| Court of Appeal of Newfoundland and Labrador |
|---|
 Coat of Arms of the Supreme Court [1] |
| Established | 1975 |
|---|
| Country | Canada: Province of Newfoundland and Labrador  |
|---|
| Location | St. John's |
|---|
| Authorized by | Judicature Amendment Act, 1974 |
|---|
| No. of positions | 6 |
|---|
| Website | |
|---|
| Chief Justice |
|---|
| Currently | Deborah E. Fry |
|---|
| Since | June 22, 2018 |
|---|
The Court of Appeal of Newfoundland and Labrador is at the top of the hierarchy of courts for the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The Court of Appeal derives its powers and jurisdiction from the Court of Appeal Act.

Newfoundland and Labrador is the most easterly province of Canada. Situated in the country's Atlantic region, it is composed of the insular region of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador to the northwest, with a combined area of 405,212 square kilometres (156,500 sq mi). In 2018, the province's population was estimated at 525,073. About 92% of the province's population lives on the island of Newfoundland, of whom more than half live on the Avalon Peninsula.
The independent Court of Appeal was established in 2018 and comprises the Chief Justice and 5 other justices. [2] At any given time there may be one or more additional justices who sit as supernumerary justices. [3] From 1975 until 2018 the Court of Appeal was constituted as the appeal division of the Supreme Court of Newfoundland and Labrador with judges appointed specifically to hear appeals from the Trial Division of the Supreme Court. Prior to 1975 both trial and appeals were carried out in the Supreme Court, where the individual judges routinely acted as a trial judges but, in the event of an appeal, would sit together (en banc) to hear it. [4]

The Supreme Court of Newfoundland and Labrador is the superior court for the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The Supreme Court of Newfoundland and Labrador has jurisdiction to hear appeals in both criminal and civil matters from the Supreme Court of Newfoundland and Labrador, Supreme Court of Newfoundland and Labrador, Provincial Court and designated boards and administrative tribunals.
The Court now hears appeals of all type from the Supreme Court of Newfoundland and Labrador's General Division and Family Division, the Provincial Court, and a number of boards and tribunals. Decisions are subject to final appeal to the Supreme Court of Canada. Prior to 1949, when Newfoundland became a province of Canada, final appeals passed to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, which was the highest court for the British Empire and Commonwealth. (For a list of Newfoundland decisions from the Judicial Committee, see: List of Newfoundland Cases of the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (pre-1949)).

The Supreme Court of Canada is the highest court of Canada, the final court of appeals in the Canadian justice system. The court grants permission to between 40 and 75 litigants each year to appeal decisions rendered by provincial, territorial and federal appellate courts. Its decisions are the ultimate expression and application of Canadian law and binding upon all lower courts of Canada, except to the extent that they are overridden or otherwise made ineffective by an Act of Parliament or the Act of a provincial legislative assembly pursuant to section 33 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.

The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) is the highest court of appeal for certain British territories and Commonwealth countries. Established on 13 August 1833 to hear appeals formerly heard by the King-in-Council, the Privy Council formerly acted as the court of last resort for the entire British Empire, and continues to act as the highest court of appeal for several independent Commonwealth nations, the Crown Dependencies, and the British Overseas Territories.
The Queen's Bench is the superior court in a number of jurisdictions within some of the Commonwealth realms. The original King's Bench, founded in 1215 in England, was one of the ancient courts of the land and is now a division of the High Court of Justice of England and Wales.
The Court of Appeal for Ontario is an appellate court in Ontario that is based at historic Osgoode Hall in downtown Toronto.

The Nova Scotia Supreme Court is a superior court in the province of Nova Scotia.
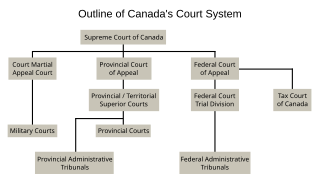
The court system of Canada forms the judicial branch of government, formally known as "The Queen on the Bench", which interprets the law and is made up of many courts differing in levels of legal superiority and separated by jurisdiction. Some of the courts are federal in nature, while others are provincial or territorial.

The Court of Appeal for Nova Scotia is the highest appeal court in the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. There are currently 8 judicial seats including one assigned to the Chief Justice of Nova Scotia. At any given time there may be one or more additional justices who sit as supernumerary justices. The court sits in Halifax, which is the capital of Nova Scotia. Cases are heard by a panel of three judges. They publish approximately 80 cases each year.

The Court of Appeal of Quebec is the highest judicial court in Quebec, Canada. It hears cases in Quebec City and Montreal.

The Federal Court is a Canadian trial court that hears cases arising under certain areas of federal law. The Federal Court is a lower court with nationwide jurisdiction.

The Supreme Court of British Columbia (BCSC) is the superior trial court for the province of British Columbia, Canada. The BCSC hears civil and criminal law cases as well as appeals from the Provincial Court of British Columbia. There are 90 judicial positions on the BCSC bench in addition to supernumary judges, making for a grant total of 108 judges. There are also 13 Supreme Court masters who hear and dispose of a wide variety of applications in chambers.

The British Columbia Court of Appeal (BCCA) is the highest appellate court in the province of British Columbia, Canada. It was established in 1910 following the 1907 Court of Appeal Act.

The Court of Queen's Bench of Alberta is the superior court of the Canadian province of Alberta. The Court of Queen's Bench of Alberta in Calgary was relocated to the Calgary Courts Centre in 2007. The Court of Queen's Bench has been located at the Law Courts building in Edmonton since the 1970s.
The Court of Appeal of New Brunswick is the appellate court in the province of New Brunswick. There are five Justices, one Chief Justice, any former judge of the Court of Appeal who is a supernumerary judge and any former Chief Justice of New Brunswick who is a judge or a supernumerary judge. The court sits in Fredericton, New Brunswick. Cases are heard by a panel of three judges.
The Superior Court of Quebec is the highest trial Court in the Province of Quebec, Canada. It consists of 157 judges who are appointed by the federal government. Appeals from this Court are taken to the Quebec Court of Appeal.
The Manitoba Court of Appeal is the highest court of appeal in the Canadian province of Manitoba. It was established in 1906. It is located in the Old Law Courts building at 408 York Avenue in Winnipeg, the capital city of Manitoba. It hears criminal, civil and family law cases, as well as appeals from various administrative boards and tribunals.
The Supreme Court of Prince Edward Island is the superior court of the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island.
Horace Harvey was a lawyer, jurist, and a Chief Justice of Alberta, Canada.
The Court of Appeal of Alberta is a Canadian appellate court.
The Judiciary of Sri Lanka are the civil and criminal courts responsible for the administration of justice in Sri Lanka. The Constitution of Sri Lanka defines courts as independent institutions within the traditional framework of checks and balances. They apply Sri Lankan Law which is an amalgam of English common law, Roman-Dutch civil law and Customary Law; and are established under the Judicature Act No 02 of 1978 of the Parliament of Sri Lanka.
Arthur Samuel Mifflin was a Canadian politician and judge. He represented the electoral district of Trinity North in the Newfoundland and Labrador House of Assembly from 1956 to 1966. He was a member of the Liberal Party of Newfoundland and Labrador.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











