Related Research Articles

The Amstrad CPC is a series of 8-bit home computers produced by Amstrad between 1984 and 1990. It was designed to compete in the mid-1980s home computer market dominated by the Commodore 64 and the ZX Spectrum, where it successfully established itself primarily in the United Kingdom, France, Spain, and the German-speaking parts of Europe.
A RAM drive is a block of random-access memory that a computer's software is treating as if the memory were a disk drive. RAM drives provide high-performance temporary storage for demanding tasks and protect non-volatile storage devices from wearing down, since RAM is not prone to wear from writing, unlike non-volatile flash memory. They are in a sense the reverse of virtual memory: RAM drive uses a volatile fast memory as if it's a nonvolatile slow memory. Virtual memory is the opposite.
The Multiface was a hardware peripheral released by Romantic Robot for several 1980s home computers. The primary function of the device was to dump the computer's memory to external storage. Pressing a red button on the Multiface activated it. As most games of the era did not have a save game feature, the Multiface allowed players to save their position by saving a loadable snapshot of the game. Home computer software of the early 1980s was typically loaded into RAM in one go, with copy protection measures concentrating the loading phase or just after it. The snapshot feature could be used after copy protection routines had been executed, to create a backup that was effectively unprotected against unauthorised distribution. Later models of the Multiface mitigated this by requiring the device to be present when re-loading the dumps into memory, making the dumps useless to people without a Multiface. Software producers also reacted to the threat by using routines that would prevent execution of the product if it detected that a Multiface was present and by loading the software in multiple parts, thus requiring the presence of the original, copy-protected media.

The SAM Coupé is an 8-bit British home computer manufactured by Miles Gordon Technology (MGT), based in Swansea in the United Kingdom and released in December 1989.
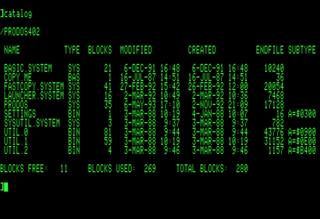
ProDOS is the name of two similar operating systems for the Apple II of personal computer. The original ProDOS, renamed ProDOS 8 in version 1.2, is the last official operating system usable by all 8-bit Apple II computers, and was distributed from 1983 to 1993. The other, ProDOS 16, was a stop-gap solution for the 16-bit Apple IIGS that was replaced by GS/OS within two years.
Sinclair BASIC is a dialect of the programming language BASIC used in the 8-bit home computers from Sinclair Research, Timex Sinclair and Amstrad. The Sinclair BASIC interpreter was written by Nine Tiles Networks Ltd.
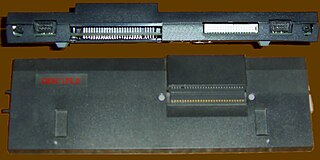
The DISCiPLE is a floppy disk interface for the ZX Spectrum home computer. Designed by Miles Gordon Technology, it was marketed by Rockfort Products and launched in 1986.
The +D was a floppy disk and printer interface for the ZX Spectrum home computer, developed as a successor to Miles Gordon Technology's earlier product, the DISCiPLE. It was designed to be smaller, cheaper, simpler and thus more reliable.
GHOST, now called Symantec™ GHOST Solution Suite (GSS) for enterprise, is a disk cloning and backup tool originally developed by Murray Haszard in 1995 for Binary Research. The technology was bought in 1998 by Symantec.

Atari DOS is the disk operating system used with the Atari 8-bit computers. Operating system extensions loaded into memory were required in order for an Atari computer to manage files stored on a disk drive. These extensions to the operating system added the disk handler and other file management features.

The ATM Turbo, also known simply as ATM is a ZX Spectrum clone, developed in Moscow in 1991, by two firms, MicroArt and ATM.

Beta BASIC is a BASIC interpreter for the Sinclair Research ZX Spectrum microcomputer, written by Dr Andrew Wright in 1983 and sold by his one-man software house BetaSoft. BetaSoft also produced a regular newsletter/magazine, BetaNews.

A fast loader is a software program for a home computer, such as the Commodore 64 or ZX Spectrum, that accelerates the speed of file loading from floppy disk or compact cassette.
The ZX Spectrum's software library was very diverse. While the majority of the software produced for the system was video games, others included programming language implementations, Sinclair BASIC extensions, databases, word processors, spread sheets, drawing and painting tools, and 3D modelling tools.
iS-DOS is a disk operating system (DOS) for Soviet/Russian ZX Spectrum clones. iS-DOS was developed in 1990 or 1991, by Iskra Soft, in Leningrad, Soviet Union, now Saint Petersburg, Russia.

Beta Disk Interface is a disk interface for ZX Spectrum computers, developed by Technology Research Ltd. in 1984 and released in 1985, with a price of £109.25.
The Kay 1024 was a Russian ZX Spectrum clone introduced in 1998. Created by the NEMO company of St. Petersburg, it has 1024 KB of RAM. It was a rival to Scorpion ZS 256, having a slightly lower price. It offered a controller for a PC keyboard and HDD, but not for floppy disks. Adding a General Sound card was easy, and the CPU had a 7 Mhz turbo mode.
Amiga support and maintenance software performs service functions such as formatting media for a specific filesystem, diagnosing failures that occur on formatted media, data recovery after media failure, and installation of new software for the Amiga family of personal computers—as opposed to application software, which performs business, education, and recreation functions.

Romantic Robot is a small independent British company that publishes classical music recordings. In the 1980s it designed and produced peripherals and software for home computers.
References
- ↑ "Beta Disk Interface - World of Spectrum". Worldofspectrum.org. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
- ↑ Woodcock, Colin (7 May 2012). The ZX Spectrum on Your PC. Lulu.com. ISBN 9781471696121 . Retrieved 9 December 2018– via Google Books.
- ↑ Woodcock, Colin (December 2003). "TR-DOS". ZXF. No. 6.
- ↑ Pavlov, Paul; Striker (2022). "Virtual TR-DOS". Virtual TR-DOS. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
- ↑ Technology Research BETA 128 Disk Interface - User Manual. Technology Research Ltd. 1986. Archived from the original on 2016-09-23.
- ↑ "Customized ROM". speccy4ever. Archived from the original on 2016-09-18. Retrieved 2016-08-19.
- ↑ DISK INTERFACE Manual Supplement for version 4 of TR-DOS (PDF). Technology Research Limited. 1984.