A personal communications service (PCS) is set of communications capabilities that provide a combination of terminal mobility, personal mobility, and service profile management. This class of services comprises several types of wireless voice or wireless data communications systems, typically incorporating digital technology, providing services similar to advanced cellular mobile or paging services. In addition, PCS can also be used to provide other wireless communications services, including services that allow people to place and receive communications while away from their home or office, as well as wireless communications to homes, office buildings and other fixed locations. Described in more commercial terms, PCS is a generation of wireless cellular-phone technology, that combines a range of features and services surpassing those available in analogue- and first-generation (2G) digital-cellular phone systems, providing a user with an all-in-one wireless phone, paging, messaging, and data service.
Very high-speed digital subscriber line (VDSL) and very high-speed digital subscriber line 2 (VDSL2) are digital subscriber line (DSL) technologies providing data transmission faster than the earlier standards of asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) G.992.1, G.992.3 (ADSL2) and G.992.5 (ADSL2+).

Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) is a family of wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) options.
4G is the fourth generation of broadband cellular network technology, succeeding 3G and preceding 5G. A 4G system must provide capabilities defined by ITU in IMT Advanced. Potential and current applications include amended mobile web access, IP telephony, gaming services, high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing, and 3D television.
OMA SpecWorks, previously the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) is a standards organization which develops open, international technical standards for the mobile phone industry. It is a nonprofit Non-governmental organization (NGO), not a formal government-sponsored standards organization as is the International Telecommunication Union (ITU): a forum for industry stakeholders to agree on common specifications for products and services.

Internet Protocol television (IPTV) is the delivery of television content over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. This is in contrast to delivery through traditional terrestrial, satellite, and cable television formats. Unlike downloaded media, IPTV offers the ability to stream the source media continuously. As a result, a client media player can begin playing the content almost immediately. This is known as streaming media.
The next-generation network (NGN) is a body of key architectural changes in telecommunication core and access networks. The general idea behind the NGN is that one network transports all information and services by encapsulating these into IP packets, similar to those used on the Internet. NGNs are commonly built around the Internet Protocol, and therefore the term all IP is also sometimes used to describe the transformation of formerly telephone-centric networks toward NGN.

Radvision was a provider of video conferencing solution and enabling products for IP communication developers based in Tel Aviv, Israel. Radvision was acquired by Avaya in June 2012. Spirent Communications acquired Radvision's Technology Business Unit from Avaya in July 2014, to become Spirent Developer Tools Business Unit.
Qualcomm Atheros is a developer of semiconductor chips for network communications, particularly wireless chipsets. The company was founded under the name T-Span Systems in 1998 by experts in signal processing and VLSI design from Stanford University, the University of California, Berkeley, and private industry. The company was renamed Atheros Communications in 2000 and it completed an initial public offering in February 2004, trading on the NASDAQ under the symbol ATHR.
Spirent Communications plc is a British multinational telecommunications testing company headquartered in Crawley, West Sussex, in the United Kingdom. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.
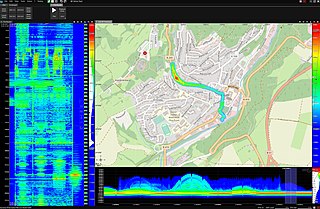
RF Drive testing is a method of measuring and assessing the coverage, capacity and Quality of Service (QoS) of a mobile radio network.
Carrier Ethernet is a marketing term for extensions to Ethernet for communications service providers that utilize Ethernet technology in their networks.
G.hn is a specification for home networking with data rates up to 2 Gbit/s and operation over four types of legacy wires: telephone wiring, coaxial cables, power lines and plastic optical fiber. A single G.hn semiconductor device is able to network over any of the supported home wire types. Some benefits of a multi-wire standard are lower equipment development costs and lower deployment costs for service providers.
Wireless Home Digital Interface (WHDI) is a consumer electronic specification for a wireless HDTV connectivity throughout the home.

LTE Advanced is a mobile communication standard and a major enhancement of the Long Term Evolution (LTE) standard. It was formally submitted as a candidate 4G to ITU-T in late 2009 as meeting the requirements of the IMT-Advanced standard, and was standardized by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) in March 2011 as 3GPP Release 10.

In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by using a different radio interface and core network improvements. LTE is the upgrade path for carriers with both GSM/UMTS networks and CDMA2000 networks. Because LTE frequencies and bands differ from country to country, only multi-band phones can use LTE in all countries where it is supported.
Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co KG is an international electronics group specializing in the fields of electronic test equipment, broadcast & media, cybersecurity, radiomonitoring and radiolocation, and radiocommunication. The company provides products for the wireless communications, broadcast & media, cybersecurity and electronics industry, aerospace and defense, homeland security and critical infrastructures.
Empirix Inc. is a privately held company which designs and manufactures service assurance testing and monitoring equipment for IP-based communications networks such as Voice-over-Internet-Protocol (VoIP), IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)-based, next generation network and 4G wireless networks. Empirix offers enterprise and carrier grade products as well as quality assurance products for network equipment manufacturers. Empirix is headquartered in Billerica, MA. On April 21, 2021, Empirix has been acquired by Infovista, a Network automation software. Infovista, which is majority owned by Apax Partners, says the deal “brings together a team of over 1,000 professionals serving over 1,700 customers across more than 150 countries, including 23 of the top 30 CSPs globally.”
Perceptual Objective Listening Quality Analysis (POLQA) was the working title of an ITU-T standard that covers a model to predict speech quality by means of analyzing digital speech signals. The model was standardized as Recommendation ITU-T P.863 in 2011. The second edition of the standard appeared in 2014, and the third, currently in-force edition was adopted in 2018 under the title Perceptual objective listening quality prediction.
High Power User Equipment (HPUE) is a special class of user equipment for the LTE cellular network.





