Sockets connected in cascade
When there is only one socket in a house or apartment, the incoming line is connected to the two lower receptacles and the upper receptacles are left unused. When a subscriber has more than one telephone socket, they typically are connected so that two telephones can not be connected to the telephone exchange at the same time. This is done by connecting the two upper receptacles of a socket to the lower receptacles of the next socket. When a connected telephone's handset is lifted, the two twisted pair connections are separated, thus disconnecting any telephones downward in the chain.
The plastic pin adds a presence function. When not inserted into a jack, the jack itself (mechanically) connects the incoming line to the next socket.
The cascade topology makes installing a DSL splitter a matter of plugging it in the first socket since this socket provides both direct access to the PSTN and connections to the remaining sockets.

Category 5 cable (Cat 5) is a twisted pair cable for computer networks. Since 2001, the variant commonly in use is the Category 5e specification (Cat 5e). The cable standard provides performance of up to 100 MHz and is suitable for most varieties of Ethernet over twisted pair up to 2.5GBASE-T but more commonly runs at 1000BASE-T speeds. Cat 5 is also used to carry other signals such as telephone and video.

LocalTalk is a particular implementation of the physical layer of the AppleTalk networking system from Apple Computer.

A 600 series connector is an obsolete three-pin connector with up to six conductors.

Components of an electrical circuit are electrically connected if an electric current can run between them through an electrical conductor. An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to create an electrical connection between parts of an electrical circuit, or between different electrical circuits, thereby joining them into a larger circuit.

A phone connector is a family of cylindrically-shaped electrical connectors primarily for analog audio signals. Invented in the late 19th century for telephone switchboards, the phone connector remains in use for interfacing wired audio equipment, such as headphones, speakers, microphones, mixing consoles, and electronic musical instruments. A male connector, is mated into a female connector, though other terminology is used.

A registered jack (RJ) is a standardized telecommunication network interface for connecting voice and data equipment to a computer service provided by a local exchange carrier or long distance carrier. Registered interfaces were first defined in the Universal Service Ordering Code (USOC) system of the Bell System in the United States for complying with the registration program for customer-supplied telephone equipment mandated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the 1970s. Subsequently, in 1980 they were codified in title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations Part 68. Registered jack connections began to see use after their invention in 1973 by Bell Labs. The specification includes physical construction, wiring, and signal semantics. Accordingly, registered jacks are primarily named by the letters RJ, followed by two digits that express the type. Additional letter suffixes indicate minor variations. For example, RJ11, RJ14, and RJ25 are the most commonly used interfaces for telephone connections for one-, two-, and three-line service, respectively. Although these standards are legal definitions in the United States, some interfaces are used worldwide.

A DC connector is an electrical connector that supplies direct current (DC) power.

The DIN connector is an electrical connector that was standardized by the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN), the German Institute for Standards, in the mid 1950s, initially with 3 pins for mono, but when stereo connections and gear appeared in late 1950s, versions with 5 pins or more were launched. The male DIN connectors (plugs) feature a 13.2 mm diameter metal shield with a notch that limits the orientation in which plug and socket can mate. The range of DIN connectors, different only in the configuration of the pins, have been standardized as DIN 41524 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 ; DIN 45322 ; DIN 45329 / IEC/DIN EN 60130–9 ; and DIN 45326 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9.

A telephone jack and a telephone plug are electrical connectors for connecting a telephone set or other telecommunications apparatus to the telephone wiring inside a building, establishing a connection to a telephone network. The plug is inserted into its counterpart, the jack, which is commonly affixed to a wall or baseboard. The standards for telephone jacks and plugs vary from country to country, though the 6P2C style modular plug has become by far the most common type.

A lineman's handset is a special type of telephone used by technicians for installing and testing local loop telephone lines. It is also called a test set, butt set, or buttinski.

Industrial and multiphase plugs and sockets provide a connection to the electrical mains rated at higher voltages and currents than household plugs and sockets. They are generally used in polyphase systems, with high currents, or when protection from environmental hazards is required. Industrial outlets may have weatherproof covers, waterproofing sleeves, or may be interlocked with a switch to prevent accidental disconnection of an energized plug. Some types of connectors are approved for hazardous areas such as coal mines or petrochemical plants, where flammable gas may be present.
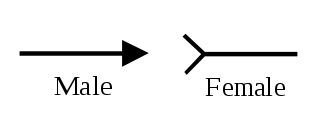
In electrical and mechanical trades and manufacturing, each half of a pair of mating connectors or fasteners is conventionally assigned the designation male or female. The female connector is generally a receptacle that receives and holds the male connector. Alternative terminology such as plug and socket or jack are sometimes used, particularly for electrical connectors.
The Freebox is an ADSL-VDSL-FTTH modem and a set-top box that the French Internet service provider named Free provides to its DSL-FTTH subscribers.

In telecommunications, structured cabling is building or campus cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements called subsystems. Structured cabling components include twisted pair and optical cabling, patch panels and patch cables.

A modular connector is a type of electrical connector for cords and cables of electronic devices and appliances, such as in computer networking, telecommunication equipment, and audio headsets.
Communications Specification for Fitness Equipment (CSAFE) is a fitness industry-wide communications specification developed in 1997 for exercise equipment. As this specification was originally developed by the company FitLinxx, sometimes it is also referred to as FitLinxx.

A coaxial power connector is an electrical power connector used for attaching extra-low voltage devices such as consumer electronics to external electricity. Also known as barrel connectors, concentric barrel connectors or tip connectors, these small cylindrical connectors come in an enormous variety of sizes.
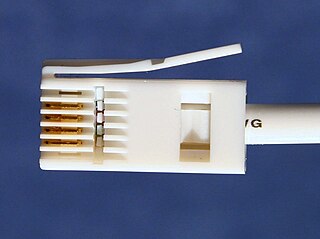
British telephone sockets were introduced in their current plug and socket form on 19 November 1981 by British Telecom to allow subscribers to connect their own telephones. The connectors are specified in British Standard BS 6312. Electrical characteristics of the telephone interface are specified by individual network operators, e.g. in British Telecom's SIN 351. Electrical characteristics required of British telephones used to be specified in BS 6305.

The Danish telephone plug is the special flat round telephone plug used in Denmark for POTS (analog) telephone lines and some "raw copper" telephone lines. The plug has 3 flat pins arranged at right angles to each other. This plug is used in few if any other places in the world, and most equipment now made uses the US/International RJ11 socket on the device end and includes either a cable with the Danish telephone plug at the wall end, or a standard RJ11 to RJ11 cable with a bundled Telephone Adapter.
ANSI/TIA-568 is a technical standard for commercial building cabling for telecommunications products and services. The title of the standard is Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard and is published by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), a body accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
















