Related Research Articles

The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid.

The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea, the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing.
Articles related to anatomy include:
A suspensory ligament is a ligament that supports a body part, especially an organ.

The cricoid cartilage, or simply cricoid or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment site for muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in producing speech.

The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the laryngeal skeleton, the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx.

The cricothyroid ligament is a ligament in the neck. It connects the cricoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage. It prevents these cartilages from moving too far apart. It is cut during an emergency cricothyrotomy to treat upper airway obstruction.

The cricothyroid muscle is the only tensor muscle of the larynx aiding with phonation. It is innervated by the superior laryngeal nerve. Its action tilts the thyroid forward to help tense the vocal cords, thus increasing the pitch of the voice.

In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.

The sternohyoid muscle is a bilaterally paired, long, thin, narrow strap muscle of the anterior neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It is innervated by the ansa cervicalis. It acts to depress the hyoid bone.

The lateral thyrohyoid ligament is a round elastic cord, which forms the posterior border of the thyrohyoid membrane and passes between the tip of the superior cornu of the thyroid cartilage and the extremity of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. The internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve typical lies lateral to this ligament.

The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.

Tenon's capsule, also known as the Tenon capsule, fascial sheath of the eyeball or the fascia bulbi, is a thin membrane which envelops the eyeball from the optic nerve to the corneal limbus, separating it from the orbital fat and forming a socket in which it moves.
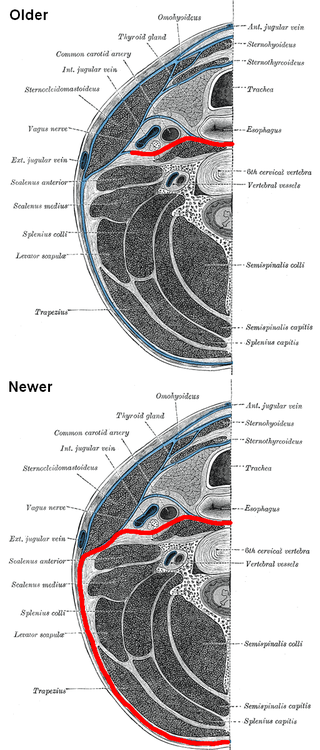
The prevertebral fascia is the layer of deep cervical fascia that surrounds the vertebral column. It is the deepest layer of deep cervical fascia.

The pretracheal fascia is a layer of the deep cervical fascia at the front of the neck. It attaches to the hyoid bone above, and - extending down into the thorax - blends with the fibrous pericardium below. It encloses the thyroid gland and parathyroid glands, trachea, and esophagus. It extends medially in front of the carotid vessels. It assists in forming the carotid sheath.
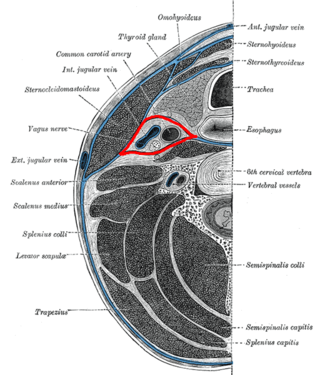
The buccopharyngeal fascia is a fascia of the pharynx. It represents the posterior portion of the pretracheal fascia. It covers the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscles, and buccinator muscle.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

In human male anatomy, the radix or root of the penis is the internal and most proximal portion of the human penis that lies in the perineum. Unlike the pendulous body of the penis, which is suspended from the pubic symphysis, the root is attached to the pubic arch of the pelvis and is not visible externally. It is triradiate in form, consisting of three masses of erectile tissue; the two diverging crura, one on either side, and the median bulb of the penis or urethral bulb. Approximately one third to one half of the penis is embedded in the pelvis and can be felt through the scrotum and in the perineum.
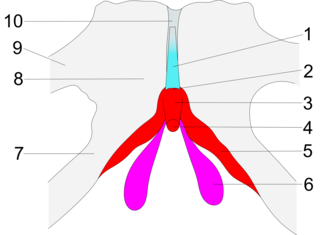
The suspensory ligament of the clitoris is a fibrous band at the deep fascial level that extends from the pubic symphysis to the deep fascia of the clitoris, anchoring the clitoris to the pubic symphysis. By virtue of this connection, the pubic symphysis supports the clitoris.
References
- ↑ Lathrop Stedman, Thomas, ed. (2006). "Suspensory ligament of thyroid gland". Stedman's Medical Dictionary (28th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0781764506. OCLC 61162300 . Retrieved 3 October 2012.
- ↑ Sabiston Textbook of Surgery 20th ed.