
The 2011Bahraini uprising was a series of anti-government protests in Bahrain led by the Shia-dominant and some Sunni minority Bahraini opposition from 2011 until 2014. The protests were inspired by the unrest of the 2011 Arab Spring and protests in Tunisia and Egypt and escalated to daily clashes after the Bahraini government repressed the revolt with the support of the Gulf Cooperation Council and Peninsula Shield Force. The Bahraini protests were a series of demonstrations, amounting to a sustained campaign of non-violent civil disobedience and some violent resistance in the Persian Gulf country of Bahrain. As part of the revolutionary wave of protests in the Middle East and North Africa following the self-immolation of Mohamed Bouazizi in Tunisia, the Bahraini protests were initially aimed at achieving greater political freedom and equality for the 70% Shia population.

Hossam el-Hamalawy is an Egyptian journalist, blogger, photographer and socialist activist. He is a member of the Revolutionary Socialists and the Center for Socialist Studies.
The following is a timeline of the Syrian Civil War from May to August 2011, including the escalation of violence in many Syrian cities.

Since the start of the Syrian Civil War, all sides have used social media to try to discredit their opponents by using negative terms such as 'Syrian regime' for the government, 'armed gangs/terrorists' for the rebels, 'Syrian government/US State Department propaganda', 'biased', 'US/Western/foreign involvement'. According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, given the complexity of the Syrian conflict, media bias in reporting remains a key challenge, plaguing the collection of useful data and misinforming researchers and policymakers regarding the actual events taking place.

The 2011 siege of Hama was among the many nationwide crackdowns by the Syrian government during the Syrian revolution, the early stage of the Syrian civil war. Anti-government protests had been ongoing in the Syrian city of Hama since 15 March 2011, when large protests were first reported in the city, similar to the protests elsewhere in Syria. The events beginning in July 2011 were described by anti-government activists in the city as a "siege" or "blockade".

The Free Syrian Army is a big-tent coalition of decentralized Syrian opposition rebel groups in the Syrian civil war founded on 29 July 2011 by Colonel Riad al-Asaad and six officers who defected from the Syrian Armed Forces. The officers announced that the immediate priority of the Free Syrian Army was to safeguard the lives of protestors and civilians from the deadly crackdown by Bashar al-Assad's security apparatus; with the ultimate goal of accomplishing the objectives of the Syrian revolution, namely, the end to the decades-long reign of the ruling al-Assad family. In late 2011, the FSA was the main Syrian military defectors group. Initially a formal military organization at its founding, its original command structure dissipated by 2016, and the FSA identity has since been used by various Syrian opposition groups.
Protests began in Syria as early as 26 January 2011, and erupted on 15 March 2011 with a "Day of Rage" protest generally considered to mark the start of a nationwide uprising. The Syrian government's reaction to the protests became violent on 16 March, and deadly on 18 March, when four unarmed protesters were killed in Daraa.
The following is a timeline of the Syrian uprising from September to December 2011. This period saw the uprising take on many of the characteristics of a civil war, according to several outside observers, including the United Nations Commission on Human Rights, as armed elements became better organized and began carrying out successful attacks in retaliation for the ongoing crackdown by the Syrian government on demonstrators and defectors.
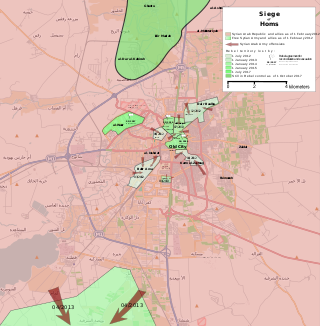
The siege of Homs was a military confrontation between the Syrian military and the Syrian opposition in the city of Homs, a major rebel stronghold during the Syrian Civil War. The siege lasted three years from May 2011 to May 2014, and ultimately resulted in an opposition withdrawal from the city.

The 2011–2013 Daraa Governorate clashes are a series of military confrontations between the Syrian Army and the Free Syrian Army in Daraa Governorate, Syria, which began in November 2011, after widescale protests and crackdown on protesters in Daraa had lasted since April 2011. The clashes had been ongoing as part of the Syrian civil war, until the U.N. brokered cease fire came into effect on 14 April 2012. Sporadic clashes continued since then, however.
The Rif Dimashq clashes were a series of unrests and armed clashes in and around Damascus, the capital of Syria, from November 2011 until a stalemate in March 2012. The violence was part of the wider early insurgency phase of the Syrian civil war. Large pro-government and anti-government protests took place in the suburbs and center of Damascus, with the situation escalating when members of the Free Syrian Army (FSA) started attacking military targets in November.

The 2012 Aleppo Governorate clashes were a series of battles as part of the early insurgency phase of the Syrian civil war in the Aleppo Governorate of Syria.

The September 2011 – March 2012 Idlib Governorate clashes were the violent incidents that took place in Idlib Governorate, a province of Syria, from September 2011 and prior to the April 2012 Idlib Governorate Operation.
On 6 January 2012, a bomb exploded in the Al-Midan district of Damascus, Syria. According to the Syrian government, a suicide bomber attacked buses carrying riot police shortly before an anti-government protest was to begin. It said that 26 people were killed and over 60 were injured. Most of the victims were civilians, though the Syrian government showed footage of what it claimed to be the funeral of 11 police officers killed in the attack.
The Battle of Zabadani took place in January through February 2012, during the Syrian civil war. During the initial stages of the battle, the rebel FSA took control of the town. However, less than a month later, the Army retook control of Zabadani, forcing rebel fighters to withdraw towards the Lebanese border.
This article details the Syrian government's response to protests and civilian uprisings of the Syrian revolution which began in early 2011, that unravelled the socio-political stability of Syria, eventually plunging the country into a nationwide civil war by mid-2012.

The Battle of Idlib was fought in the city of Idlib, located in the north of Syria, starting on 10 March 2012. The battle took place in a province considered a stronghold of the armed opposition to the Syrian government and was fought in the wider context of the Syrian Army trying to retake several rebel strongholds. After three days of fighting, the Syrian Army recaptured the city.
The siege of Daraa occurred within the context of the 2011 Arab Spring protests in Syria, in which Daraa was the center of unrest. On 25 April 2011, the Syrian Army began a ten-day siege of the city, an operation that helped escalate the uprising into an armed rebellion and subsequent civil war.

Women played a variety of roles in the Arab Spring, but its impact on women and their rights is unclear. The Arab Spring was a series of demonstrations, protests, and civil wars against authoritarian regimes that started in Tunisia and spread to much of the Arab world. The leaders of Tunisia, Egypt, Libya, and Yemen were overthrown; Bahrain has experienced sustained civil disorder, and the protests in Syria have become a civil war. Other Arab countries experienced protests as well.

The Syrian revolution, also known as the Syrian Revolution of Dignity, was a series of mass protests and uprisings in Syria – with a subsequent violent reaction by the Syrian Arab Republic – lasting from March 2011 to June 2012, as part of the wider Arab Spring in the Arab world. The revolution, which demanded the end of the decades-long Assad family rule, began as minor demonstrations during January 2011 and transformed into large nation-wide protests in March. The uprising was marked by mass protests against the Ba'athist dictatorship of president Bashar al-Assad meeting police and military violence, massive arrests and a brutal crackdown, resulting in thousands of deaths and tens of thousands wounded.












