
Majapahit, also known as Wilwatikta, was a Javanese Hindu-Buddhist thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was based on the island of Java. It existed from 1293 to circa 1527 and reached its peak of glory during the era of Hayam Wuruk, whose reign from 1350 to 1389 was marked by conquests that extended throughout Southeast Asia. His achievement is also credited to his prime minister, Gajah Mada. According to the Nagarakretagama written in 1365, Majapahit was an empire of 98 tributaries, stretching from Sumatra to New Guinea; consisting of present-day Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Brunei, southern Thailand, Timor Leste, southwestern Philippines although the scope of Majapahit sphere of influence is still the subject of debate among historians. The nature of Majapahit relations and influences upon its overseas vassals and also its status as an empire still provokes discussion.

The Kingdom of Pajang or Sultanate of Pajang was a short-lived Muslim state in Java. It was established by Hadiwijaya or Jaka Tingkir, Lord of Boyolali, after a civil war and was a successor to Sultanate of Demak. Hadiwijaya claimed to be a descendant of Brawijaya V, the last king of the Majapahit empire, and Trenggana, the sultan of Demak.

Demak Great Mosque is one of the oldest mosques in Indonesia, located in the center town of Demak, Central Java, Indonesia. The mosque is believed to be built by the Wali Songo with the most prominent figure Sunan Kalijaga, during the first Demak Sultanate ruler, Raden Patah during the 15th century.
Sunan Kalijaga was one of the "nine saints" of Javanese Islam. The "Kalijaga" title was derived from an orchard known as "Kalijaga" in Cirebon. Other accounts suggest the name derives from his hobby of submerging himself in Kali. Others note that the name Kalijaga derived its nature from the Arabic notion of qadli dzaqa which means "holy leader" in the sultanate.

The history of the arrival of Islam in Indonesia is somewhat unclear. One theory states that Islam arrived directly from Arabia as early as the 9th century, during the time of the Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates. Another theory credits Sufi travelers for bringing Islam in the 12th or 13th century, either from Gujarat in India or from Persia. Before the archipelago's conversion to Islam, the predominant religions in Indonesia were Hinduism and Buddhism.
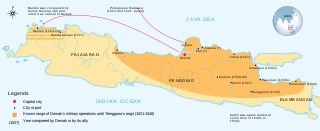
The Demak Sultanate was a Javanese Muslim state located on Java's north coast in Indonesia, at the site of the present-day city of Demak. A port fief to the Hindu-Buddhist Majapahit kingdom thought to have been founded in the last quarter of the 15th century, it was influenced by Islam brought by Muslim traders from China, Gujarat, Arabia and also Islamic kingdoms in the region, such as Samudra Pasai, Malacca and Bani (Muslim) Champa. The sultanate was the first Muslim state in Java, and once dominated most of the northern coast of Java and southern Sumatra.

Demak is a regency located in the Indonesian province of Central Java, on the northern coast of the island. It is bordered by Jepara Regency and the Java Sea to the north, Kudus and Grobogan Regencies to the east, Grobogan and Semarang Regencies to the south, while to the west are Semarang Regency and the city of Semarang, to which the districts of Mranggen and Sayung within Demak Regency are essentially suburban. The regency covers an area of 995.32 km2 (384.30 sq mi) and had a population of 1,055,579 at the 2010 Census and 1,203,956 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 1,223,217. It was originally the centre of the Demak Sultanate, once a dominant power in the region. Due to its strong relation with the spread of Islam in Java and the Wali Sanga, it is sometimes referred to with the nickname Kota Wali.
Sunan Ampel was one of the Javanese nine revered saints Wali Songo, credited for the spread Islam in Java. According to local history around Demak the mosque of Demak Masjid Agung Demak was built by Sunan Ampel in 1479 CE, but other source credited the construction of the mosque to Sunan Kalijaga.

The Yuan dynasty under Kublai Khan attempted in 1293 to invade Java, an island in modern Indonesia, with 20,000 to 30,000 soldiers. This was intended as a punitive expedition against Kertanegara of Singhasari, who had refused to pay tribute to the Yuan and maimed one of their emissaries. However, in the intervening years between Kertanegara's refusal and the expedition's arrival on Java, Kertanegara had been killed and Singhasari had been usurped by Kediri. Thus, the Yuan expeditionary force was directed to obtain the submission of its successor state, Kediri, instead. After a fierce campaign, Kediri surrendered, but the Yuan forces were betrayed by their erstwhile ally, Majapahit, under Raden Wijaya. In the end, the invasion ended with Yuan failure and victory for the new state, Majapahit.

Raden Patah, also known as Jin Bun was the first sultan of the Demak Sultanate. Ascending to the throne in 1475, his remained a vassal of the Majapahit Empire until 1478. Raden Patah took the title Panembahan Jimbun after legitimizing the Sultanate of Demak as the successor state to the Majapahit Empire, with Wali Sanga appointing him as the Sultan of Demak.
The Regreg War was a civil war that took place in 1404–1406 within the Javanese empire of Majapahit. The conflict was fought as a war of independence between the Western court led by Wikramawardhana against the breakaway Eastern court led by Bhre Wirabhumi. This war of rivalry and secession had caused the calamity, crisis, court's preoccupation, the drain of financial resources, and exhaustion, that is thought to be one of the causes of Majapahit decline in the following years.
The Kingdomship of Bali was a series of Hindu-Buddhist kingdoms that once ruled some parts of the volcanic island of Bali, in Lesser Sunda Islands, Indonesia. With a history of native Balinese kingship spanning from the early 10th to early 20th centuries, Balinese kingdoms demonstrated sophisticated Balinese court culture where native elements of spirit and ancestral reverence combined with Hindu influences – adopted from India through ancient Java intermediary – flourished, enriched and shaped Balinese culture.
Arya Penangsang was king of the Sultanate of Demak between 1549 and 1554.
Prabhu Natha Girindrawardhana Dyah Ranawijaya was the ruler of the Majapahit Empire between 1474 and 1498. He is referred in a Jiyu inscription as Sri Wilwatikta Jenggala Kediri, which means ruler of Majapahit, Janggala and Kediri, and as Pa Bu Ta La in Chinese literature.

The Sultanate of Palembang Darussalam was a sultanate in Indonesia whose capital was the city of Palembang in the southern part of the Indonesian island of Sumatra. It was proclaimed in 1659 by Susuhunan Abdurrahman (1659–1706) and dissolved by the colonial government of the Dutch East Indies on October 7, 1823. In 1825, its last ruler, Sultan Ahmad Najamuddin, was arrested and sent into exile on the island of Banda Neira in the Moluccas.

The history of Sunda Kingdom spanned almost a millennium, between 7th to 16th century. It is not sure however, whether the Sunda Kingdom was actually a continuous polity or not, nor whether its rulers belongs to a single continuous lineage of dynasty or not. This is because the scarcity of evidences, historical records and archaeological findings that plausibly connected to this kingdom.
Raden Kusen, also known as Kin San was the Duke of Terung and one of the last commanders of the Majapahit Imperial Army. His father was the Duke of Palembang, Arya Damar while his mother was Siu Ban Ci, the former concubine of Majapahit Emperor. He was a half-brother of Raden Patah, the founder of the Demak Sultanate. He supposedly was to succeed his father at the Duchy of Palembang, as the Duke of Palembang, but he along with his brother moved to Java island. His descendants, the sultans of Palembang from the 17th century until 19th century were his rightful successors.
Pati Unus aka Yat Sun known as Pangeran Sabrang Lor (1488–1521) was the second Sultan of Demak who reigned from 1518 to 1521. Pati Unus' real name is Raden Abdul Qadir. He is the crown prince of Raden Patah, the founder of Demak.

Kertawijaya or Dyah Kertawijaya was the seventh monarch of Majapahit reigning from 1447 to 1451 by the regnal name Sri Maharaja Wijayaparakramawardhana.










