Related Research Articles

In macroeconomics, an industry is a branch of an economy that produces a closely related set of raw materials, goods, or services. For example, one might refer to the wood industry or to the insurance industry.

The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model. The others are the primary sector and the secondary sector (manufacturing).
ISO 3166 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines codes for the names of countries, dependent territories, special areas of geographical interest, and their principal subdivisions. The official name of the standard is Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions.
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a globally used medical classification used in epidemiology, health management and for clinical purposes. The ICD is maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO), which is the directing and coordinating authority for health within the United Nations System. The ICD is originally designed as a health care classification system, providing a system of diagnostic codes for classifying diseases, including nuanced classifications of a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or disease. This system is designed to map health conditions to corresponding generic categories together with specific variations, assigning for these a designated code, up to six characters long. Thus, major categories are designed to include a set of similar diseases.

Confectionery is the art of making confections, which are food items that are rich in sugar and carbohydrates. Exact definitions are difficult. In general, however, confectionery is divided into two broad and somewhat overlapping categories: bakers' confections and sugar confections. The occupation of confectioner encompasses the categories of cooking performed by both the French patissier and the confiseur.

The North American Industry Classification System or NAICS is a classification of business establishments by type of economic activity. It is used by governments and business in Canada, Mexico, and the United States of America. It has largely replaced the older Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) system, except in some government agencies, such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
The Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) was a system for classifying industries by a four-digit code as a method of standardizing industry classification for statistical purposes across agencies. Established in the United States in 1937, it is used by government agencies to classify industry areas. Similar SIC systems are also used by agencies in other countries, e.g., by the United Kingdom's Companies House.

A developed country, or high-income country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are the gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. Different definitions of developed countries are provided by the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; moreover, HDI ranking is used to reflect the composite index of life expectancy, education, and income per capita. Another commonly used measure of a developed country is the threshold of GDP (PPP) per capita of at least US$22,000. In 2023, 40 countries fit all four criteria, while an additional 15 countries fit three out of four.
Seo or SEO may refer to:

ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes are two-letter country codes defined in ISO 3166-1, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), to represent countries, dependent territories, and special areas of geographical interest. They are the most widely used of the country codes published by ISO, and are used most prominently for the Internet's country code top-level domains. They are also used as country identifiers extending the postal code when appropriate within the international postal system for paper mail, and have replaced the previous one consisting one-letter codes. They were first included as part of the ISO 3166 standard in its first edition in 1974.
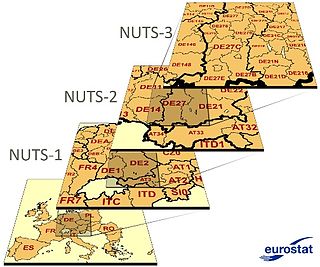
Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics or NUTS is a geocode standard for referencing the administrative divisions of countries for statistical purposes. The standard, adopted in 2003, is developed and regulated by the European Union, and thus only covers the EU member states in detail. The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics is instrumental in the European Union's Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund delivery mechanisms and for locating the area where goods and services subject to European public procurement legislation are to be delivered.
SNI may refer to:
There are several classification systems for the economic evaluation of mineral deposits worldwide. The most commonly used schemes base on the International Reporting Template, developed by the CRIRSCO - Committee for Mineral Reserves International Reporting Standards, like the Australian Joint Ore Reserves Committee - JORC Code 2012, the Pan-European Reserves & Resources Reporting Committee' – PERC Reporting Standard from 2021, the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum - CIM classification and the South African Code for the Reporting of Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves (SAMREC). A more detailed description of the historical development concerning reporting about mineral deposits can be found on the PERC web site.
The United Kingdom Standard Industrial Classification of Economic Activities (UKSIC) is a Standard Industrial Classification that is intended to help classify businesses according to the type of their economic activity. One or more SIC codes can be attributed to a business. SIC codes identify what a business does.
The International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC) is a United Nations industry classification system. Wide use has been made of ISIC in classifying data according to kind of economic activity in the fields of employment and health data.

The Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community, commonly referred to as NACE, is the industry standard classification system used in the European Union. The current version is revision 2 and was established by Regulation (EC) No 1893/2006. It is the European implementation of the UN classification ISIC, revision 4.
Asian people are the people of Asia. The term may also refer to their descendants. According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary, an Asian is “a person of Asian descent”.
Product classification or product taxonomy is a type of economic taxonomy which organizes products for a variety of purposes. However, not only products can be referred to in a standardized way but also sales practices in form of the “Incoterms” and industries can be classified into categories.
The Refinitiv Business Classification (TRBC) is an industry classification of global companies. It was developed by the Reuters Group under the name Reuters Business Sector Scheme (RBSS), was rebranded to Thomson Reuters Business Classification (TRBC) when the Thomson Corporation acquired the Reuters Group in 2008, forming Thomson Reuters, and was rebranded again, to The Refinitiv Business Classification (TRBC), in 2020. Since the creation of Refinitiv in October 2018, TRBC has been owned and operated by Refinitiv and is the basis for Refinitiv Indices.
The National Standardization Agency of Indonesia is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) member body for Indonesia. BSN is a non-ministerial Indonesian government agency with the main task of carrying out governmental tasks in the field of standardization and conformity assessment in Indonesia. The agency is also responsible to develop and maintain the Indonesian National Standard.