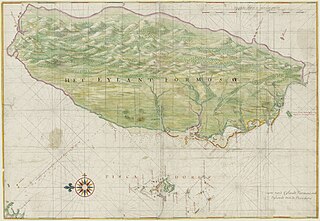
The history of the island of Taiwan dates back tens of thousands of years to the earliest known evidence of human habitation. The sudden appearance of a culture based on agriculture around 3000 BC is believed to reflect the arrival of the ancestors of today's Taiwanese indigenous peoples. People from China gradually came into contact with Taiwan by the time of the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) and Han Chinese people started settling there by the early 17th century. Named Formosa by Portuguese explorers, the south of the island was colonized by the Dutch in the 17th century whilst the Spanish built a settlement in the north which lasted until 1642. The Dutch colonial administration encouraged an influx of Hoklo and Hakka immigrants from Fujian and Guangdong.

Taiwanese indigenous peoples, also known as Formosans, Native Taiwanese or Austronesian Taiwanese, and formerly as Taiwanese aborigines, Takasago people or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 600,303 or 3% of the island's population. This total is increased to more than 800,000 if the indigenous peoples of the plains in Taiwan are included, pending future official recognition. When including those of mixed ancestry, such a number is possibly more than a million. Academic research suggests that their ancestors have been living on Taiwan for approximately 15,000 years. A wide body of evidence suggests that the Taiwanese indigenous peoples had maintained regular trade networks with numerous regional cultures of Southeast Asia before the Han Chinese colonists began settling on the island from the 17th century, at the behest of the Dutch colonial administration and later by successive governments towards the 20th century.

Miaoli County is a county in western Taiwan. Miaoli is bordered by Hsinchu County and Hsinchu City to the north, Taichung to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the west. Miaoli is classified as "central Taiwan" by the National Development Council and "northern Taiwan" by the Taiwan Central Weather Bureau. Miaoli City is the capital of the county, and is also known as "Mountain Town", owing to the number of mountains nearby, making it a destination for hiking.

The Musha Incident (Chinese and Japanese: 霧社事件; pinyin: Wùshè Shìjiàn; Wade–Giles: Wu4-she4 Shih4-chien4; rōmaji: Musha Jiken; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Bū-siā Sū-kiāⁿ), also known as the Wushe Rebellion and several other similar names, began in October 1930 and was the last major uprising against colonial Japanese forces in Japanese Taiwan. In response to long-term oppression by Japanese authorities, the Seediq indigenous group in the settlement of Musha (Wushe) attacked a school, killing 134 Japanese and two Han Taiwanese children. In response, the Japanese led a counter-attack, killing 354 Seediq in retaliation. The handling of the incident by the Japanese authorities was strongly criticised, leading to many changes in Aboriginal policy.
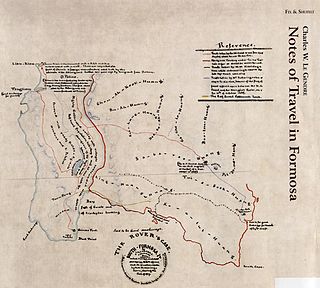
The Rover Incident occurred on 12 March 1867 when the American merchant ship Rover, captained by Joseph Hunt who was accompanied by his wife Mercy G. Beerman Hunt, and en route from Shantou to Niuzhuang, was wrecked off the coast of Taiwan, then ruled by the Qing dynasty. The ship struck a coral reef called Qixingyan near Cape Eluanbi and drifted into the area of Kenting in modern-day Hengchun, Pingtung County, Taiwan. Fourteen American sailors, including Hunt and his wife, were killed by Taiwanese Aborigines in revenge for earlier killings of Kaolut (Koalut/Ku-a-lut/etc) tribe members by foreigners. Subsequently, the U.S. military decided to send a military expedition against the tribe members responsible.

Anping District is a district of Tainan, Taiwan. In March 2012, it was named one of the Top 10 Small Tourist Towns by the Tourism Bureau of Taiwan. It is home to 64,408 people according to the 2020 census.

The island of Taiwan, also commonly known as Formosa, was partly under colonial rule by the Dutch Republic from 1624 to 1662 and from 1664 to 1668. In the context of the Age of Discovery, the Dutch East India Company established its presence on Formosa to trade with the Ming Empire in neighbouring China and Tokugawa shogunate in Japan, and also to interdict Portuguese and Spanish trade and colonial activities in East Asia.

The Kingdom of Tungning, also known as Tywan by the English at the time, was a dynastic maritime state that ruled part of southwestern Taiwan and the Penghu islands between 1661 and 1683. It is the first predominantly ethnic Han state in Taiwanese history. At its zenith, the kingdom's maritime power dominated varying extents of coastal regions of southeastern China and controlled the major sea lanes across both China Seas, and its vast trade network stretched from Japan to Southeast Asia.

The Japanese punitive expedition to Taiwan in 1874, referred to in Japan as the Taiwan Expedition and in Taiwan and Mainland China as the Mudan incident, was a punitive expedition launched by the Japanese ostensibly in retaliation for the murder of 54 Ryukyuan sailors by Paiwan aborigines near the southwestern tip of Taiwan in December 1871. In May 1874, the Imperial Japanese Army and Imperial Japanese Navy attacked the indigenous Taiwanese peoples in southern Taiwan and retreated in December after the Qing dynasty agreed to pay an indemnity of 500,000 taels, with Japan conceding that China had sovereignty over Taiwan. Some ambiguous wording in the agreed terms were later argued by Japan to be confirmation of Chinese renunciation of suzerainty over the Ryukyu Islands, paving the way for de facto Japanese incorporation of the Ryukyu in 1879.

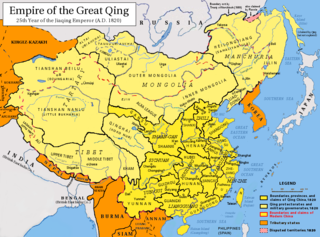
The Qing dynasty ruled over the island of Taiwan from 1683 to 1895. The Qing dynasty sent an army led by general Shi Lang and defeated the Ming loyalist Kingdom of Tungning in 1683. Taiwan was then formally annexed in April 1684.

Taokas is one of a number of Indigenous ethno-linguistic groups that inhabited the plains of western Taiwan. The Taokas were located in the areas around today's Hsinchu City/Hsinchu County, Miaoli County, and Taichung City region. Several Taokas groups have been historically linked to many revolts that plagued Taiwan during the Qing era (1683–1895). The Taokas were not always opposed to Han encroachment on their lands as several Taokas groups were involved in building the Ta-Chia Mazu Temple. Today, only a small number of people in the central city of Puli identify themselves as ethnic Taokas or even Taiwanese Aborigines. The Taokas people have a long history of fishing and preserving their traditions and beliefs, including the worship of sea gods and the performance of traditional dances and music.

The Kingdom of Middag, also known as the Kingdom of Dadu, was a supra-tribal alliance located in the central-western plains of Taiwan in the 17th century. This polity was established by the Taiwanese indigenous peoples of Papora, Babuza, Pazeh, and Hoanya. It ruled as many as 27 villages, occupying the western part of present-day Taichung county and the northern part of modern Changhua county. Having survived the rule of European colonists and the Kingdom of Tungning, the aboriginal peoples who previously comprised Middag were eventually subjugated to the rule of the Qing Empire in the 18th century.

The cultural history of Taiwan can be traced back to prehistoric Stone Age. Later the development of written languages made it easier to maintain traditions of the Taiwanese culture.

The Guo Huaiyi rebellion was a peasant revolt by Chinese farmers against Dutch rule in Taiwan in 1652. Sparked by dissatisfaction with heavy Dutch taxation on them but not the aborigines and extortion by low-ranking Dutch officials and servicemen, the rebellion initially gained ground before being crushed by a coalition of Dutch soldiers and their aboriginal allies. It is considered the most important uprising against the Dutch during the 37-year period of their colonisation of Taiwan.

Zhuluo County was a political division in Taiwan from 1684 to 1787, during Qing Dynasty rule of the island. Initially encompassing the underdeveloped northern two-thirds of Taiwan, the county shrank in size as the population and economy of the northern and central western plains grew and new counties were created out of the developed areas; the Zhuluo county was eventually reduced to an under-developed area in south-western Taiwan. In 1787, the county underwent further restructuring and was renamed Chiayi County.
The Miao rebellion of 1854–1873, also known as the Qian rebellion was an uprising of ethnic Miao and other groups in Guizhou province during the reign of the Qing dynasty. Despite its name, Robert Jenks estimates that ethnic Miao made up less than half of the uprising's participants. The uprising was preceded by Miao rebellions in 1735–36 and 1795–1806, and was one of many ethnic uprisings sweeping China in the 19th century. The rebellion spanned the Xianfeng and Tongzhi periods of the Qing dynasty, and was eventually suppressed with military force. Estimates place the number of casualties as high as 4.9 million out of a total population of 7 million, though these figures are likely overstated.

Plains indigenous peoples, also known as Pingpu people and previously as plain aborigines, are Taiwanese indigenous peoples originally residing in lowland regions, as opposed to Highland indigenous peoples. Plains indigenous peoples consist of anywhere from eight to twelve individual groups, or tribes, rather than being a single ethnic group. They are part of the Austronesian family. Beginning in the 17th century, plains indigenous peoples have been heavily influenced by external forces from Dutch, Spanish, and Han Chinese colonization of Taiwan. This ethnic group has since been extensively assimilated with Han Chinese language and culture; they have lost their cultural identity, and it is almost impossible without careful inspection to distinguish plains indigenous peoples from Taiwanese Han people.
The history of Hsinchu extends over more than 400 years, making it one of the oldest cities in northern Taiwan.
The Qing dynasty in Inner Asia was the expansion of the Qing dynasty's realm in Inner Asia in the 17th and the 18th century AD, including both Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia, both Manchuria and Outer Manchuria, Tibet, Qinghai and Xinjiang.















