
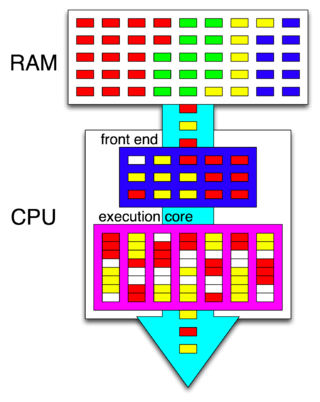
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the most important processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs).

In computing, multitasking is the concurrent execution of multiple tasks over a certain period of time. New tasks can interrupt already started ones before they finish, instead of waiting for them to end. As a result, a computer executes segments of multiple tasks in an interleaved manner, while the tasks share common processing resources such as central processing units (CPUs) and main memory. Multitasking automatically interrupts the running program, saving its state and loading the saved state of another program and transferring control to it. This "context switch" may be initiated at fixed time intervals, or the running program may be coded to signal to the supervisory software when it can be interrupted.
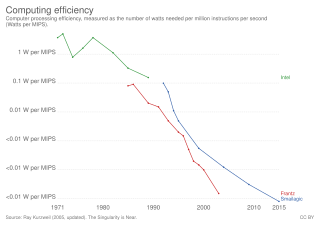
Instructions per second (IPS) is a measure of a computer's processor speed. For complex instruction set computers (CISCs), different instructions take different amounts of time, so the value measured depends on the instruction mix; even for comparing processors in the same family the IPS measurement can be problematic. Many reported IPS values have represented "peak" execution rates on artificial instruction sequences with few branches and no cache contention, whereas realistic workloads typically lead to significantly lower IPS values. Memory hierarchy also greatly affects processor performance, an issue barely considered in IPS calculations. Because of these problems, synthetic benchmarks such as Dhrystone are now generally used to estimate computer performance in commonly used applications, and raw IPS has fallen into disuse.
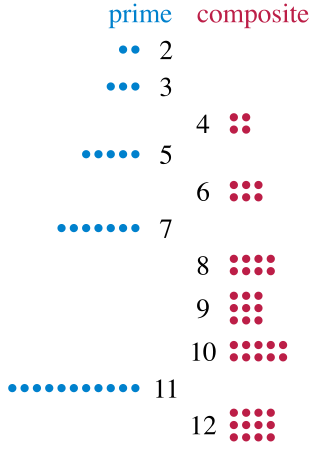
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.
Floating point operations per second is a measure of computer performance in computing, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations.

Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling. As power consumption by computers has become a concern in recent years, parallel computing has become the dominant paradigm in computer architecture, mainly in the form of multi-core processors.
Hyper-threading is Intel's proprietary simultaneous multithreading (SMT) implementation used to improve parallelization of computations performed on x86 microprocessors. It was introduced on Xeon server processors in February 2002 and on Pentium 4 desktop processors in November 2002. Since then, Intel has included this technology in Itanium, Atom, and Core 'i' Series CPUs, among others.
Oz is a multiparadigm programming language, developed in the Programming Systems Lab at Université catholique de Louvain, for programming-language education. It has a canonical textbook: Concepts, Techniques, and Models of Computer Programming.

OpenMP is an application programming interface (API) that supports multi-platform shared-memory multiprocessing programming in C, C++, and Fortran, on many platforms, instruction-set architectures and operating systems, including Solaris, AIX, FreeBSD, HP-UX, Linux, macOS, and Windows. It consists of a set of compiler directives, library routines, and environment variables that influence run-time behavior.
Trial division is the most laborious but easiest to understand of the integer factorization algorithms. The essential idea behind trial division tests to see if an integer n, the integer to be factored, can be divided by each number in turn that is less than the square root of n.
The Whetstone benchmark is a synthetic benchmark for evaluating the performance of computers. It was first written in ALGOL 60 in 1972 at the Technical Support Unit of the Department of Trade and Industry in the United Kingdom. It was derived from statistics on program behaviour gathered on the KDF9 computer at NPL National Physical Laboratory, using a modified version of its Whetstone ALGOL 60 compiler. The workload on the machine was represented as a set of frequencies of execution of the 124 instructions of the Whetstone Code. The Whetstone Compiler was built at the Atomic Power Division of the English Electric Company in Whetstone, Leicestershire, England, hence its name. Dr. B.A. Wichman at NPL produced a set of 42 simple ALGOL 60 statements, which in a suitable combination matched the execution statistics.

In computing, a benchmark is the act of running a computer program, a set of programs, or other operations, in order to assess the relative performance of an object, normally by running a number of standard tests and trials against it.

Super PI is a computer program that calculates pi to a specified number of digits after the decimal point—up to a maximum of 32 million. It uses Gauss–Legendre algorithm and is a Windows port of the program used by Yasumasa Kanada in 1995 to compute pi to 232 digits.

A multi-core processor (MCP) is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit (IC) with two or more separate central processing units (CPUs), called cores to emphasize their multiplicity. Each core reads and executes program instructions, specifically ordinary CPU instructions. However, the MCP can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single IC die, known as a chip multiprocessor (CMP), or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. As of 2024, the microprocessors used in almost all new personal computers are multi-core.

The table below is a brief chronology of computed numerical values of, or bounds on, the mathematical constant pi. For more detailed explanations for some of these calculations, see Approximations of π.

The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non-distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coincides with the International Supercomputing Conference in June, and the second is presented at the ACM/IEEE Supercomputing Conference in November. The project aims to provide a reliable basis for tracking and detecting trends in high-performance computing and bases rankings on HPL benchmarks, a portable implementation of the high-performance LINPACK benchmark written in Fortran for distributed-memory computers.
The AMD Bulldozer Family 15h is a microprocessor microarchitecture for the FX and Opteron line of processors, developed by AMD for the desktop and server markets. Bulldozer is the codename for this family of microarchitectures. It was released on October 12, 2011, as the successor to the K10 microarchitecture.
The Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) was a UK government agency providing computer and telecoms support to government departments.

Intel Galileo is the first in a line of Arduino-certified development boards based on Intel x86 architecture and is designed for the maker and education communities. Intel released two versions of Galileo, referred to as Gen 1 and Gen 2. These development boards are sometimes called "Breakout boards".
WPrime is a computer program that calculates a set number of square roots using Newton's method for estimating functions verifying the results by squaring them then comparing them with the original numbers.












