Related Research Articles

Integrins are transmembrane receptors that help cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, organization of the intracellular cytoskeleton, and movement of new receptors to the cell membrane. The presence of integrins allows rapid and flexible responses to events at the cell surface.
Morphogenesis is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of developmental biology along with the control of tissue growth and patterning of cellular differentiation.

Fibronectin is a high-molecular weight glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. It is approved for marketing as a topical solution in India by Central Drugs Standard Control organization in 2020 under the brand name FIBREGA for chronic wounds. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans.

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.

Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for infectious organisms, such as bacteria or viruses, to cause diseases.

Cadherins (named for "calcium-dependent adhesion") are cell adhesion molecules important in forming adherens junctions that let cells adhere to each other. Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins, and they depend on calcium (Ca2+) ions to function, hence their name. Cell-cell adhesion is mediated by extracellular cadherin domains, whereas the intracellular cytoplasmic tail associates with numerous adaptors and signaling proteins, collectively referred to as the cadherin adhesome.
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a subset of cell surface proteins that are involved in the binding of cells with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM), in a process called cell adhesion. In essence, CAMs help cells stick to each other and to their surroundings. CAMs are crucial components in maintaining tissue structure and function. In fully developed animals, these molecules play an integral role in generating force and movement and consequently ensuring that organs are able to execute their functions normally. In addition to serving as "molecular glue", CAMs play important roles in the cellular mechanisms of growth, contact inhibition, and apoptosis. Aberrant expression of CAMs may result in a wide range of pathologies, ranging from frostbite to cancer.

Cell junctions or junctional complexes, are a class of cellular structures consisting of multiprotein complexes that provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix in animals. They also maintain the paracellular barrier of epithelia and control paracellular transport. Cell junctions are especially abundant in epithelial tissues. Combined with cell adhesion molecules and extracellular matrix, cell junctions help hold animal cells together.

Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major constituents of the basement membrane, namely the basal lamina. Laminins are vital to biological activity, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion.

In mammalian cells, vinculin is a membrane-cytoskeletal protein in focal adhesion plaques that is involved in linkage of integrin adhesion molecules to the actin cytoskeleton. Vinculin is a cytoskeletal protein associated with cell-cell and cell-matrix junctions, where it is thought to function as one of several interacting proteins involved in anchoring F-actin to the membrane.

In cell biology, focal adhesions are large macromolecular assemblies through which mechanical force and regulatory signals are transmitted between the extracellular matrix (ECM) and an interacting cell. More precisely, focal adhesions are the sub-cellular structures that mediate the regulatory effects of a cell in response to ECM adhesion.
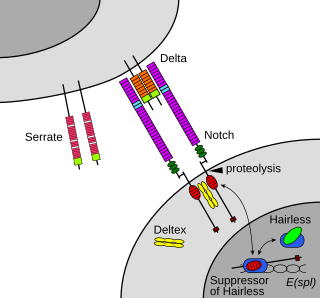
In biology, juxtacrine signalling is a type of cell–cell or cell–extracellular matrix signalling in multicellular organisms that requires close contact. In this type of signalling, a ligand on one surface binds to a receptor on another adjacent surface. Hence, this stands in contrast to releasing a signaling molecule by diffusion into extracellular space, the use of long-range conduits like membrane nanotubes and cytonemes or the use of extracellular vesicles like exosomes or microvesicles. There are three types of juxtacrine signaling:
- A membrane-bound ligand and a membrane protein of two adjacent cells interact.
- A communicating junction links the intracellular compartments of two adjacent cells, allowing transit of relatively small molecules.
- An extracellular matrix glycoprotein and a membrane protein interact.

Galectins are a class of proteins that bind specifically to β-galactoside sugars, such as N-acetyllactosamine, which can be bound to proteins by either N-linked or O-linked glycosylation. They are also termed S-type lectins due to their dependency on disulphide bonds for stability and carbohydrate binding. There have been about 15 galectins discovered in mammals, encoded by the LGALS genes, which are numbered in a consecutive manner. Only galectin-1, -2, -3, -4, -7, -7B, -8, -9, -9B, 9C, -10, -12, -13, -14, and -16 have been identified in humans. Galectin-5 and -6 are found in rodents, whereas galectin-11 and -15 are uniquely found in sheep and goats. Members of the galectin family have also been discovered in other mammals, birds, amphibians, fish, nematodes, sponges, and some fungi. Unlike the majority of lectins they are not membrane bound, but soluble proteins with both intra- and extracellular functions. They have distinct but overlapping distributions but found primarily in the cytosol, nucleus, extracellular matrix or in circulation. Although many galectins must be secreted, they do not have a typical signal peptide required for classical secretion. The mechanism and reason for this non-classical secretion pathway is unknown.

Integrin beta-1 (ITGB1), also known as CD29, is a cell surface receptor that in humans is encoded by the ITGB1 gene. This integrin associates with integrin alpha 1 and integrin alpha 2 to form integrin complexes which function as collagen receptors. It also forms dimers with integrin alpha 3 to form integrin receptors for netrin 1 and reelin. These and other integrin beta 1 complexes have been historically known as very late activation (VLA) antigens.

Leukocyte extravasation is the movement of leukocytes out of the circulatory system and towards the site of tissue damage or infection. This process forms part of the innate immune response, involving the recruitment of non-specific leukocytes. Monocytes also use this process in the absence of infection or tissue damage during their development into macrophages.

Intercellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM3) also known as CD50, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ICAM3 gene. The protein is constitutively expressed on the surface of leukocytes, which are also called white blood cells and are part of the immune system. ICAM3 mediates adhesion between cells by binding to specific integrin receptors. It plays an important role in the immune cell response through its facilitation of interactions between T cells and dendritic cells, which allows for T cell activation. ICAM3 also mediates the clearance of cells undergoing apoptosis by attracting and binding macrophages, a type of cell that breaks down infected or dying cells through a process known as phagocytosis, to apoptotic cells.
Platelet membrane glycoproteins are surface glycoproteins found on platelets (thrombocytes) which play a key role in hemostasis. When the blood vessel wall is damaged, platelet membrane glycoproteins interact with the extracellular matrix.
Collagen receptors are membrane proteins that bind the extracellular matrix protein collagen, the most abundant protein in mammals. They control mainly cell proliferation, migration and adhesion, coagulation cascade activation and they affect ECM structure by regulation of MMP.

Collagen α-1 (XXIII) chain is a protein encoded by COL23A1 gene, which is located on chromosome 5q35 in humans, and on chromosome 11B1+2 in mice. The location of this gene was discovered by genomic sequence analysis.

Integrin-like receptors (ILRs) are found in plants and carry unique functional properties similar to true integrin proteins. True homologs of integrins exist in mammals, invertebrates, and some fungi but not in plant cells. Mammalian integrins are heterodimer transmembrane proteins that play a large role in bidirectional signal transduction. As transmembrane proteins, integrins connect the extracellular matrix (ECM) to the plasma membrane of the animal cell. The extracellular matrix of plant cells, fungi, and some protist is referred to as the cell wall. The plant cell wall is composed of a tough cellulose polysaccharide rather than the collagen fibers of the animal ECM. Even with these differences, research indicates that similar proteins involved in the interaction between the ECM and animals cells are also involved in the interaction of the cell wall and plant cells.
References
- ↑ Schwab, Manfred, ed. (2001). "Cell Adhesion Molecules". Encyclopedic reference of cancer, Volume 1. Springer. p. 183. ISBN 978-3-540-66527-4.
- ↑ Barry, John Michael (2002). Molecular embryology: how molecules give birth to animals. Taylor & Francis. p. 30. ISBN 978-1-56032-936-7.
- ↑ Cruse, Julius M. & Lewis, Robert Edwin (2004). Atlas of immunology . CRC Press. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-8493-1567-1.
- ↑ Kollins, Katherine M.; Davenport, Roger W. (2006). "Branching morphogenesis in vertebrate neurons". In Davies, Jamie A. (ed.). Branching morphogenesis. Birkhäuser. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-387-25615-3.