
Bosnia and Herzegovina, abbreviated BiH or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. The capital and largest city is Sarajevo. Bosnia and Herzegovina borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest. It is not entirely landlocked; in the south it has a narrow coast on the Adriatic Sea within the Mediterranean, which is about 20 kilometres long and surrounds the town of Neum. Bosnia, which is the inland region of the country, has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. In the central and eastern regions of the country, the geography is mountainous, in the northwest it is moderately hilly, and in the northeast it is predominantly flat. Herzegovina, which is the smaller, southern region of the country, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous.

Gavrilo Princip was a Bosnian Serb student who assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria and his wife Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914.

Sarajevo is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,569 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo Canton, East Sarajevo and nearby municipalities is home to 555,210 inhabitants. Located within the greater Sarajevo valley of Bosnia, it is surrounded by the Dinaric Alps and situated along the Miljacka River in the heart of the Balkans, a region of Southern Europe.

The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina, also known as the Dayton Agreement or the Dayton Accords, is the peace agreement reached at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base near Dayton, Ohio, United States, on 21 November 1995, and formally signed in Paris, on 14 December 1995. These accords put an end to the three-and-a-half-year-long Bosnian War, one of the Yugoslav Wars.

The Bosnian language is the standardized variety of Serbo-Croatian mainly used by ethnic Bosniaks. Bosnian is one of three such varieties considered official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina, along with Croatian and Serbian. It is also an officially recognized minority language in Croatia, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia and Kosovo.

The siege of Sarajevo Serbo-Croatian: Opsada Sarajeva / Опсада Сарајева was a prolonged blockade of Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia and Herzegovina, during the Bosnian War. After initially being besieged by the forces of the Yugoslav People's Army, the city was then besieged by the Army of Republika Srpska from 5 April 1992 to 29 February 1996. It lasted three times longer than the Battle of Stalingrad and more than a year longer than the siege of Leningrad, and was the longest siege of a capital city in the history of modern warfare.

Republika Srpska is one of the two entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located in the north and east of the country. Its largest city and administrative centre is Banja Luka, lying on the Vrbas river.

The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is one of the two entities within the State of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Republika Srpska. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina consists of 10 autonomous cantons with their own governments and legislatures.

The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies fought in the former Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001, leading up to and resulting from the breakup of the Yugoslav federation in 1992. Its constituent republics declared independence due to unresolved tensions between ethnic minorities in the new countries, which fueled the wars.
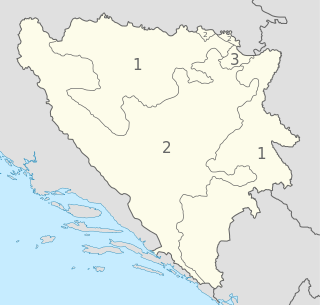
The political divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina were created by the Dayton Agreement. The Agreement divides the country into two federal entities:

The Bosnian War was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started on 6 April 1992, following a number of earlier violent incidents. The war ended on 14 December 1995. The main belligerents were the forces of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and those of Herzeg-Bosnia and Republika Srpska, proto-states led and supplied by Croatia and Serbia, respectively.

The Football Association of Bosnia and Herzegovina, based in Sarajevo, is the chief officiating body of football in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Bosnian football association was founded as the Sarajevo football sub-association of Yugoslavia in 1920. In 1992 the association was re-founded as the football association of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The Bosnia and Herzegovina national football team represents Bosnia and Herzegovina in international football competitions, and is governed by the Football Association of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Until 1992, Bosnian footballers played for Yugoslavia.

The Bosnian genocide refers to either the Srebrenica massacre or the wider crimes against humanity and ethnic cleansing campaign throughout areas controlled by the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) during the Bosnian War of 1992–1995. The events in Srebrenica in 1995 included the killing of more than 8,000 Bosniak men and boys, as well as the mass expulsion of another 25,000–30,000 Bosniak civilians by VRS units under the command of General Ratko Mladić.

The Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina are one of the three constitutive nations of the country, predominantly residing in the political-territorial entity of Republika Srpska.

The Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina was a state in Southeastern Europe, existing from 1992 to 1995. It is the direct legal predecessor to the modern-day state of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, commonly referred to as Socialist Bosnia or simply Bosnia, was one of the six constituent federal states forming the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. It was a predecessor of the modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina, existing between 1945 and 1992, under a number of different formal names, including Democratic Bosnia and Herzegovina (1943–1946) and People's Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (1946–1963).

The Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia was an unrecognised geopolitical entity and proto-state in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was proclaimed on 18 November 1991 under the name Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia as a "political, cultural, economic and territorial whole" in the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Bosniaks or Bosniacs are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

Herzegovina is the southern and smaller of two main geographical regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia. It has never had strictly defined geographical or cultural-historical borders, nor has it ever been defined as an administrative whole in the geopolitical and economic subdivision of Bosnia and Herzegovina.



















