| Synchysis scintillans | |
|---|---|
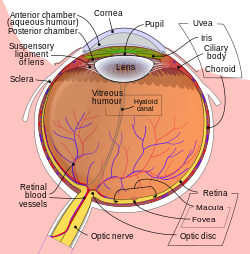 | |
| Human eye (vitreous humor in the middle) | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
Synchysis scintillans is a degenerative condition of the eye resulting in liquefied vitreous humor and the accumulation of cholesterol crystals within the vitreous. It is also known as cholesterolosis bulbi. The vitreous liquifies in a process known as syneresis. Synchysis scintillans appears as small white floaters that freely move in the posterior part of the eye, giving a snow globe effect. It is most commonly seen in eyes that have suffered from a degenerative disease and are end-stage. [1]
The condition is seen rarely. Associated with the advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy, but the exact pathogenesis is unknown.[ citation needed ]
The condition is symptomless and untreatable. In ophthalmoscopic examination it appears as small, flat, yellow, highly refractive crystals of cholesterol floating freely in the vitreous. These will settle, due to gravity, if the eye is immobilized.[ citation needed ]