
In meteorology, a cyclone is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above. Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale. Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within the smaller mesoscale.

Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity. When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow.
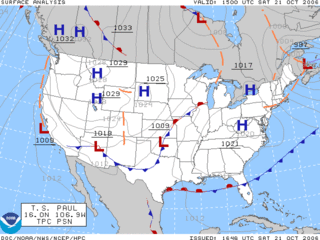
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations.

An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above. Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure.
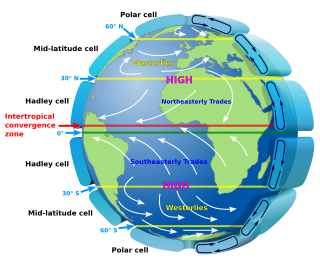
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller-scale weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory.
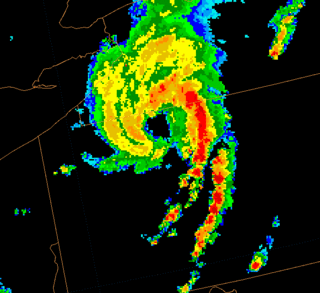
A squall line, or more accurately a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS), is a line of thunderstorms, often forming along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front. Linear thunderstorm structures often contain heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and occasionally tornadoes or waterspouts. Particularly strong straight-line winds can occur where the linear structure forms into the shape of a bow echo. Tornadoes can occur along waves within a line echo wave pattern (LEWP), where mesoscale low-pressure areas are present. Some bow echoes can grow to become derechos as they move swiftly across a large area. On the back edge of the rainband associated with mature squall lines, a wake low can be present, on very rare occasions associated with a heat burst.

A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation.

In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather, while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places:

In meteorology, the synoptic scale is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1,000 km (620 mi) or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions. Most high- and low-pressure areas seen on weather maps are synoptic-scale systems, driven by the location of Rossby waves in their respective hemisphere. Low-pressure areas and their related frontal zones occur on the leading edge of a trough within the Rossby wave pattern, while high-pressure areas form on the back edge of the trough. Most precipitation areas occur near frontal zones. The word synoptic is derived from the Ancient Greek word συνοπτικός (sunoptikós), meaning "seen together".

In meteorology, convective available potential energy, is a measure of the capacity of the atmosphere to support upward air movement that can lead to cloud formation and storms. Some atmospheric conditions, such as very warm, moist, air in an atmosphere that cools rapidly with height, can promote strong and sustained upward air movement, possibly stimulating the formation of cumulus clouds or cumulonimbus. In that situation the potential energy of the atmosphere to cause upward air movement is very high, so CAPE would be high and positive. By contrast, other conditions, such as a less warm air parcel or a parcel in an atmosphere with a temperature inversion have much less capacity to support vigorous upward air movement, thus the potential energy level (CAPE) would be much lower, as would the probability of thunderstorms.

A pressure system is a peak or lull in the sea level pressure distribution. The surface pressure at sea level varies minimally, with the lowest value measured 87 kilopascals (26 inHg) and the highest recorded 108.57 kilopascals (32.06 inHg). High- and low-pressure systems evolve due to interactions of temperature differentials in the atmosphere, temperature differences between the atmosphere and water within oceans and lakes, the influence of upper-level disturbances, as well as the amount of solar heating or radiationized cooling an area receives. Pressure systems cause weather to be experienced locally. Low-pressure systems are associated with clouds and precipitation that minimize temperature changes throughout the day, whereas high-pressure systems normally associate with dry weather and mostly clear skies with larger diurnal temperature changes due to greater radiation at night and greater sunshine during the day. Pressure systems are analyzed by those in the field of meteorology within surface weather maps.

A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For instance, cold fronts can bring bands of thunderstorms and cumulonimbus precipitation or be preceded by squall lines, while warm fronts are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation and fog. In summer, subtler humidity gradients known as dry lines can trigger severe weather. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably a wind shift.

A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure without a closed isobaric contour that would define it as a low pressure area. Since low pressure implies a low height on a pressure surface, troughs and ridges refer to features in an identical sense as those on a topographic map.
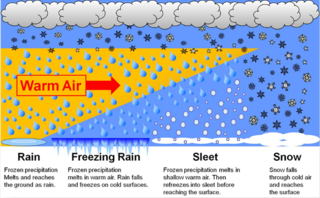
In meteorology, the different types of precipitation often include the character, formation, or phase of the precipitation which is falling to ground level. There are three distinct ways that precipitation can occur. Convective precipitation is generally more intense, and of shorter duration, than stratiform precipitation. Orographic precipitation occurs when moist air is forced upwards over rising terrain and condenses on the slope, such as a mountain.

An air-mass thunderstorm, also called an "ordinary", "single cell", "isolated" or "garden variety" thunderstorm, is a thunderstorm that is generally weak and usually not severe. These storms form in environments where at least some amount of Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE) is present, but with very low levels of wind shear and helicity. The lifting source, which is a crucial factor in thunderstorm development, is usually the result of uneven heating of the surface, though they can be induced by weather fronts and other low-level boundaries associated with wind convergence. The energy needed for these storms to form comes in the form of insolation, or solar radiation. Air-mass thunderstorms do not move quickly, last no longer than an hour, and have the threats of lightning, as well as showery light, moderate, or heavy rainfall. Heavy rainfall can interfere with microwave transmissions within the atmosphere.

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day expands the height of the planetary boundary layer, leading to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Convection involving moist air masses leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.

A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface trough of low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone, at the leading edge of its cold air advection pattern—known as the cyclone's dry "conveyor belt" flow. Temperature differences across the boundary can exceed 30 °C (54 °F) from one side to the other. When enough moisture is present, rain can occur along the boundary. If there is significant instability along the boundary, a narrow line of thunderstorms can form along the frontal zone. If instability is weak, a broad shield of rain can move in behind the front, and evaporative cooling of the rain can increase the temperature difference across the front. Cold fronts are stronger in the fall and spring transition seasons and are weakest during the summer.

A wake low, or wake depression, is a mesoscale low-pressure area which trails the mesoscale high following a squall line. Due to the subsiding warm air associated with the system's formation, clearing skies are associated with the wake low. Once difficult to detect in surface weather observations due to their broad spacing, the formation of mesoscale weather station networks, or mesonets, has increased their detection. Severe weather, in the form of high winds, can be generated by the wake low when the pressure difference between the mesohigh preceding it and the wake low is intense enough. When the squall line is in the process of decay, heat bursts can be generated near the wake low. Once new thunderstorm activity along the squall line concludes, the wake low associated with it weakens in tandem.
The following is a glossary of tornado terms. It includes scientific as well as selected informal terminology.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.

















