
Photoionization is the physical process in which an ion is formed from the interaction of a photon with an atom or molecule. [2]

Photoionization is the physical process in which an ion is formed from the interaction of a photon with an atom or molecule. [2]
Not every interaction between a photon and an atom, or molecule, will result in photoionization. The probability of photoionization is related to the photoionization cross section of the species – the probability of an ionization event conceptualized as a hypothetical cross-sectional area. This cross section depends on the energy of the photon (proportional to its wavenumber) and the species being considered i.e. it depends on the structure of the molecular species. In the case of molecules, the photoionization cross-section can be estimated by examination of Franck-Condon factors between a ground-state molecule and the target ion. This can be initialized by computing the vibrations of a molecule and associated cation (post ionization) using quantum chemical software e.g. QChem. For photon energies below the ionization threshold, the photoionization cross-section is near zero. But with the development of pulsed lasers it has become possible to create extremely intense, coherent light where multi-photon ionization may occur via sequences of excitations and relaxations. At even higher intensities (around 1015 – 1016 W/cm2 of infrared or visible light), non-perturbative phenomena such as barrier suppression ionization [3] and rescattering ionization [4] are observed.
Several photons of energy below the ionization threshold may actually combine their energies to ionize an atom. This probability decreases rapidly with the number of photons required, but the development of very intense, pulsed lasers still makes it possible. In the perturbative regime (below about 1014 W/cm2 at optical frequencies), the probability of absorbing N photons depends on the laser-light intensity I as IN. [5] For higher intensities, this dependence becomes invalid due to the then occurring AC Stark effect. [6]
Resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization (REMPI) is a technique applied to the spectroscopy of atoms and small molecules in which a tunable laser can be used to access an excited intermediate state.[ citation needed ]
Above-threshold ionization (ATI) [7] is an extension of multi-photon ionization where even more photons are absorbed than actually would be necessary to ionize the atom. The excess energy gives the released electron higher kinetic energy than the usual case of just-above threshold ionization. More precisely, the system will have multiple peaks in its photoelectron spectrum which are separated by the photon energies, indicating that the emitted electron has more kinetic energy than in the normal (lowest possible number of photons) ionization case. The electrons released from the target will have approximately an integer number of photon-energies more kinetic energy.[ citation needed ]
When either the laser intensity is further increased or a longer wavelength is applied as compared with the regime in which multi-photon ionization takes place, a quasi-stationary approach can be used and results in the distortion of the atomic potential in such a way that only a relatively low and narrow barrier between a bound state and the continuum states remains. Then, the electron can tunnel through or for larger distortions even overcome this barrier. These phenomena are called tunnel ionization and over-the-barrier ionization, respectively.[ citation needed ]

The Auger effect or Auger−Meitner effect is a physical phenomenon in which atoms eject electrons. It occurs when an inner-shell vacancy in an atom is filled by an electron, releasing energy that causes the emission of another electron from a different shell of the same atom.

The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons from a material caused by electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, solid state, and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms, molecules and solids. The effect has found use in electronic devices specialized for light detection and precisely timed electron emission.

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules, electrons, positrons, protons, antiprotons and ions, or through the interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.
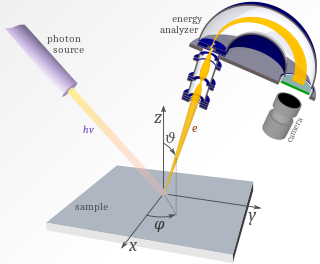
Photoemission spectroscopy (PES), also known as photoelectron spectroscopy, refers to energy measurement of electrons emitted from solids, gases or liquids by the photoelectric effect, in order to determine the binding energies of electrons in the substance. The term refers to various techniques, depending on whether the ionization energy is provided by X-ray, XUV or UV photons. Regardless of the incident photon beam, however, all photoelectron spectroscopy revolves around the general theme of surface analysis by measuring the ejected electrons.
In physics, tunnel ionization is a process in which electrons in an atom tunnel through the potential barrier and escape from the atom. In an intense electric field, the potential barrier of an atom (molecule) is distorted drastically. Therefore, as the length of the barrier that electrons have to pass decreases, the electrons can escape from the atom's potential more easily. Tunneling ionization is a quantum mechanical phenomenon since in the classical picture an electron does not have sufficient energy to overcome the potential barrier of the atom.

Extreme ultraviolet radiation or high-energy ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum spanning wavelengths shorter than the hydrogen Lyman-alpha line from 121 nm down to the X-ray band of 10 nm. By the Planck–Einstein equation the EUV photons have energies from 10.26 eV up to 124.24 eV where we enter the X-ray energies. EUV is naturally generated by the solar corona and artificially by plasma, high harmonic generation sources and synchrotron light sources. Since UVC extends to 100 nm, there is some overlap in the terms.
Rydberg ionization spectroscopy is a spectroscopy technique in which multiple photons are absorbed by an atom causing the removal of an electron to form an ion.

Resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization (REMPI) is a technique applied to the spectroscopy of atoms and small molecules. In practice, a tunable laser can be used to access an excited intermediate state. The selection rules associated with a two-photon or other multiphoton photoabsorption are different from the selection rules for a single photon transition. The REMPI technique typically involves a resonant single or multiple photon absorption to an electronically excited intermediate state followed by another photon which ionizes the atom or molecule. The light intensity to achieve a typical multiphoton transition is generally significantly larger than the light intensity to achieve a single photon photoabsorption. Because of this, subsequent photoabsorption is often very likely. An ion and a free electron will result if the photons have imparted enough energy to exceed the ionization threshold energy of the system. In many cases, REMPI provides spectroscopic information that can be unavailable to single photon spectroscopic methods, for example rotational structure in molecules is easily seen with this technique.
Ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) refers to the measurement of kinetic energy spectra of photoelectrons emitted by molecules that have absorbed ultraviolet photons, in order to determine molecular orbital energies in the valence region.
High-harmonic generation (HHG) is a non-linear process during which a target is illuminated by an intense laser pulse. Under such conditions, the sample will emit the high order harmonics of the generation beam. Due to the coherent nature of the process, high-harmonics generation is a prerequisite of attosecond physics.

A photoionization mode is a mode of interaction between a laser beam and matter involving photoionization.
Photoelectrochemical processes are processes in photoelectrochemistry; they usually involve transforming light into other forms of energy. These processes apply to photochemistry, optically pumped lasers, sensitized solar cells, luminescence, and photochromism.

In atomic, molecular, and optical physics, above-threshold ionization (ATI) is a multi-photon effect where an atom is ionized with more than the energetically required number of photons. It was first observed in 1979 by Pierre Agostini and colleagues in xenon gas.
Atmospheric pressure laser ionization is an atmospheric pressure ionization method for mass spectrometry (MS). Laser light in the UV range is used to ionize molecules in a resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization (REMPI) process. It is a selective and sensitive ionization method for aromatic and polyaromatic compounds. Atmospheric photoionization is the latest in development of atmospheric ionization methods.
Photoelectron photoion coincidence spectroscopy (PEPICO) is a combination of photoionization mass spectrometry and photoelectron spectroscopy. It is largely based on the photoelectric effect. Free molecules from a gas-phase sample are ionized by incident vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) radiation. In the ensuing photoionization, a cation and a photoelectron are formed for each sample molecule. The mass of the photoion is determined by time-of-flight mass spectrometry, whereas, in current setups, photoelectrons are typically detected by velocity map imaging. Electron times-of-flight are three orders of magnitude smaller than those of ions, which allows electron detection to be used as a time stamp for the ionization event, starting the clock for the ion time-of-flight analysis. In contrast with pulsed experiments, such as REMPI, in which the light pulse must act as the time stamp, this allows to use continuous light sources, e.g. a discharge lamp or a synchrotron light source. No more than several ion–electron pairs are present simultaneously in the instrument, and the electron–ion pairs belonging to a single photoionization event can be identified and detected in delayed coincidence.
Double ionization is a process of formation of doubly charged ions when laser radiation or charged particles like electrons, positrons or heavy ions are exerted on neutral atoms or molecules. Double ionization is usually less probable than single-electron ionization. Two types of double ionization are distinguished: sequential and non-sequential.
Bond softening is an effect of reducing the strength of a chemical bond by strong laser fields. To make this effect significant, the strength of the electric field in the laser light has to be comparable with the electric field the bonding electron "feels" from the nuclei of the molecule. Such fields are typically in the range of 1–10 V/Å, which corresponds to laser intensities 1013–1015 W/cm2. Nowadays, these intensities are routinely achievable from table-top Ti:Sapphire lasers.
Bond hardening is a process of creating a new chemical bond by strong laser fields—an effect opposite to bond softening. However, it is not opposite in the sense that the bond becomes stronger, but in the sense that the molecule enters a state that is diametrically opposite to the bond-softened state. Such states require laser pulses of high intensity, in the range of 1013–1015 W/cm2, and they disappear once the pulse is gone.
Quantum microscopy allows microscopic properties of matter and quantum particles to be measured and imaged. Various types of microscopy use quantum principles. The first microscope to do so was the scanning tunneling microscope, which paved the way for development of the photoionization microscope and the quantum entanglement microscope.

Resonance ionization is a process in optical physics used to excite a specific atom beyond its ionization potential to form an ion using a beam of photons irradiated from a pulsed laser light. In resonance ionization, the absorption or emission properties of the emitted photons are not considered, rather only the resulting excited ions are mass-selected, detected and measured. Depending on the laser light source used, one electron can be removed from each atom so that resonance ionization produces an efficient selectivity in two ways: elemental selectivity in ionization and isotopic selectivity in measurement.