Related Research Articles

DeWitt is a town (township) in Onondaga County, New York, USA. As of the 2010 census, the town's population was 25,838. The town is named after Major Moses DeWitt, a judge and soldier. An eastern suburb of Syracuse, DeWitt also is "the site of most of the campus and all of the academic buildings of Le Moyne College".

East Syracuse is an incorporated village and a suburb of the City of Syracuse in eastern Onondaga County, New York. United States. As of the 2010 U.S. census, the village had a population of 3,084. It is located immediately east of Syracuse, in the town of DeWitt.
Interstate 481 (I-481) is an auxiliary Interstate Highway that serves as an eastern bypass of Syracuse, New York, in the United States. It begins at its parent, I-81, in the city's southern end and travels through the eastern Syracuse suburbs of Jamesville, DeWitt, and Cicero before rejoining I-81 in the suburb of North Syracuse. After crossing I-81 in North Syracuse, I-481 continues northwest to Fulton and Oswego as New York State Route 481 (NY 481). I-481 is part of the Veterans Memorial Highway, which extends northward onto NY 481.
Interstate 690 (I-690) is an auxiliary Interstate Highway that extends for 14.19 miles (22.84 km) through the vicinity of Syracuse, New York, in the United States. It is a spur of I-90 that travels southeast from Thruway exit 39 in Van Buren to I-481 in DeWitt. In between, I-690 passes through the western suburbs of Syracuse before heading east through the city itself, where it meets I-81 in downtown Syracuse. The expressway continues northwest of the Thruway as New York State Route 690 (NY 690).

Thomas De Witt Talmage was a preacher, clergyman and divine in the United States who held pastorates in the Reformed Church in America and Presbyterian Church. He was one of the most prominent religious leaders in the United States during the mid- to late-19th century, equaled as a pulpit orator perhaps only by Henry Ward Beecher. He also preached to crowds in England. During the 1860s and 70s, Talmage was a well-known reformer in New York City and was often involved in crusades against vice and crime.

Burnet Park is the largest park in Syracuse, New York, USA, covering an area of 88 acres (36 ha). It is located on the west end of the city, in the Far Westside in a neighborhood called Tipperary Hill.

New York State Railways was a subsidiary of the New York Central Railroad that controlled several large city streetcar and electric interurban systems in upstate New York. It included the city transit lines in Rochester, Syracuse, Utica, Oneida and Rome, plus various interurban lines connecting those cities. New York State Railways also held a 50% interest in the Schenectady Railway Company, but it remained a separate independent operation. The New York Central took control of the Rochester Railway Company, the Rochester and Eastern Rapid Railway and the Rochester and Sodus Bay Railway in 1905, and the Mohawk Valley Company was formed by the railroad to manage these new acquisitions. New York State Railways was formed in 1909 when the properties controlled by the Mohawk Valley Company were merged. In 1912 it added the Rochester and Suburban Railway, the Syracuse Rapid Transit Railway, the Oneida Railway, and the Utica and Mohawk Valley Railway. The New York Central Railroad was interested in acquiring these lines in an effort to control the competition and to gain control of the lucrative electric utility companies that were behind many of these streetcar and interurban railways. Ridership across the system dropped through the 1920s as operating costs continued to rise, coupled with competition from better highways and private automobile use. New York Central sold New York State Railways in 1928 to a consortium led by investor E. L. Phillips, who was looking to gain control of the upstate utilities. Phillips sold his stake to Associated Gas & Electric in 1929, and the new owners allowed the railway bonds to default. New York State Railways entered receivership on December 30, 1929. The company emerged from receivership in 1934, and local operations were sold off to new private operators between 1938 and 1948.
New York State Route 635 (NY 635) is a state highway located in the vicinity of Syracuse in Onondaga County, New York, in the United States. It extends for 2.25 miles (3.62 km) along Thompson Road from an intersection with Erie Boulevard (NY 5) in Syracuse to Carrier Circle in DeWitt, where NY 635 connects to both the New York State Thruway and NY 298. Along the way NY 635 also meets I-690. The route was assigned in 1980 after the section of Thompson Road between NY 290 and Carrier Circle was acquired by the state of New York.
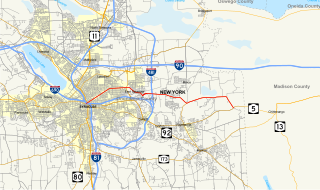
New York State Route 290 (NY 290) is a state highway located entirely within Onondaga County, New York, extending from downtown Syracuse to the east side of the county. It provides access to Green Lakes State Park from the north.
New York State Route 92 (NY 92) is a state highway located in central New York in the United States. The western terminus of the route is at an intersection with U.S. Route 11 in downtown Syracuse. Its eastern terminus is at a junction with US 20 west of the village of Cazenovia. NY 92 is known as East Genesee Street through Syracuse and DeWitt; from DeWitt to Cazenovia, its name varies by location. It heads generally eastward through Syracuse to DeWitt, where it crosses Interstate 481 (I-481) while concurrent with NY 5. At the east end of the overlap, it splits off follows a more southeasterly routing through the village of Manlius to Cazenovia.
The Holy Cross Cemetery Line was a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, running as a short branch of the Nostrand Avenue Line east to Holy Cross Cemetery on Tilden Avenue. Originally a streetcar line, it was replaced by a bus route, which is no longer operated.
New York State Route 598 (NY 598) is a north–south state highway located within Onondaga County, New York, in the United States. It extends for 2.31 miles (3.72 km) from an intersection with NY 5 in the city of Syracuse to a junction with NY 298 in the adjacent town of Salina. The route intersects Interstate 690 (I-690) near its southern terminus and passes through Syracuse's Eastwood neighborhood near its midpoint, where it meets NY 290.
New York State Route 20SY (NY 20SY) was a state highway in the vicinity of Syracuse, New York, in the United States. It connected U.S. Route 20 (US 20) to downtown Syracuse via Skaneateles, Camillus, Manlius, and Cazenovia in Onondaga County and Madison County. The highway began at an intersection with US 20 and NY 321 in the village of Skaneateles and ended at a junction with US 20, NY 20N, and NY 92 near the village of Cazenovia. Most of NY 20SY overlapped another route; however, two sections of NY 20SY—one in the town of Camillus and another near the village of Fayetteville—were not concurrent with another highway.
The Railroad industry in Syracuse, New York got its start in October 1831 when a convention held in the city marked one of the earliest moves to stimulate the era of railroad building which ultimately brought steam railroad service to New York State.
The Syracuse and East Side Street Railway, an interurban rail in Syracuse, New York, was chartered on August 25, 1894, and was a successor to the Syracuse, Eastwood Heights and DeWitt Railroad Company. The company was also known as the Syracuse and East Side Railroad.
The Genesee and Water Street Railroad, a horse-drawn street trolley in Syracuse, New York, was established in 1865. The company was one of three different railways that were awarded operation franchise rights to run cars in James Street. The firm also secured the franchise to operate cars in Westcott Street, to South Beech Street, Euclid Avenue, College Place, University Place, Walnut Avenue and Madison Street.
The New Brighton and Onondaga Valley Railroad, a horse-drawn street trolley line, was chartered on May 5, 1869, in Syracuse, New York. The road was also known as the New Brighton and Onondaga Railroad.
The Seventh Ward Railroad, a street trolley line in Syracuse, New York, was established in 1886 and held the city railway franchise rights to East Fayette Street. The total length of the road was 3 miles (4.8 km). The route followed Fayette Street from Salina Street to Montgomery Street, Jefferson, Grape, Kennedy, Renwick Avenue with final destination Oakwood Cemetery.
The Eleventh Ward Railroad, a street trolley line in Syracuse, New York, was established in 1889 and held the city railway franchise rights to East Fayette Street. The line followed East Fayette Street to Montgomery Street and from there through Burt, Cortland Avenue, Midland Avenue, Colvin Street, Mulberry, Elizabeth, Baker Avenue and terminating on Kennedy street.
The Rochester Railway Company operated a streetcar transit system throughout the city of Rochester from 1890 until its acquisition by Rochester Transit Corp. in 1938. Formed by a group of Pittsburgh investors, the Rochester Railway Company purchased the Rochester City & Brighton Railroad in 1890, followed by a lease of the Rochester Electric Railway in 1894. The Rochester and Suburban Railway was leased in 1905, extending the system's reach to Irondequoit and Sea Breeze. Rochester Railways was acquired by the Mohawk Valley Company, a subsidiary of the New York Central Railroad set up to take control of electric railways in its territory. In 1909 the holdings of the Mohawk Valley Company were consolidated as the New York State Railways.
References
- ↑ "First Streetcars Operated Here in 1860". Syracuse Herald . Syracuse, New York. December 14, 1922.
- ↑ "Study for Bus Franchise Recalls Early Trolley Lines". Syracuse Herald-Journal . Syracuse, New York. May 23, 1940.
- ↑ The Electrical World, Volume 14, Applications of Power. The N. J. Johnston Company, Ltd., November 27, 1889, p.847. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ↑ "Receiver Sale". The Evening Herald . Syracuse, New York. May 17, 1894.