a mountainous area and farming valleys northeast of the lake and southeast of the Snake River Plain. It flows through northeastern Utah, southwestern Wyoming, southeastern Idaho, and back into northern Utah, in the United States. Approximately 350 miles (560 km) long it is the longest river in North America that does not ultimately reach the sea.

The Sevier River is a 400-mile (640 km)-long river in the Great Basin of southwestern Utah in the United States. Originating west of Bryce Canyon National Park, the river flows north through a chain of high farming valleys and steep canyons along the west side of the Sevier Plateau before turning southwest and terminating in the endorheic basin of Sevier Lake in the Sevier Desert. It is used extensively for irrigation along its course, with the consequence that Sevier Lake is usually dry.

The Pick–Sloan Missouri Basin Program, formerly called the Missouri River Basin Project, was initially authorized by the Flood Control Act of 1944, which approved the plan for the conservation, control, and use of water resources in the Missouri River Basin.

Ashley National Forest is a National Forest located in northeastern Utah and southwestern Wyoming. Within the Forest's bounds are 1,382,346 acres (5,594 km2) of vast forests, lakes, and mountains, with elevations ranging from 6,000 to 13,500 feet. The forest covers portions of Daggett, Duchesne, Summit, Uintah, and Utah counties in Utah and Sweetwater County in Wyoming. Some of the most popular landmarks located in the forest include the Flaming Gorge National Recreation Area and the Uinta Mountains, which contains the highest mountain peak in Utah. The forest also includes 276,175 acres (1,117.64 km2), or about 60.5%, of the High Uintas Wilderness. The headquarters for the Ashley National Forest are located in Vernal, Utah with ranger district offices in Vernal; Duchesne, Utah; Roosevelt, Utah; Manila, Utah; and Green River, Wyoming.

The Weber River is a c. 125-mile (201 km) long river of northern Utah, United States. It begins in the northwest of the Uinta Mountains and empties into the Great Salt Lake. The Weber River was named for American fur trapper John Henry Weber.
Strawberry Reservoir is a large reservoir in the U.S. state of Utah, located on the Strawberry River. It is Utah's most popular fishery, receiving over 1.5 million angling hours annually and is part of the Blue Ribbon Fisheries program. Game fish in the reservoir include sterilized rainbow trout, bear lake cutthroat trout, kokanee salmon and crayfish. It is located 23 miles (37 km) southeast of Heber, Utah on U.S. Route 40. The reservoir is situated in Strawberry Valley. This valley is normally part of the Colorado River drainage. The dam was constructed to divert water into Utah Valley.
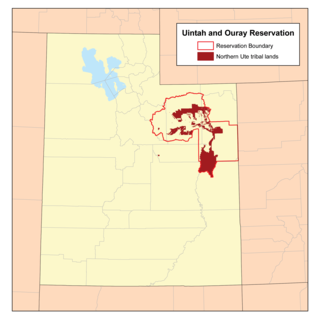
The Uintah and Ouray Indian Reservation is located in northeastern Utah, United States. It is the homeland of the Ute Indian Tribe, and is the largest of three Indian reservations inhabited by members of the Ute Tribe of Native Americans.

The Uinta Basin is a physiographic section of the larger Colorado Plateaus province, which in turn is part of the larger Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. It is also a geologic structural basin in eastern Utah, east of the Wasatch Mountains and south of the Uinta Mountains. The Uinta Basin is fed by creeks and rivers flowing south from the Uinta Mountains. Many of the principal rivers flow into the Duchesne River which feeds the Green River—a tributary of the Colorado River. The Uinta Mountains form the northern border of the Uinta Basin. They contain the highest point in Utah, Kings Peak, with a summit 13,528 feet above sea level. The climate of the Uinta Basin is semi-arid, with occasionally severe winter cold.

The Ute Indian Tribe of the Uinta and Ouray Reservation is a federally recognized tribe of Indians in northeastern Utah, United States. Three bands of Utes comprise the Ute Indian Tribe: the Whiteriver Band, the Uncompahgre Band and the Uintah Band. The Tribe has a membership of more than three thousand individuals, with over half living on the Uintah and Ouray Indian Reservation. The Ute Indian Tribe operates its own tribal government and oversees approximately 1.3 million acres of trust land which contains significant oil and gas deposits.
The Central Utah Project is a United States federal water project that was authorized for construction under the Colorado River Storage Project Act of April 11, 1956, as a participating project. In general, the Central Utah Project develops a portion of Utah's share of the yield of the Colorado River, as set out in the Colorado River Compact of 1922.
The Uintah Indian Irrigation Project is the principal Indian irrigation project in the Uintah Basin. The United States Bureau of Indian Affairs designed and constructed this project. The project was authorized in 1906, soon after the US Indian Irrigation Service was established as part of the Bureau of Indian Affairs. However, non-Indian irrigators largely controlled the infrastructure, generally benefiting more from the project than Ute Indians in the Uinta Basin.
In Section 203(a) of the Central Utah Project Completion Act, the United States Congress authorized a federally authorized and funded replacement project to replace the Uinta and Upalco Units of the Central Utah Project (CUP) which were not constructed. The replacement project is the Uinta Basin Replacement Project (UBRP). The UBRP will provide: 2,500 acre-feet (3,100,000 m3) of irrigation water; 3,000 acre-feet (3,700,000 m3) of municipal and industrial water; reduced wilderness impacts; increased instream flows; and improved recreation. Design work began in 2002. Construction began in 2004 and is anticipated to be completed in 2011. The Central Utah Water Conservancy District is responsible for construction. The United States Department of the Interior oversees funding and compliance with law and environmental regulation.

Fred Hayes State Park at Starvation is a state park in Duchesne County, Utah, United States, featuring the 3,495-acre (1,414 ha) Starvation Reservoir. The park is 4 miles (6.4 km) northwest of the city of Duchesne.
Strawberry is an unincorporated community in western Duchesne County, Utah, United States. Most of the inhabitants live along the Strawberry River between the Strawberry River pinnacles and Starvation Reservoir west of the city of Duchesne, the county seat of Duchesne County.

The Duchesne River, located in the Uintah Basin region of Utah in the western United States, is a tributary of the Green River. The watershed of the river covers the Northeastern corner of Utah. The Duchesne River is 115 miles (185 km) long, and drains a total land area of 3,790 square miles (9,800 km2).

Soldier Creek Dam is an earthen dam on the Strawberry River, located within the Uinta National Forest in southern Wasatch County, Utah, United States.
References
- ↑ William D. Rowley, The Bureau of Reclamation: Origins and Growth to 1945, vol. 1, (US Department of the Interior, 2006).
- ↑ Kathryn L. MacKay, "The Strawberry Valley Reclamation Project and the Opening of the Uintah Indian Reservation," Utah Historical Quarterly 50 no 1 (1982)
- ↑ Thomas G. Alexander, "An Investment in Progress: Utah's First Reclamation Project, the Strawberry Valley Project," Utah Historical Quarterly 39 no 3 (1971)