Yellow Dog Linux (YDL) is a discontinued free and open-source operating system for high-performance computing on multi-core processor computer architectures, focusing on GPU systems and computers using the POWER7 processor. The original developer was Terra Soft Solutions, which was acquired by Fixstars in October 2008. Yellow Dog Linux was first released in the spring of 1999 for Apple Macintosh PowerPC-based computers. The most recent version, Yellow Dog Linux 7, was released on August 6, 2012. Yellow Dog Linux lent its name to the popular YUM Linux software updater, derived from YDL's YUP and thus called Yellowdog Updater, Modified.

Kodi is a free and open-source media player and technology convergence software application developed by the Kodi Foundation, a non-profit technology consortium. Kodi is available for multiple operating systems and hardware platforms, with a software 10-foot user interface for use with televisions and remote controls. It allows users to play and view most streaming media, such as videos, music, podcasts, and videos from the Internet, as well as all common digital media files from local and network storage media, or TV gateway viewer.

QEMU is a free and open-source emulator. It emulates a computer's processor through dynamic binary translation and provides a set of different hardware and device models for the machine, enabling it to run a variety of guest operating systems. It can interoperate with Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) to run virtual machines at near-native speed. QEMU can also do emulation for user-level processes, allowing applications compiled for one processor architecture to run on another.
Homebrew, when applied to video games, refers to software produced by hobbyists for proprietary video game consoles which are not intended to be user-programmable. The official documentation is often only available to licensed developers, and these systems may use storage formats that make distribution difficult, such as ROM cartridges or encrypted CD-ROMs. Many consoles have hardware restrictions to prevent unauthorized development.

Gnash is a media player for playing SWF files. Gnash is available both as a standalone player for desktop computers and embedded devices, as well as a plugin for the browsers still supporting NPAPI. It is part of the GNU Project and is a free and open-source alternative to Adobe Flash Player. It was developed from the gameswf project.
The following is a timeline of virtualization development. In computing, virtualization is the use of a computer to simulate another computer. Through virtualization, a host simulates a guest by exposing virtual hardware devices, which may be done through software or by allowing access to a physical device connected to the machine.
Orb was a freeware streaming software that enabled users to remotely access all their personal digital media files including pictures, music, videos and television. It could be used from any Internet-enabled device, including laptops, pocket PC, smartphones, PS3, Xbox 360 and Wii video game consoles.

Remote Play is a feature of Sony video game consoles that allow the PlayStation 3, PlayStation 4 and PlayStation 5 to transmit video and audio output to another device; previously this could only be a PlayStation Portable or PlayStation Vita. In 2014, it was expanded to include the use of PlayStation TV, Xperia smartphones and tablets, and PlayStation Now. In 2016, it was expanded to Microsoft Windows PCs and macOS. In 2019, support for Android and iOS devices was eventually added. Support for remote play of PlayStation 5 games to other devices was added in November 2020 just prior to the new console's launch.

Parallels Desktop for Mac is software providing hardware virtualization for Macintosh computers with Intel processors, and since version 16.5 also for Apple silicon-based Macintosh computers. It is developed by Parallels, since 2018 a subsidiary of Corel.
OtherOS is a feature of early versions of the PlayStation 3 video game console, allowing user installed software, such as Linux or FreeBSD. The feature was removed since system firmware update 3.21, released on April 1, 2010.

Microsoft Hyper-V, codenamed Viridian, and briefly known before its release as Windows Server Virtualization, is a native hypervisor; it can create virtual machines on x86-64 systems running Windows. Starting with Windows 8, Hyper-V superseded Windows Virtual PC as the hardware virtualization component of the client editions of Windows NT. A server computer running Hyper-V can be configured to expose individual virtual machines to one or more networks. Hyper-V was first released with Windows Server 2008, and has been available without additional charge since Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8. A standalone Windows Hyper-V Server is free, but has a command-line interface only. The last version of free Hyper-V Server is Hyper-V Server 2019, which is based on Windows Server 2019.

Crysis 2 is a first-person shooter video game developed by Crytek, published by Electronic Arts and released in North America, Australia and Europe in March 2011 for Microsoft Windows, PlayStation 3, and Xbox 360. Officially announced on June 1, 2009, the game is the second main installment of the Crysis series, and a sequel to the 2007 video game Crysis, and its expansion Crysis Warhead. The story was written by Richard Morgan, while Peter Watts was consulted and wrote a novel adaptation of the game. It was the first game to showcase the CryEngine 3 game engine and the first game using the engine to be released on consoles. A sequel, Crysis 3, was released in 2013. A remastered version, titled Crysis 2 Remastered and following in the steps of Crysis Remastered, was released in 2021 for Nintendo Switch, PlayStation 4, Windows, and Xbox One, also bundled as part of the Crysis Remastered Trilogy compilation.
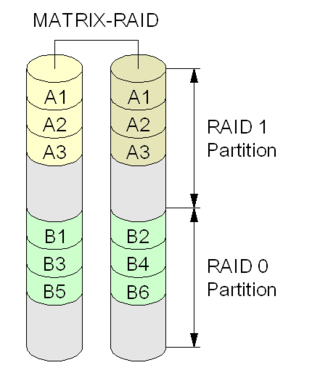
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a driver SATA AHCI and a firmware-based RAID solution built into a wide range of Intel chipsets. Currently also is installed as a driver for Intel Optane temporary storage units.

The Skytone Alpha-400 is a Linux-based low-cost netbook with a 7 in 800×480 LCD screen, introduced in 2008. Its measurements (length×width×depth) are 210 mm × 140 mm × 32 mm and it weighs 0.65 kg.

OnLive was a provider of cloud virtualization technologies based in Mountain View, California. OnLive's flagship product was its cloud gaming service, which allowed subscribers to rent or demo computer games without installing them. Games were delivered as streaming video rendered by the service's servers, rather than running on the local device. This setup allowed the games to run on computers and devices that would normally be unable to run them due to insufficient hardware. OnLive also enabled other features such as the ability for players to record game-play and to spectate.
Cloud gaming, sometimes called gaming on demand or game streaming, is a type of online gaming that runs video games on remote servers and streams the game's output directly to a user's device, or more colloquially, playing a game remotely from a cloud. It contrasts with traditional means of gaming, wherein a game is run locally on a user's video game console, personal computer, or mobile device.

Wireless Display (WiDi) is technology developed by Intel that enables users to stream music, movies, photos, videos and apps without cables from a compatible computer to a compatible HDTV or through the use of an adapter with other HDTVs or computer monitors. Intel WiDi supports HD 1080p video quality, 5.1 surround sound, and low latency for interacting with applications sent to the TV from a PC running Windows 7 or later.
SteamOS is a Linux distribution developed by Valve. It incorporates Valve's popular namesake Steam video game storefront and is the primary operating system for the Steam Deck, Valve's portable gaming device, as well as Valve's earlier Steam Machines. SteamOS is open source with some closed source components.
Jellyfin is a free and open-source media server and suite of multimedia applications designed to organize, manage, and share digital media files to networked devices. Jellyfin consists of a server application installed on a machine running Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux or in a Docker container, and another application running on a client device such as a smartphone, tablet, smart TV, streaming media player, game console or in a web browser. Jellyfin also can serve media to DLNA and Chromecast-enabled devices. It is a fork of Emby.













