
Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and joints' that create the form and shape of human-made structures. Structural engineers also must understand and calculate the stability, strength, rigidity and earthquake-susceptibility of built structures for buildings and nonbuilding structures. The structural designs are integrated with those of other designers such as architects and building services engineer and often supervise the construction of projects by contractors on site. They can also be involved in the design of machinery, medical equipment, and vehicles where structural integrity affects functioning and safety. See glossary of structural engineering.

Forensic engineering has been defined as "the investigation of failures—ranging from serviceability to catastrophic—which may lead to legal activity, including both civil and criminal". The forensic engineering field is very broad in terms of the many disciplines that it covers, investigations that use forensic engineering are case of environmental damages to structures, system failures of machines, explosions, electrical, fire point of origin, vehicle failures and many more.

Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band, or dislocation.
The field of strength of materials typically refers to various methods of calculating the stresses and strains in structural members, such as beams, columns, and shafts. The methods employed to predict the response of a structure under loading and its susceptibility to various failure modes takes into account the properties of the materials such as its yield strength, ultimate strength, Young's modulus, and Poisson's ratio. In addition, the mechanical element's macroscopic properties such as its length, width, thickness, boundary constraints and abrupt changes in geometry such as holes are considered.

In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure.
Stress–strain analysis is an engineering discipline that uses many methods to determine the stresses and strains in materials and structures subjected to forces. In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighboring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material.

In solid mechanics, a stress concentration is a location in an object where the stress is significantly greater than the surrounding region. Stress concentrations occur when there are irregularities in the geometry or material of a structural component that cause an interruption to the flow of stress. This arises from such details as holes, grooves, notches and fillets. Stress concentrations may also occur from accidental damage such as nicks and scratches.
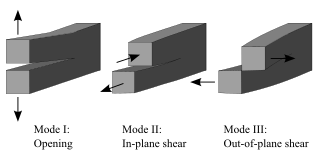
Fracture mechanics is the field of mechanics concerned with the study of the propagation of cracks in materials. It uses methods of analytical solid mechanics to calculate the driving force on a crack and those of experimental solid mechanics to characterize the material's resistance to fracture.
In engineering, damage tolerance is a property of a structure relating to its ability to sustain defects safely until repair can be effected. The approach to engineering design to account for damage tolerance is based on the assumption that flaws can exist in any structure and such flaws propagate with usage. This approach is commonly used in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, and civil engineering to manage the extension of cracks in structure through the application of the principles of fracture mechanics. A structure is considered to be damage tolerant if a maintenance program has been implemented that will result in the detection and repair of accidental damage, corrosion and fatigue cracking before such damage reduces the residual strength of the structure below an acceptable limit.
Failure causes are defects in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying cause of a failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Where failure depends on the user of the product or process, then human error must be considered.
Failure analysis is the process of collecting and analyzing data to determine the cause of a failure, often with the goal of determining corrective actions or liability. According to Bloch and Geitner, ”machinery failures reveal a reaction chain of cause and effect… usually a deficiency commonly referred to as the symptom…”. Failure analysis can save money, lives, and resources if done correctly and acted upon. It is an important discipline in many branches of manufacturing industry, such as the electronics industry, where it is a vital tool used in the development of new products and for the improvement of existing products. The failure analysis process relies on collecting failed components for subsequent examination of the cause or causes of failure using a wide array of methods, especially microscopy and spectroscopy. Nondestructive testing (NDT) methods are valuable because the failed products are unaffected by analysis, so inspection sometimes starts using these methods.
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to structural engineering. For a broad overview of engineering, please see List of engineering topics. For biographies please see List of engineers.
Failing badly and failing well are concepts in systems security and network security describing how a system reacts to failure. The terms have been popularized by Bruce Schneier, a cryptographer and security consultant.
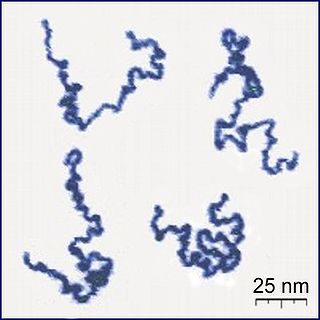
Forensic polymer engineering is the study of failure in polymeric products. The topic includes the fracture of plastic products, or any other reason why such a product fails in service, or fails to meet its specification. The subject focuses on the material evidence from crime or accident scenes, seeking defects in those materials that might explain why an accident occurred, or the source of a specific material to identify a criminal. Many analytical methods used for polymer identification may be used in investigations, the exact set being determined by the nature of the polymer in question, be it thermoset, thermoplastic, elastomeric or composite in nature.
Material failure theory is an interdisciplinary field of materials science and solid mechanics which attempts to predict the conditions under which solid materials fail under the action of external loads. The failure of a material is usually classified into brittle failure (fracture) or ductile failure (yield). Depending on the conditions most materials can fail in a brittle or ductile manner or both. However, for most practical situations, a material may be classified as either brittle or ductile.
Metallurgical failure analysis is the process to determine the mechanism that has caused a metal component to fail. It can identify the cause of failure, providing insight into the root cause and potential solutions to prevent similar failures in the future, as well as culpability, which is important in legal cases. Resolving the source of metallurgical failures can be of financial interest to companies. The annual cost of corrosion in the United States was estimated by NACE International in 2012 to be $450 billion a year, a 67% increase compared to estimates for 2001. These failures can be analyzed to determine their root cause, which if corrected, would save reduce the cost of failures to companies.

According to the classical theories of elastic or plastic structures made from a material with non-random strength (ft), the nominal strength (σN) of a structure is independent of the structure size (D) when geometrically similar structures are considered. Any deviation from this property is called the size effect. For example, conventional strength of materials predicts that a large beam and a tiny beam will fail at the same stress if they are made of the same material. In the real world, because of size effects, a larger beam will fail at a lower stress than a smaller beam.

Structural integrity and failure is an aspect of engineering that deals with the ability of a structure to support a designed structural load without breaking and includes the study of past structural failures in order to prevent failures in future designs.

Engineering disasters often arise from shortcuts in the design process. Engineering is the science and technology used to meet the needs and demands of society. These demands include buildings, aircraft, vessels, and computer software. In order to meet society’s demands, the creation of newer technology and infrastructure must be met efficiently and cost-effectively. To accomplish this, managers and engineers need a mutual approach to the specified demand at hand. This can lead to shortcuts in engineering design to reduce costs of construction and fabrication. Occasionally, these shortcuts can lead to unexpected design failures.

Fatigue testing is a specialised form of mechanical testing that is performed by applying cyclic loading to a coupon or structure. These tests are used either to generate fatigue life and crack growth data, identify critical locations or demonstrate the safety of a structure that may be susceptible to fatigue. Fatigue tests are used on a range of components from coupons through to full size test articles such as automobiles and aircraft.












