
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an infection of the vagina caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urination may occur. Itching is uncommon. Occasionally, there may be no symptoms. Having BV approximately doubles the risk of infection by a number of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV/AIDS. It also increases the risk of early delivery among pregnant women.

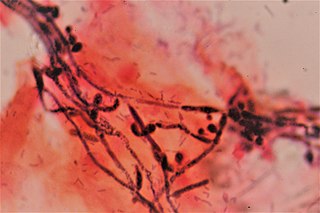
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any species of the genus Candida. When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers, among other symptoms.

Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula B(OH)3. It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves in water, and occurs in nature as the mineral sassolite. It is a weak acid that yields various borate anions and salts, and can react with alcohols to form borate esters.
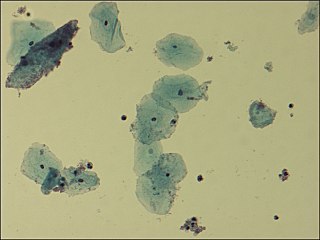
Gardnerella vaginalis is a species of Gram-variable-staining facultative anaerobic bacteria. The organisms are small non-spore-forming, nonmotile coccobacilli.
Vaginitis, also known as vulvovaginitis, is inflammation of the vagina and vulva. Symptoms may include itching, burning, pain, discharge, and a bad smell. Certain types of vaginitis may result in complications during pregnancy.

Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media, and endocarditis. It can also be used to treat acne, and some cases of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In combination with quinine, it can be used to treat malaria. It is available by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as a cream or a gel to be applied to the skin or in the vagina.

Terconazole is an antifungal drug used to treat vaginal yeast infection. It comes as a lotion or a suppository and disrupts the biosynthesis of fats in a yeast cell. It has a relatively broad spectrum compared to azole compounds but not triazole compounds. Testing shows that it is a suitable compound for prophylaxis for those that suffer from chronic vulvovaginal candidiasis.

Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, amount, and quality of discharge varies between individuals and can vary throughout the menstrual cycle and throughout the stages of sexual and reproductive development. Normal vaginal discharge may have a thin, watery consistency or a thick, sticky consistency, and it may be clear or white in color. Normal vaginal discharge may be large in volume but typically does not have a strong odor, nor is it typically associated with itching or pain. While most discharge is considered physiologic or represents normal functioning of the body, some changes in discharge can reflect infection or other pathological processes. Infections that may cause changes in vaginal discharge include vaginal yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and sexually transmitted infections. The characteristics of abnormal vaginal discharge vary depending on the cause, but common features include a change in color, a foul odor, and associated symptoms such as itching, burning, pelvic pain, or pain during sexual intercourse.

Vaginal flora, vaginal microbiota or vaginal microbiome are the microorganisms that colonize the vagina. They were discovered by the German gynecologist Albert Döderlein in 1892 and are part of the overall human flora. The amount and type of bacteria present have significant implications for an individual's overall health. The primary colonizing bacteria of a healthy individual are of the genus Lactobacillus, such as L. crispatus, and the lactic acid they produce is thought to protect against infection by pathogenic species.
A vaginal disease is a pathological condition that affects part or all of the vagina.
Vaginal yeast infection, also known as candidal vulvovaginitis and vaginal thrush, is excessive growth of yeast in the vagina that results in irritation. The most common symptom is vaginal itching, which may be severe. Other symptoms include burning with urination, a thick, white vaginal discharge that typically does not smell bad, pain during sex, and redness around the vagina. Symptoms often worsen just before a woman's period.
Anaerobic infections are caused by anaerobic bacteria. Obligately anaerobic bacteria do not grow on solid media in room air ; facultatively anaerobic bacteria can grow in the presence or absence of air. Microaerophilic bacteria do not grow at all aerobically or grow poorly, but grow better under 10% carbon dioxide or anaerobically. Anaerobic bacteria can be divided into strict anaerobes that can not grow in the presence of more than 0.5% oxygen and moderate anaerobic bacteria that are able of growing between 2 and 8% oxygen. Anaerobic bacteria usually do not possess catalase, but some can generate superoxide dismutase which protects them from oxygen.
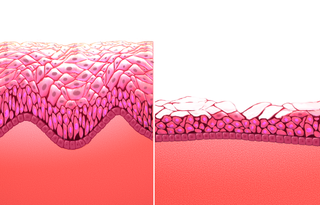
Atrophic vaginitis is inflammation of the vagina as a result of tissue thinning due to low estrogen levels. Symptoms may include pain with sex, vaginal itchiness or dryness, and an urge to urinate or burning with urination. It generally does not resolve without ongoing treatment. Complications may include urinary tract infections. Atrophic vaginitis as well as vulvovaginal atrophy, bladder and urethral dysfunctions are a group of conditions that constitute genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms.
A vulvar disease is a particular abnormal, pathological condition that affects part or all of the vulva. Several pathologies are defined. Some can be prevented by vulvovaginal health maintenance.
The vaginal flora in pregnancy, or vaginal microbiota in pregnancy, is different from the vaginal flora before sexual maturity, during reproductive years, and after menopause. A description of the vaginal flora of pregnant women who are immunocompromised is not covered in this article. The composition of the vaginal flora significantly differs in pregnancy. Bacteria or viruses that are infectious most often have no symptoms.
Paul Nyirjesy is a professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Drexel University, Philadelphia, and the director of Drexel Vaginitis Center. In 2016, Nyirjesy announced positive results from a clinical trial for a potential vaccine against Vaginitis.

Lactobacillus vaccines are used in the therapy and prophylaxis of non-specific bacterial vaginitis and trichomoniasis. The vaccines consist of specific inactivated strains of Lactobacilli, called "aberrant" strains in the relevant literature dating from the 1980s. These strains were isolated from the vaginal secretions of patients with acute colpitis. The lactobacilli in question are polymorphic, often shortened or coccoid in shape and do not produce an acidic, anti-pathogenic vaginal environment. A colonization with aberrant lactobacilli has been associated with an increased susceptibility to vaginal infections and a high rate of relapse following antimicrobial treatment. Intramuscular administration of inactivated aberrant lactobacilli provokes a humoral immune response. The production of specific antibodies both in serum and in the vaginal secretion has been demonstrated. As a result of the immune stimulation, the abnormal lactobacilli are inhibited, the population of normal, rod-shaped lactobacilli can grow and exert its defense functions against pathogenic microorganisms.
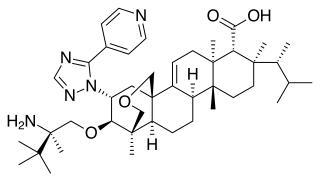
Ibrexafungerp, sold under the brand name Brexafemme, is an antifungal medication used to treat vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC). It is taken orally. It is also currently undergoing clinical trials for other indications via an intravenous (IV) formulation. An estimated 75% of women will have at least one episode of VVC and 40 to 45% will have two or more episodes in their lifetime.

Oteseconazole, a novel orally bioavailable and selective inhibitor of fungal cytochrome P450 enzyme 51 (CYP51), has shown promising efficacy in the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC) in patients.
LACTIN-V, also known as CTV-05 or as Lactobacillus crispatus CTV-05, is a live biopharmaceutical medication containing a strain of Lactobacillus crispatus which is under development for the treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and bacterial vaginosis (BV). It is administered intravaginally and is described as the first vaginal microbiome (VMB)-based live biotherapeutic product (LBP).














