
Futaba is a town in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 April 2020, the town had an actual population of zero, although as of 2017, the official registered population was 6,093 in 2,301 households. The total area of the town is 51.42 square kilometres (19.85 sq mi). As of March 2011, the entire population was evacuated as a result of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. However in the decade since then, 3% of the town has been open to visitors and residents, with the first residents returning on a permanent basis as of February 2022.

Namie is a town located in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. As of 29 February 2020 the town has a population of 1,238 in 794 households, although the official registered population was 17,114 in 6853 households. The total area of the town is 223.14 square kilometres (86.15 sq mi). The town was evacuated as a result of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster—being directly downwind from the power plant—and was within the exclusion zone set up in response to the disaster. Following ongoing clean-up efforts, Namie's business district and town hall have reopened, but access to more heavily contaminated western parts of the town remains restricted.

Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Incorporated, also known as Toden or TEPCO, is a Japanese electric utility holding company servicing Japan's Kantō region, Yamanashi Prefecture, and the eastern portion of Shizuoka Prefecture. This area includes Tokyo. Its headquarters are located in Uchisaiwaicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo, and international branch offices exist in Washington, D.C., and London. It is a founding member of strategic consortiums related to energy innovation and research; such as JINED, INCJ and MAI.

Prior to the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, Japan had generated 30% of its electrical power from nuclear reactors and planned to increase that share to 40%. Nuclear power energy was a national strategic priority in Japan. As of March 2020, of the 54 nuclear reactors in Japan, there were 42 operable reactors but only 9 reactors in 5 power plants were actually operating. A total of 24 reactors are scheduled for decommissioning or are in the process of being decommissioned. Others are in the process of being reactivated, or are undergoing modifications aimed to improve resiliency against natural disasters; Japan's 2030 energy goals posit that at least 33 will be reactivated by a later date.

The Onagawa Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power plant located on a 1,730,000 m2 site in Onagawa in the Oshika District and Ishinomaki city, Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It is managed by the Tohoku Electric Power Company. It was the most quickly constructed nuclear power plant in the world.

The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is a disabled nuclear power plant located on a 3.5-square-kilometre (860-acre) site in the towns of Ōkuma and Futaba in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. The plant suffered major damage from the magnitude 9.0 earthquake and tsunami that hit Japan on March 11, 2011. The chain of events caused radiation leaks and permanently damaged several of its reactors, making them impossible to restart. The working reactors were not restarted after the events.

The Fukushima Daini Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear power plant located on a 150 ha (370-acre) site in the town of Naraha and Tomioka in the Futaba District of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. The Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) runs the plant.

On 11 March 2011, at 14:46 JST, a 9.0–9.1 undersea megathrust earthquake occurred in the Pacific Ocean, 72 km (45 mi) east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region. It lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the "Great East Japan Earthquake", among other names. The disaster is often referred to as simply 3.11.

On 11 March 2011, a nuclear accident occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which remains the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan. The earthquake triggered a powerful tsunami, with 13- to 14-meter-high waves damaging the nuclear power plant's emergency diesel generators, leading to a loss of electric power. The result was the most severe nuclear accident since the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, classified as level seven on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES) after initially being classified as level five, and thus joining Chernobyl as the only other accident to receive such classification. While the 1957 explosion at the Mayak facility was the second worst by radioactivity released, the INES ranks incidents by impact on population, so Chernobyl and Fukushima rank higher than the 10,000 evacuated from the Mayak site in the rural southern Urals.

The Japanese reaction occurred after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, following the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. A nuclear emergency was declared by the government of Japan on 11 March. Later Prime Minister Naoto Kan issued instructions that people within a 20 km (12 mi) zone around the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant must leave, and urged that those living between 20 km and 30 km from the site to stay indoors. The latter groups were also urged to evacuate on 25 March.

The aftermath of the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami included both a humanitarian crisis and massive economic impacts. The tsunami created over 300,000 refugees in the Tōhoku region of Japan, and resulted in shortages of food, water, shelter, medicine and fuel for survivors. 15,900 deaths have been confirmed. In response to the crisis, the Japanese government mobilized the Self-Defence Forces, while many countries sent search and rescue teams to help search for survivors. Aid organizations both in Japan and worldwide also responded, with the Japanese Red Cross reporting $1 billion in donations. The economic impact included both immediate problems, with industrial production suspended in many factories, and the longer term issue of the cost of rebuilding which has been estimated at ¥10 trillion.

Masao Yoshida was a nuclear engineer who served as plant manager of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant during the Fukushima nuclear disaster.
The Investigation Committee on the Accident at the Fukushima Nuclear Power Stations of Tokyo Electric Power Company was formed June 7, 2011 by the Japanese government as an independent body to investigate the March Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. The Investigation Committee issued an interim report in December 2011, and issued its final report in July 2012.

3.11: Surviving Japan is a documentary film about the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in Japan written and directed by volunteer and resident Christopher Noland.

The Reconstruction Agency is an agency of the Japanese government established on February 10, 2012 to coordinate reconstruction activities related to the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.

Long one of the world's most committed promoters of civilian nuclear power, Japan's nuclear industry was not hit as hard by the effects of the 1979 Three Mile Island accident (USA) or the 1986 Chernobyl disaster (USSR) as some other countries. Construction of new plants continued to be strong through the 1980s and into the 1990s. However, starting in the mid-1990s there were several nuclear related accidents and cover-ups in Japan that eroded public perception of the industry, resulting in protests and resistance to new plants. These accidents included the Tokaimura nuclear accident, the Mihama steam explosion, cover-ups after accidents at the Monju reactor, and the 21 month shut down of the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant following an earthquake in 2007. Because of these events, Japan's nuclear industry has been scrutinized by the general public of the country.

Unit 3 of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant was one of the reactors in operation on 11 March 2011, when the plant was struck by the tsunami produced by the Tohoku earthquake. In the aftermath, the reactor experienced hydrogen gas explosions and suffered a partial meltdown, along with the other two reactors in operation at the time the tsunami struck, unit 1 and unit 2. Efforts to remove debris and coolant water contaminated with radiation are ongoing and expected to last several decades.

The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident was a series of equipment failures, nuclear meltdowns, and releases of radioactive materials at the Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant, following the Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami on 11 March 2011. It was the largest nuclear disaster since the Chernobyl disaster of 1986, and the radiation released exceeded official safety guidelines. Despite this, there were no deaths caused by acute radiation syndrome. Given the uncertain health effects of low-dose radiation, cancer deaths cannot be ruled out. However, studies by the World Health Organisation and Tokyo University have shown that no discernible increase in the rate of cancer deaths is expected. Predicted future cancer deaths due to accumulated radiation exposures in the population living near Fukushima have ranged in the academic literature from none to hundreds.

Investigations into the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster (or Accident) began on 11 March 2011 when a series of equipment failures, core melt and down, and releases of radioactive materials occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station from the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake and tsunami on the same day.
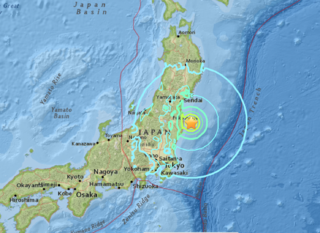
The 2016 Fukushima earthquake struck Japan east-southeast of Namie, Fukushima Prefecture at 05:59 JST on November 22 with depth of 11.4 km (7.1 mi). The shock had a maximum intensity of VII (Very strong) on the Mercalli scale. The earthquake was initially reported as a 7.3 magnitude by Japan Meteorological Agency, and was later revised to 7.4, while the United States Geological Survey and GFZ Potsdam determined a magnitude of 6.9.















