
The Noongar are Aboriginal Australian people who live in the south-west corner of Western Australia, from Geraldton on the west coast to Esperance on the south coast. There are 14 different groups in the Noongar cultural bloc: Amangu, Ballardong, Yued, Kaneang, Koreng, Mineng, Njakinjaki, Njunga, Pibelmen, Pindjarup, Wadandi, Whadjuk, Wiilman and Wudjari. The Noongar people refer to their land as Noongar boodja.
Keith Windschuttle is an Australian historian. He was appointed to the board of the Australian Broadcasting Corporation in 2006. He was editor of Quadrant from 2007 to 2015 when he became chair of the board and editor-in-chief. He was the publisher of Macleay Press, which operated from 1994 to 2010.

Sir Douglas Ralph Nicholls was a prominent Aboriginal Australian from the Yorta Yorta people. He was a professional athlete, Churches of Christ pastor and church planter, ceremonial officer and a pioneering campaigner for reconciliation.

Marn Grook, marn-grook or marngrook is the popular collective name for traditional Indigenous Australian football games played at gatherings and celebrations by sometimes more than 100 players. From the Woiwurung language of the Kulin people, it means "ball" and "game".

The Day of Mourning was a protest held by Aboriginal Australians on 26 January 1938, the 150th anniversary of the arrival of the First Fleet and the British colonisation of Australia. It was held to draw attention to the poor treatment of Aboriginal people and entrenched racial discrimination. The protest purposefully coincided with Australia Day celebrations, with protests with similar aims continuing to be held on 26 January under the names Invasion Day or Survival Day.
The Australian colonies in the nineteenth century created offices involved in managing the affairs of Indigenous people in their jurisdictions.
John Kundereri "Jumbana" Moriarty is an Aboriginal Australian artist, government advisor and former soccer player. He is also known as founder of the Balarinji Design Studio, for painting two Qantas jets with Aboriginal motifs.

V-Tech Rampage is a 2007 action game created by Australian amateur video game developer Ryan Lambourn. The game recreates the Virginia Tech shooting, and was released in 12 May 2007 on Newgrounds, less than a month after the shooting occurred.
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, and/or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of present day Australia prior to British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups, which include many ethnic groups: the Aboriginal Australians of the mainland and many islands, including Tasmania, and the Torres Strait Islanders of the seas between Queensland and Papua New Guinea, located in Melanesia.
Media portrayals of Indigenous Australians have been described by academics and commentators as often negative or stereotyped. It is said that in issues which concern them, the voices of Indigenous Australians are drowned out by non-Indigenous voices, which present them as problems for the rest of society.
This is a timeline of Aboriginal history of Western Australia.
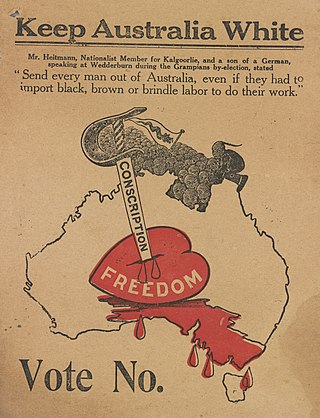
Racism in Australia comprises negative attitudes and views on race or ethnicity which are held by various people and groups in Australia, and have been reflected in discriminatory laws, practices and actions at various times in the history of Australia against racial or ethnic groups.
Various examples of violence have been attributed to racial factors during the recorded history of Australia since white settlement, and a level of intertribal rivalry and violence among Indigenous Australians pre-dates the arrival of white settlers from the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1788.

Change.org is a website which allows users to create and sign petitions in an attempt to advance various social causes by raising awareness and influencing decision-makers. The site is a US-based for-profit company and claims to have nearly 500 million users as of December 2022. Petitions often focus on causes such as general justice, economic justice, criminal justice, human rights, education, environmental protection, animal rights, health, and sustainable food.

The Australian Aborigines' League was established in Melbourne, Australia, in 1933 by William Cooper and others, including Margaret Tucker, Eric Onus, Anna and Caleb Morgan, and Shadrach James. Cooper was secretary of the League.
Censorship by Apple refers to Apple Inc.'s removal, omission, or disruption of the spread of content or information from its services or subsidiaries, such as the iTunes Store and the App Store, in order to comply with Apple's company policies, legal demands, or various government censorship laws.

Utopia is a 2013 documentary film written, produced and presented by John Pilger and directed by Pilger and Alan Lowery, that explores the experiences of Aboriginal Australians in modern Australia. The title is derived from the Aboriginal homeland community of Utopia, Northern Territory, one of the poorest and most desolate areas in Australia.

Cube Life: Island Survival is an indie open world sandbox survival video game developed and published by Cypronia. It was released for Wii U in June 2015. An HD remake was released for Steam in April 2018, for Android and iOS in August 2018, and for Nintendo Switch in December 2020.

The Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders (FCAATSI), founded in Adelaide, South Australia, as the Federal Council for Aboriginal Advancement (FCAA) on 16 February 1958, was a civil rights organisation which campaigned for the welfare of Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders, and the first national body representing Aboriginal interests. It was influential in lobbying in favour of the 1967 Referendum on Aboriginal Australians. It was renamed to National Aboriginal and Islander Liberation Movement (NAILM) in the early to mid 1970s, before disbanding in 1978.

William Henry Willshire was an Australian police officer who worked in Alice Springs in the Northern Territory of Australia. He was the first police officer to be charged for murder in Australian history, after killing a group of Aboriginal people at Tempe Downs Station.












