
In neurology, the Chiari malformation is a structural defect in the cerebellum, characterized by a downward displacement of one or both cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum.
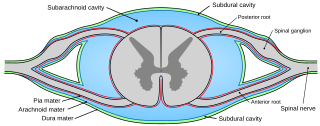
Pia mater, often referred to as simply the pia, is the delicate innermost layer of the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Pia mater is medieval Latin meaning "tender mother". The other two meningeal membranes are the dura mater and the arachnoid mater. Both the pia and arachnoid mater are derivatives of the neural crest while the dura is derived from embryonic mesoderm. The pia mater is a thin fibrous tissue that is permeable to water and small solutes. The pia mater allows blood vessels to pass through and nourish the brain. The perivascular space between blood vessels and pia mater is proposed to be part of a pseudolymphatic system for the brain. When the pia mater becomes irritated and inflamed the result is meningitis.

The dura mater, is the outermost of the three meningeal membranes. The dura mater has two layers, an outer periosteal layer closely adhered to the neurocranium, and an inner meningeal layer known as the dural border cell layer. The two dural layers are for the most part fused together forming a thick fibrous tissue membrane that covers the brain and the vertebrae of the spinal column. But the layers are separated at the dural venous sinuses to allow blood to drain from the brain. The dura covers the arachnoid mater and the pia mater the other two meninges in protecting the central nervous system.
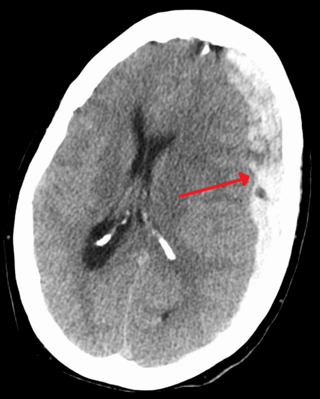
A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of bleeding in which a collection of blood—usually but not always associated with a traumatic brain injury—gathers between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the meninges surrounding the brain. It usually results from rips in bridging veins that cross the subdural space.

Arachnoiditis is an inflammatory condition of the arachnoid mater or 'arachnoid', one of the membranes known as meninges that surround and protect the central nervous system. The outermost layer of the meninges is the dura mater and adheres to inner surface of the skull and vertebrae. The arachnoid is under or "deep" to the dura and is a thin membrane that adheres directly to the surface of the brain and spinal cord.

The arachnoid mater is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural crest mesoectoderm in the embryo.

Encephalocele is a neural tube defect characterized by sac-like protrusions of the brain and the membranes that cover it through openings in the skull. These defects are caused by failure of the neural tube to close completely during fetal development. Encephaloceles cause a groove down the middle of the skull, or between the forehead and nose, or on the back side of the skull. The severity of encephalocele varies, depending on its location.
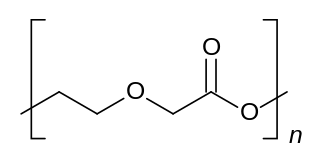
Polydioxanone or poly-p-dioxanone is a colorless, crystalline, biodegradable synthetic polymer.

Cranioplasty is a surgical operation on the repairing of cranial defects caused by previous injuries or operations, such as decompressive craniectomy. It is performed by filling the defective area with a range of materials, usually a bone piece from the patient or a synthetic material. Cranioplasty is carried out by incision and reflection of the scalp after applying anaesthetics and antibiotics to the patient. The temporalis muscle is reflected, and all surrounding soft tissues are removed, thus completely exposing the cranial defect. The cranioplasty flap is placed and secured on the cranial defect. The wound is then sealed.

Sealant is a substance used to block the passage of fluids through openings in materials, a type of mechanical seal. In building construction sealant is sometimes synonymous with caulk and also serve the purposes of blocking dust, sound and heat transmission. Sealants may be weak or strong, flexible or rigid, permanent or temporary. Sealants are not adhesives but some have adhesive qualities and are called adhesive-sealants or structural sealants.
Lyodura was a medical product used in neurosurgery that has been shown to transmit Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, a degenerative neurological disorder that is incurable, from affected donor cadavers to surgical recipients. Lyodura was introduced in 1969 as a product of B. Braun Melsungen AG, a leading hospital supply company based in Germany.
Tachosil is an equine collagen sponge coated with the human plasma-derived coagulation factors fibrinogen and thrombin. It is used during surgery to stop local bleeding on internal organs (hemostasis). Tachosil reacts upon contact with blood, other body fluids or saline to form a clot that glues it to the tissue surface.

An external ventricular drain (EVD), also known as a ventriculostomy or extraventricular drain, is a device used in neurosurgery to treat hydrocephalus and relieve elevated intracranial pressure when the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the brain is obstructed. An EVD is a flexible plastic catheter placed by a neurosurgeon or neurointensivist and managed by intensive care unit (ICU) physicians and nurses. The purpose of external ventricular drainage is to divert fluid from the ventricles of the brain and allow for monitoring of intracranial pressure. An EVD must be placed in a center with full neurosurgical capabilities, because immediate neurosurgical intervention can be needed if a complication of EVD placement, such as bleeding, is encountered.

Orthostatic headache is a medical condition in which a person develops a headache while vertical and the headache is relieved when horizontal. Previously it was often misdiagnosed as different primary headache disorders such as migraine or tension headaches. Increasing awareness of the symptom and its causes has prevented delayed or missed diagnosis.

A cerebrospinal fluid leak is a medical condition where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord leaks out of one or more holes or tears in the dura mater. A CSF leak is classed as either spontaneous (primary), having no known cause, or nonspontaneous (secondary) where it is attributed to an underlying condition. Causes of a primary CSF leak are those of trauma including from an accident or intentional injury, or arising from a medical intervention known as iatrogenic. A basilar skull fracture as a cause can give the sign of CSF leakage from the ear, nose or mouth. A lumbar puncture can give the symptom of a post-dural-puncture headache.
A fibrin scaffold is a network of protein that holds together and supports a variety of living tissues. It is produced naturally by the body after injury, but also can be engineered as a tissue substitute to speed healing. The scaffold consists of naturally occurring biomaterials composed of a cross-linked fibrin network and has a broad use in biomedical applications.
Endoscopic endonasal surgery is a minimally invasive technique used mainly in neurosurgery and otolaryngology. A neurosurgeon or an otolaryngologist, using an endoscope that is entered through the nose, fixes or removes brain defects or tumors in the anterior skull base. Normally an otolaryngologist performs the initial stage of surgery through the nasal cavity and sphenoid bone; a neurosurgeon performs the rest of the surgery involving drilling into any cavities containing a neural organ such as the pituitary gland. The use of endoscope was first introduced in Transsphenoidal Pituitary Surgery by R Jankowsky, J Auque, C Simon et al. in 1992 G.
Tissuemed is a medical device developer and manufacturer based in Leeds, UK.
William D. Spotnitz is a cardiothoracic surgeon and medical researcher who has made significant contributions to the development and testing of surgical techniques. He is a notable researcher in the United States in use of fibrin glue. Spotnitz serves as a heart surgeon in the University of Virginia Health System. He also previously served as the director of the hospital's Tissue Adhesive Center, which promoted and advanced the use of adhesives in surgery. He currently serves as the director of the Surgical Therapeutic Advancement Center, a successor program conducting more generalized research in surgical procedures.
Neuroplastic or neuroplastic and reconstructive surgery is the surgical specialty involved in reconstruction or restoration of patients who undergo surgery of the central or peripheral nervous system. The field includes a wide variety of surgical procedures that seek to restore or replace a patient's skull, face, scalp, dura, the spine and/or its overlying tissues.












