Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned with the way in which electrons are arranged around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change. This comprises ions, neutral atoms and, unless otherwise stated, it can be assumed that the term atom includes ions.
Atomic, molecular, and optical physics (AMO) is the study of matter–matter and light–matter interactions, at the scale of one or a few atoms and energy scales around several electron volts. The three areas are closely interrelated. AMO theory includes classical, semi-classical and quantum treatments. Typically, the theory and applications of emission, absorption, scattering of electromagnetic radiation (light) from excited atoms and molecules, analysis of spectroscopy, generation of lasers and masers, and the optical properties of matter in general, fall into these categories.

Photoluminescence is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons. It is one of many forms of luminescence and is initiated by photoexcitation, hence the prefix photo-. Following excitation, various relaxation processes typically occur in which other photons are re-radiated. Time periods between absorption and emission may vary: ranging from short femtosecond-regime for emission involving free-carrier plasma in inorganic semiconductors up to milliseconds for phosphoresence processes in molecular systems; and under special circumstances delay of emission may even span to minutes or hours.
Plasma diagnostics are a pool of methods, instruments, and experimental techniques used to measure properties of a plasma, such as plasma components' density, distribution function over energy (temperature), their spatial profiles and dynamics, which enable to derive plasma parameters.

Electron excitation is the transfer of a bound electron to a more energetic, but still bound state. This can be done by photoexcitation (PE), where the electron absorbs a photon and gains all its energy or by collisional excitation (CE), where the electron receives energy from a collision with another, energetic electron. Within a semiconductor crystal lattice, thermal excitation is a process where lattice vibrations provide enough energy to transfer electrons to a higher energy band such as a more energetic sublevel or energy level. When an excited electron falls back to a state of lower energy, it undergoes electron relaxation (deexcitation). This is accompanied by the emission of a photon or by a transfer of energy to another particle. The energy released is equal to the difference in energy levels between the electron energy states.

A glow discharge is a plasma formed by the passage of electric current through a gas. It is often created by applying a voltage between two electrodes in a glass tube containing a low-pressure gas. When the voltage exceeds a value called the striking voltage, the gas ionization becomes self-sustaining, and the tube glows with a colored light. The color depends on the gas used.
A Rydberg atom is an excited atom with one or more electrons that have a very high principal quantum number, n. The higher the value of n, the farther the electron is from the nucleus, on average. Rydberg atoms have a number of peculiar properties including an exaggerated response to electric and magnetic fields, long decay periods and electron wavefunctions that approximate, under some conditions, classical orbits of electrons about the nuclei. The core electrons shield the outer electron from the electric field of the nucleus such that, from a distance, the electric potential looks identical to that experienced by the electron in a hydrogen atom.

A hollow-cathode lamp (HCL) is type of cold cathode lamp used in physics and chemistry as a spectral line source and as a frequency tuner for light sources such as lasers. An HCL takes advantage of the hollow cathode effect, which causes conduction at a lower voltage and with more current than a cold cathode lamp that does not have a hollow cathode.
The Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik is a research institute in Heidelberg, Germany.

The Physical Research Laboratory is a National Research Institute for space and allied sciences, supported mainly by Department of Space, Government of India. This research laboratory has ongoing research programmes in astronomy and astrophysics, atmospheric sciences and aeronomy, planetary and geosciences, Earth sciences, Solar System studies and theoretical physics. It also manages the Udaipur Solar Observatory and Mount Abu InfraRed Observatory. The PRL is located in Ahmedabad.

Electron beam ion trap (EBIT) is an electromagnetic bottle that produces and confines highly charged ions. An EBIT uses an electron beam focused with a powerful magnetic field to ionize atoms to high charge states by successive electron impact.

Carlos A. Bertulani is a Brazilian and American theoretical physicist and professor at the department of physics of the Texas A&M University-Commerce. He graduated, PhD, at University of Bonn and works on nuclear physics and nuclear astrophysics. He was formerly a professor at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro from 1980-2000.
Photoelectrochemical processes are processes in photoelectrochemistry; they usually involve transforming light into other forms of energy. These processes apply to photochemistry, optically pumped lasers, sensitized solar cells, luminescence, and photochromism.
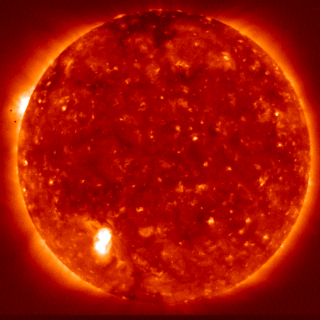
In astronomy and in astrophysics, for radiative losses of the solar corona, it is meant the energy flux radiated from the external atmosphere of the Sun, and, in particular, the processes of production of the radiation coming from the solar corona and transition region, where the plasma is optically-thin. On the contrary, in the chromosphere, where the temperature decreases from the photospheric value of 6000 K to the minimum of 4400 K, the optical depth is about 1, and the radiation is thermal.
Quantemol Ltd is based in University College London initiated by Professor Jonathan Tennyson FRS and Dr. Daniel Brown in 2004. The company initially developed a unique software tool, Quantemol-N, which provides full accessibility to the highly sophisticated UK molecular R-matrix codes, used to model electron polyatomic molecule interactions. Since then Quantemol has widened to further types of simulation, with plasmas and industrial plasma tools, in Quantemol-VT in 2013 and launched in 2016 a sustainable database Quantemol-DB, representing the chemical and radiative transport properties of a wide range of plasmas.

Ratko Janev was a Yugoslav and Serbian atomic physicist and Macedonian academician.
Kennedy J. Reed is an American theoretical atomic physicist in the Theory Group in the Physics & Advanced Technologies Directorate at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and a founder of the National Physical Science Consortium (NPSC), a group of about 30 universities that provides physics fellowships for women and minorities.
An excimer lamp is a source of ultraviolet light based on spontaneous emission of excimer (exciplex) molecules.
Oleg Ivanovich Zatsarinny (1953-2021) was a Ukrainian-American theoretical physicist noted for his contributions to all aspects of research related to electron scattering in atoms. He was awarded the status of Fellow in the American Physical Society, after he was nominated by his Division of Atomic, Molecular & Optical Physics in 2008, for "the development of the B-Spline R-matrix method with non-orthogonal orbital sets for atomic structure calculations of exceptional accuracy and benchmark calculations for excitation and ionization of complex atoms and ions by photon and electron impact."
Kate Page Kirby is an American physicist. From February 2015 to December 2020, Kirby was the chief executive officer of the American Physical Society (APS) and sits on the board of directors of the American Institute of Physics. Kate Kirby was elected a fellow of the American Physical Society (APS) in 1989 for her "innovative application of methods of quantum chemistry to the quantitative elucidation of a diverse range of molecular phenomena." She was made a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in 1996 for her contributions to physics.