
AppleScript is a scripting language created by Apple Inc. that facilitates automated control over scriptable Mac applications. First introduced in System 7, it is currently included in all versions of macOS as part of a package of system automation tools. The term "AppleScript" may refer to the language itself, to an individual script written in the language, or, informally, to the macOS Open Scripting Architecture that underlies the language.

The Finder is the default file manager and graphical user interface shell used on all Macintosh operating systems. Described in its "About" window as "The Macintosh Desktop Experience", it is responsible for the launching of other applications, and for the overall user management of files, disks, and network volumes. It was introduced with the first Macintosh computer, and also exists as part of GS/OS on the Apple IIGS. It had been rewritten completely with the release of Mac OS X in 2001.
rmdir is a command which will remove an empty directory on a Unix, Unix-like, DOS, FlexOS, OS/2, Microsoft Windows or ReactOS operating system.
Macintosh File System (MFS) is a volume format created by Apple Computer for storing files on 400K floppy disks. MFS was introduced with the original Apple Macintosh computer in January 1984.
HFS Plus or HFS+ is a file system developed by Apple Inc. It replaced the Hierarchical File System (HFS) as the primary file system of Apple computers with the 1998 release of Mac OS 8.1. HFS+ continued as the primary Mac OS X file system until it was itself replaced with the release of the Apple File System (APFS) with macOS High Sierra in 2017. HFS+ is also one of the formats used by the iPod digital music player. It is also referred to as Mac OS Extended or HFS Extended, where its predecessor, HFS, is also referred to as Mac OS Standard or HFS Standard. During development, Apple referred to this file system with the codename Sequoia.

A wallpaper or background is a digital image used as a decorative background of a graphical user interface on the screen of a computer, mobile communications device or other electronic device. On a computer it is usually for the desktop, while on a mobile phone it is usually the background for the 'home' or 'idle' screen. Though most devices come with a default picture, users can usually change it to custom files of their choosing.
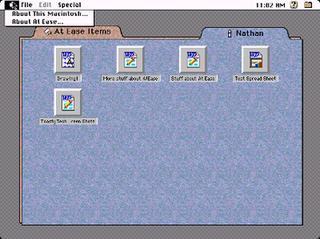
At Ease was an alternative to the Macintosh desktop developed by Apple Computer in the early 1990s for the classic Mac OS. It provided a simple environment for new Macintosh users and young children to help them to work without supervision. At Ease sits on top of the Finder desktop, providing a simple tabbed panel-oriented graphical user interface in which applications and documents are represented by icons on large buttons. Aside from its security features, its interface and basic functionality is very similar to the Packard Bell Navigator.
On the classic Mac OS, extensions were small pieces of code that extended the system's functionality. They were run initially at start-up time, and operated by a variety of mechanisms, including trap patching and other code modifying techniques. Initially an Apple developer hack, extensions became the standard way to provide a modular operating system. Large amounts of important system services such as the TCP/IP network stacks and USB and FireWire support were optional components implemented as extensions. The phrase "system extension" later came to encompass faceless background applications as well.
Speakable items is part of the speech recognition feature in the classic Mac OS and macOS operating systems. It allows the user to control their computer with natural speech, without having to train the computer beforehand. The commands must be present in the Speakable items folder though but can be created with something as simple as a shortcut, AppleScript, keyboard command, or Automator workflows.
In computing, a file shortcut is a handle in a user interface that allows the user to find a file or resource located in a different directory or folder from the place where the shortcut is located. Similarly, an Internet shortcut allows the user to open a page, file or resource located at a remote Internet location or Web site.
In computing, a virtual folder generally denotes an organizing principle for files that is not dependent on location in a hierarchical directory tree. Instead, it consists of software that coalesces results from a data store, which may be a database or a custom index, and presents them visually in the format in which folder views are presented. A virtual folder can be thought of as a view that lists all files tagged with a certain tag, and thus a simulation of a folder whose dynamic contents can be assembled on the fly, when requested. It is related in concept to several other topics in computer science, with names including saved search, saved query, and filtering.
The System folder is the directory in the classic Mac OS that holds various files required for the system to operate, such as fonts, system extensions, control panels, and preferences.

Keychain is the password management system in macOS, developed by Apple. It was introduced with Mac OS 8.6, and has been included in all subsequent versions of Mac OS, now known as macOS. A Keychain can contain various types of data: passwords, private keys, certificates, and secure notes.

Time Machine is a backup software application distributed as part of macOS, desktop operating system developed by Apple. The software is designed to work with AirPort Time Capsule, the Wi-Fi router with built-in hard disk, as well as other internal and external disk drives. It was introduced in Mac OS X Leopard.
Apple's Macintosh computer supports a wide variety of fonts. This support was one of the features that initially distinguished it from other systems.

The Apple menu is a drop-down menu that is on left side of the menu bar in the classic Mac OS, macOS and A/UX operating systems. The Apple menu's role has changed throughout the history of Apple Inc.'s operating systems, but the menu has always featured a version of the Apple logo.

In computing, the Trash is temporary storage for files that have been deleted in a file manager by the user, but not yet permanently erased from the file system. Typically, a recycle bin is presented as a special file directory to the user, allowing the user to browse deleted files, undelete those that were deleted by mistake, or delete them permanently.

DaisyDisk is a shareware disk space analyzer for macOS. It displays a sunburst diagram of files on a hard drive to help with the location or deletion of large files. It can display previews of files using Quick Look. It also allows the user to look at the file directly in Finder, in order to delete it or move it elsewhere.

Classic Mac OS is a colloquial term used to describe a series of operating systems developed for the Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Inc. from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The Macintosh operating system is credited with having popularized the graphical user interface concept. It was included with every Macintosh that was sold during the era it was developed, and many updates to the system software were done in conjunction with the introduction of new Macintosh systems.












