
Tomb KV9 in Egypt's Valley of the Kings was originally constructed by Pharaoh Ramesses V. He was interred here, but his uncle, Ramesses VI, later reused the tomb as his own. The architectural layout is typical of the 20th Dynasty – the Ramesside period – and is much simpler than that of Ramesses III's tomb (KV11). The workmen accidentally broke into KV12 as they dug one of the corridors. In 2020, the Egyptian Tourism Authority released a full 3D model of the tomb with detailed photography, available online.

Tomb KV11 is the tomb of Pharaoh Ramesses III. It is located in the main valley of the Valley of the Kings. The tomb was originally started by Setnakhte, but abandoned when it unintentionally broke into the earlier tomb of Amenmesse (KV10). Setnakhte was buried in KV14. The tomb KV11 was later restarted and extended and on a different axis for Ramesses III.
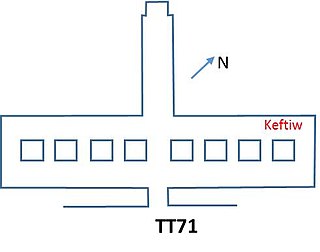
Theban Tomb TT71 is located in the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It was the tomb chapel of Senenmut, who was the steward and architect of Hatshepsut. The chapel is located in the necropolis area around Sheikh Abd el-Qurna. Previously the tomb was accessible and for most of this time the target of numerous investigations and intrusions, although early on already heavily destroyed. The tomb was visited already early. In the first half of the nineteenth century, John Gardner Wilkinson, Robert Hay and J. Wild copied scenes, although the decoration was already badly destroyed. Richard Lepsius (1842–45) took the false door to Berlin and copied some inscribed bricks. Only in 1906 Kurt Sethe copied all inscriptions. In 1930–31 Herbert Winlock cleared the whole tomb. Winlock found the fragments of a smashed sarcophagus.

Tomb KV47, located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt, was used for the burial of Pharaoh Siptah of the Nineteenth Dynasty. It was discovered on December 18, 1905 by Edward R. Ayrton, excavating on behalf of Theodore M. Davis; Siptah's mummy had been found earlier, cached in KV35. It was the last of the Nineteenth and Twentieth Dynasty kings tombs to be uncovered in the Valley. Ayrton stopped his excavation in 1907 due to safety fears, and Harry Burton returned in 1912 to dig further. The cutting of a side passage was halted after the workmen cut into Side Chamber Ja of the tomb of Tia'a (KV32). The tomb was unfinished at the time of its use.

Theban Tomb 69 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official named Menna, whose titles included ‘Overseer of Fields of Amun’, and ‘Overseer of Fields of the Lord of the Two Lands’. Traditionally, TT 69 has been dated to the reign of Thutmosis IV. However, recent art historical studies of artistic style suggest the majority of the tomb was decorated during the reign of Amenhotep III.

The ancient Egyptian noble Ibi was chief steward of the God's Wife of Amun, Nitocris I, during the reign of the 26th Dynasty pharaoh Psamtik I. He was married and had several children.
The Theban Tomb TT36 is located in El-Assasif, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Ibi, who was "Chief Steward of the Adorer of the God", during the reign of Psamtik I during the 26th dynasty.

The Theban Tomb TT81 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Ineni and his family.
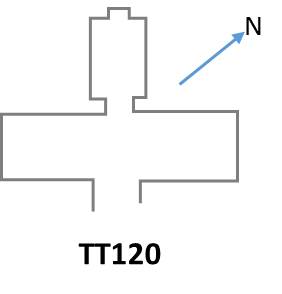
The Theban Tomb TT120 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The tomb is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Anen, who was the brother of Queen Tiye, and became Chancellor of Lower Egypt, Second Prophet of Amun, sem-priest of Heliopolis, and Divine Father under the reign of Amenhotep III.

Theban Tomb TT2 is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Khabekhnet and his family in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.

The Theban Tomb TT57 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The tomb is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Khaemhat, who was royal scribe and overseer of double granary, during the reign Amenhotep III. The relief decoration of the tomb is regarded as the best of New Kingdom art.

The Theban Tomb TT156 is located in Dra' Abu el-Naga', part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Pennesuttawy, who was a troop commander and superintendent of the Southern Desert Lands during the reign of Ramesses II in the Nineteenth Dynasty.

Maia was the wet nurse of the ancient Egyptian pharaoh Tutankhamun in the 14th century BC. Her rock-cut tomb was discovered in the Saqqara necropolis in 1996.
The Tomb of Thutmose is a small, decorated rock-cut tomb in Saqqara in Egypt that dates to the time shortly after the Amarna Period. The tomb is of special importance as one of the tomb owners was the sculptor Thutmose, often presumed to be the person who made the famous Nefertiti Bust. Another of the persons buried here was a certain Kenana.

QV75 is the tomb of Henutmire, likely the daughter and Great Wife of Ramesses II, in Egypt's Valley of the Queens. It was mentioned by Champollion and Lepsius.
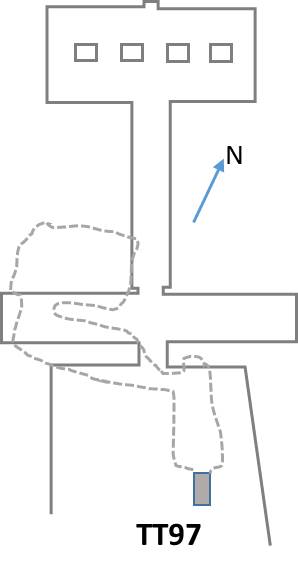
The Theban Tomb TT97 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. The tomb belongs to an ancient Egyptian named Amenemhat, who was the High Priest of Amun at Karnak, during the reign of pharaoh Amenhotep II of the 18th Dynasty. Amenemhat was the son of the wab-priest and "Overseer of the sandal makers of Amun", Djehutyhotep.
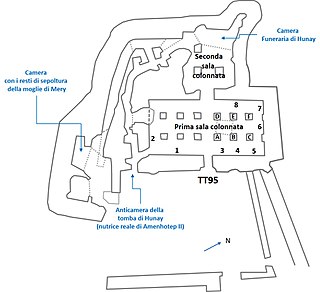
The Theban Tomb TT95 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. The tomb belongs to an ancient Egyptian named Mery, who was a High Priest of Amun at Karnak, during the reign of pharaoh Amenhotep II of the 18th Dynasty. Mery was the son of the First Prophet of Min of Koptos (Qift) named Nebpehtire and the Lady Hunayt. Mery's wife was named Dey.

The ancient Egyptian Theban Tomb no. 80 (TT80) belongs to the Overseer of the treasuries Djehutynefer, who was in office under king Amenhotep II. The tomb chapel is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna and is part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. Djehutynefer had a second tomb in Thebes TT104. Tomb TT80 is decorated with paintings and has a T-shaped ground plan. The paintings are partly well preserved.
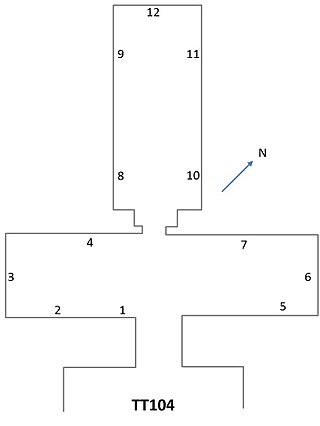
The ancient Egyptian Theban Tomb no. 104 (TT104) belongs to the Overseer of the treasuries Djehutynefer, who was in office under king Amenhotep II. The tomb chapel is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna and is part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. Djehutynefer had a second tomb in Thebes TT80. Tomb TT104 is decorated with paintings and has a T-shaped ground plan. The paintings are not always well preserved.

The Theban Tomb TT88 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna and is part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Amenemhab, also called Mahu who lived in the 18th Dynasty.


















