
Protein biosynthesis is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences.

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself or by forming a template for the production of proteins. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are nucleic acids. The nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.

Ribosomes are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis. Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.
An inverted repeat is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. The intervening sequence of nucleotides between the initial sequence and the reverse complement can be any length including zero. For example, 5'---TTACGnnnnnnCGTAA---3' is an inverted repeat sequence. When the intervening length is zero, the composite sequence is a palindromic sequence.

In biology, the SECIS element is an RNA element around 60 nucleotides in length that adopts a stem-loop structure. This structural motif directs the cell to translate UGA codons as selenocysteines. SECIS elements are thus a fundamental aspect of messenger RNAs encoding selenoproteins, proteins that include one or more selenocysteine residues.

Transfer RNA is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length. In a cell, it provides the physical link between the genetic code in messenger RNA (mRNA) and the amino acid sequence of proteins, carrying the correct sequence of amino acids to be combined by the protein-synthesizing machinery, the ribosome. Each three-nucleotide codon in mRNA is complemented by a three-nucleotide anticodon in tRNA. As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins in accordance with the genetic code.

Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form small and large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins, though this ratio differs between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

RNA editing is a molecular process through which some cells can make discrete changes to specific nucleotide sequences within an RNA molecule after it has been generated by RNA polymerase. It occurs in all living organisms and is one of the most evolutionarily conserved properties of RNAs. RNA editing may include the insertion, deletion, and base substitution of nucleotides within the RNA molecule. RNA editing is relatively rare, with common forms of RNA processing not usually considered as editing. It can affect the activity, localization as well as stability of RNAs, and has been linked with human diseases.

Pseudouridine is an isomer of the nucleoside uridine in which the uracil is attached via a carbon-carbon instead of a nitrogen-carbon glycosidic bond.
In molecular biology, small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. There are two main classes of snoRNA, the C/D box snoRNAs, which are associated with methylation, and the H/ACA box snoRNAs, which are associated with pseudouridylation. SnoRNAs are commonly referred to as guide RNAs but should not be confused with the guide RNAs that direct RNA editing in trypanosomes or the guide RNAs (gRNAs) used by Cas9 for CRISPR gene editing.
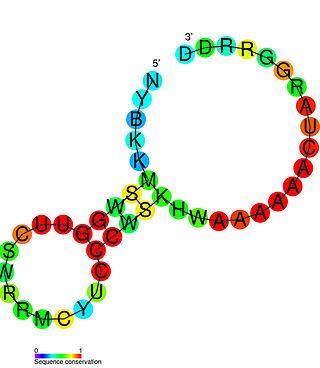
The PreQ1-I riboswitch is a cis-acting element identified in bacteria which regulates expression of genes involved in biosynthesis of the nucleoside queuosine (Q) from GTP. PreQ1 (pre-queuosine1) is an intermediate in the queuosine pathway, and preQ1 riboswitch, as a type of riboswitch, is an RNA element that binds preQ1. The preQ1 riboswitch is distinguished by its unusually small aptamer, compared to other riboswitches. Its atomic-resolution three-dimensional structure has been determined, with the PDB ID 2L1V.

U2 spliceosomal snRNAs are a species of small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules found in the major spliceosomal (Sm) machinery of virtually all eukaryotic organisms. In vivo, U2 snRNA along with its associated polypeptides assemble to produce the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP), an essential component of the major spliceosomal complex. The major spliceosomal-splicing pathway is occasionally referred to as U2 dependent, based on a class of Sm intron—found in mRNA primary transcripts—that are recognized exclusively by the U2 snRNP during early stages of spliceosomal assembly. In addition to U2 dependent intron recognition, U2 snRNA has been theorized to serve a catalytic role in the chemistry of pre-RNA splicing as well. Similar to ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), Sm snRNAs must mediate both RNA:RNA and RNA:protein contacts and hence have evolved specialized, highly conserved, primary and secondary structural elements to facilitate these types of interactions.
Ribosomal frameshifting, also known as translational frameshifting or translational recoding, is a biological phenomenon that occurs during translation that results in the production of multiple, unique proteins from a single mRNA. The process can be programmed by the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and is sometimes affected by the secondary, 3-dimensional mRNA structure. It has been described mainly in viruses, retrotransposons and bacterial insertion elements, and also in some cellular genes.

In molecular biology, non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) are RNA molecules that have a function but are not translated into proteins. Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), one of the largest classes of ncRNA, are further subdivided into the two major C/D and H/ACA snoRNA families. snoRNA serve as guide RNAs for 2'-O-methylation and pseudouridylation of specific nucleotides and indicate the site of modification by direct base pairing with the target RNA. The majority of these snoRNAs are responsible for the post-transcriptional modification of ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) and in some cases of small nuclear RNAs (sRNAs). These post-transcriptional modifications are crucial for rRNA processing, stability and maturation.
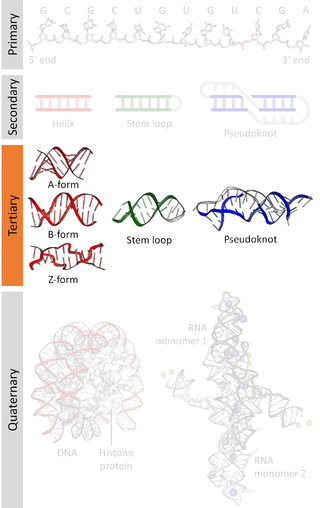
Nucleic acid tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a nucleic acid polymer. RNA and DNA molecules are capable of diverse functions ranging from molecular recognition to catalysis. Such functions require a precise three-dimensional structure. While such structures are diverse and seemingly complex, they are composed of recurring, easily recognizable tertiary structural motifs that serve as molecular building blocks. Some of the most common motifs for RNA and DNA tertiary structure are described below, but this information is based on a limited number of solved structures. Many more tertiary structural motifs will be revealed as new RNA and DNA molecules are structurally characterized.

In biochemistry, wybutosine (yW) is a heavily modified nucleoside of phenylalanine transfer RNA that stabilizes interactions between the codons and anti-codons during protein synthesis. Ensuring accurate synthesis of protein is essential in maintaining health as defects in tRNA modifications are able to cause disease. In eukaryotic organisms, it is found only in position 37, 3'-adjacent to the anticodon, of phenylalanine tRNA. Wybutosine enables correct translation through the stabilization of the codon-anticodon base pairing during the decoding process.
Within the field of molecular biology, the epitranscriptome includes all the biochemical modifications of the RNA within a cell. In analogy to epigenetics that describes "functionally relevant changes to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence", epitranscriptomics involves all functionally relevant changes to the transcriptome that do not involve a change in the ribonucleotide sequence. Thus, the epitranscriptome can be defined as the ensemble of such functionally relevant changes.

In epitranscriptomic sequencing, most methods focus on either (1) enrichment and purification of the modified RNA molecules before running on the RNA sequencer, or (2) improving or modifying bioinformatics analysis pipelines to call the modification peaks. Most methods have been adapted and optimized for mRNA molecules, except for modified bisulfite sequencing for profiling 5-methylcytidine which was optimized for tRNAs and rRNAs.
A nucleoside-modified messenger RNA (modRNA) is a synthetic messenger RNA (mRNA) in which some nucleosides are replaced by other naturally modified nucleosides or by synthetic nucleoside analogues. modRNA is used to induce the production of a desired protein in certain cells. An important application is the development of mRNA vaccines, of which the first authorized were COVID-19 vaccines.

N1-Methylpseudouridine is a natural archaeal tRNA component, and "hypermodified" pyrimidine nucleoside used in biochemistry and molecular biology for in vitro transcription and is found in the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines tozinameran (Pfizer–BioNTech) and elasomeran (Moderna).














