Related Research Articles

An ecosystem is a system that environments and their organisms form through their interaction. The biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.

An endolith or endolithic is an organism that is able to acquire the necessary resources for growth in the inner part of a rock, mineral, coral, animal shells, or in the pores between mineral grains of a rock. Many are extremophiles, living in places long considered inhospitable to life. The distribution, biomass, and diversity of endolith microorganisms are determined by the physical and chemical properties of the rock substrate, including the mineral composition, permeability, the presence of organic compounds, the structure and distribution of pores, water retention capacity, and the pH. Normally, the endoliths colonize the areas within lithic substrates to withstand intense solar radiation, temperature fluctuations, wind, and desiccation. They are of particular interest to astrobiologists, who theorize that endolithic environments on Mars and other planets constitute potential refugia for extraterrestrial microbial communities.
Soil formation, also known as pedogenesis, is the process of soil genesis as regulated by the effects of place, environment, and history. Biogeochemical processes act to both create and destroy order (anisotropy) within soils. These alterations lead to the development of layers, termed soil horizons, distinguished by differences in color, structure, texture, and chemistry. These features occur in patterns of soil type distribution, forming in response to differences in soil forming factors.

Andesite is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende.

A biogeochemical cycle, or more generally a cycle of matter, is the movement and transformation of chemical elements and compounds between living organisms, the atmosphere, and the Earth's crust. Major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. In each cycle, the chemical element or molecule is transformed and cycled by living organisms and through various geological forms and reservoirs, including the atmosphere, the soil and the oceans. It can be thought of as the pathway by which a chemical substance cycles the biotic compartment and the abiotic compartments of Earth. The biotic compartment is the biosphere and the abiotic compartments are the atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere.

A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it upwards. If the magma finds a path to the surface, then the result will be a volcanic eruption; consequently, many volcanoes are situated over magma chambers. These chambers are hard to detect deep within the Earth, and therefore most of those known are close to the surface, commonly between 1 km and 10 km down.

Peridotite ( PERR-ih-doh-tyte, pə-RID-ə-) is a dense, coarse-grained igneous rock consisting mostly of the silicate minerals olivine and pyroxene. Peridotite is ultramafic, as the rock contains less than 45% silica. It is high in magnesium (Mg2+), reflecting the high proportions of magnesium-rich olivine, with appreciable iron. Peridotite is derived from Earth's mantle, either as solid blocks and fragments, or as crystals accumulated from magmas that formed in the mantle. The compositions of peridotites from these layered igneous complexes vary widely, reflecting the relative proportions of pyroxenes, chromite, plagioclase, and amphibole.

Dolomite (also known as dolomite rock, dolostone or dolomitic rock) is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2. It occurs widely, often in association with limestone and evaporites, though it is less abundant than limestone and rare in Cenozoic rock beds (beds less than about 66 million years in age). One of the first geologists to distinguish dolomite from limestone was Déodat Gratet de Dolomieu; a French mineralogist and geologist whom it is named after. He recognized and described the distinct characteristics of dolomite in the late 18th century, differentiating it from limestone.

The chlorites are the group of phyllosilicate minerals common in low-grade metamorphic rocks and in altered igneous rocks. Greenschist, formed by metamorphism of basalt or other low-silica volcanic rock, typically contains significant amounts of chlorite.

Sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) or sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) are a group composed of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfate-reducing archaea (SRA), both of which can perform anaerobic respiration utilizing sulfate (SO2−
4) as terminal electron acceptor, reducing it to hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Therefore, these sulfidogenic microorganisms "breathe" sulfate rather than molecular oxygen (O2), which is the terminal electron acceptor reduced to water (H2O) in aerobic respiration.
Slime or slimy may refer to:
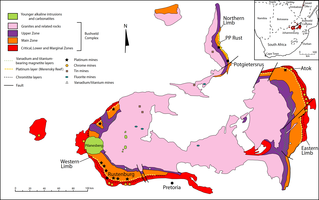
The Bushveld Igneous Complex (BIC) is the largest layered igneous intrusion within the Earth's crust. It has been tilted and eroded forming the outcrops around what appears to be the edge of a great geological basin: the Transvaal Basin. It is approximately two billion years old and is divided into four limbs: northern, eastern, southern and western. It comprises the Rustenburg Layered suite, the Lebowa Granites and the Rooiberg Felsics, that are overlain by the Karoo sediments. The site was first publicised around 1897 by Gustaaf Molengraaff who found the native South African tribes residing in and around the area.

A layered intrusion is a large sill-like body of igneous rock which exhibits vertical layering or differences in composition and texture. These intrusions can be many kilometres in area covering from around 100 km2 (39 sq mi) to over 50,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi) and several hundred metres to over one kilometre (3,300 ft) in thickness. While most layered intrusions are Archean to Proterozoic in age, they may be any age such as the Cenozoic Skaergaard intrusion of east Greenland or the Rum layered intrusion in Scotland. Although most are ultramafic to mafic in composition, the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex of Greenland is an alkalic intrusion.

A microbial mat is a multi-layered sheet or biofilm of microbial colonies, composed of mainly bacteria and/or archaea. Microbial mats grow at interfaces between different types of material, mostly on submerged or moist surfaces, but a few survive in deserts. A few are found as endosymbionts of animals.

The class Zetaproteobacteria is the sixth and most recently described class of the Pseudomonadota. Zetaproteobacteria can also refer to the group of organisms assigned to this class. The Zetaproteobacteria were originally represented by a single described species, Mariprofundus ferrooxydans, which is an iron-oxidizing neutrophilic chemolithoautotroph originally isolated from Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount in 1996 (post-eruption). Molecular cloning techniques focusing on the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene have also been used to identify a more diverse majority of the Zetaproteobacteria that have as yet been unculturable.
The Deep Carbon Observatory (DCO) is a global research program designed to transform understanding of carbon's role in Earth. DCO is a community of scientists, including biologists, physicists, geoscientists and chemists, whose work crosses several traditional disciplinary lines to develop the new, integrative field of deep carbon science. To complement this research, the DCO's infrastructure includes public engagement and education, online and offline community support, innovative data management, and novel instrumentation development.
Mars habitability analogue environments on Earth are environments that share potentially relevant astrobiological conditions with Mars. These include sites that are analogues of potential subsurface habitats, and deep subsurface habitats.

The viral shunt is a mechanism that prevents marine microbial particulate organic matter (POM) from migrating up trophic levels by recycling them into dissolved organic matter (DOM), which can be readily taken up by microorganisms. The DOM recycled by the viral shunt pathway is comparable to the amount generated by the other main sources of marine DOM.
The deep biosphere is the part of the biosphere that resides below the first few meters of the surface. It extends down below 10 kilometers below the continental surface and 21 kilometers below the sea surface, at temperatures that may reach beyond 120 °C (248 °F) which is comparable to the maximum temperature where a metabolically active organism has been found. It includes all three domains of life and the genetic diversity rivals that on the surface.

Salty subglacial lakes are controversially inferred from radar measurements to exist below the South Polar Layered Deposits (SPLD) in Ultimi Scopuli of Mars' southern ice cap. The idea of subglacial lakes due to basal melting at the polar ice caps on Mars was first hypothesized in the 1980s. For liquid water to persist below the SPLD, researchers propose that perchlorate is dissolved in the water, which lowers the freezing temperature, but other explanations such as saline ice or hydrous minerals have been offered. Challenges for explaining sufficiently warm conditions for liquid water to exist below the southern ice cap include low amounts of geothermal heating from the subsurface and overlying pressure from the ice. As a result, it is disputed whether radar detections of bright reflectors were instead caused by other materials such as saline ice or deposits of minerals such as clays. While lakes with salt concentrations 20 times that of the ocean pose challenges for life, potential subglacial lakes on Mars are of high interest for astrobiology because microbial ecosystems have been found in deep subglacial lakes on Earth, such as in Lake Whillans in Antarctica below 800 m of ice.
References
- ↑ Wilson, Edward O. (2002). The future of life (1st ed.). Vintage Books. p. 7. ISBN 9780679768111.
- ↑ Keith, DA; Iliffe, TM; Gerovasileiou, V; Gonzalez, B; Brankovits, D; Martínez García, A (2020). "S1.2 Endolithic systems". In Keith, D.A.; Ferrer-Paris, J.R.; Nicholson, E.; Kingsford, R.T. (eds.). The IUCN Global Ecosystem Typology 2.0: Descriptive profiles for biomes and ecosystem functional groups. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN. doi:10.2305/IUCN.CH.2020.13.en. ISBN 978-2-8317-2077-7. S2CID 241360441.