Related Research Articles
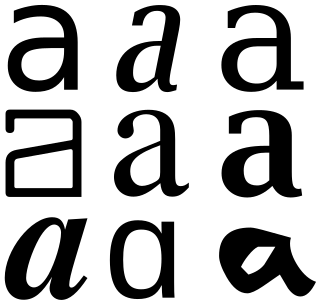
In linguistics, a grapheme is the smallest functional unit of a writing system. The word grapheme is derived from Ancient Greek γράφω (gráphō) 'write' and the suffix -eme by analogy with phoneme and other names of emic units. The study of graphemes is called graphemics. The concept of graphemes is abstract and similar to the notion in computing of a character. By comparison, a specific shape that represents any particular grapheme in a given typeface is called a glyph.

Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and written forms, and may also be conveyed through sign languages. The vast majority of human languages have developed writing systems that allow for the recording and preservation of the sounds or signs of language. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of productivity and displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning.
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to linguistics:
Lexicology is the branch of linguistics that analyzes the lexicon of a specific language. A word is the smallest meaningful unit of a language that can stand on its own, and is made up of small components called morphemes and even smaller elements known as phonemes, or distinguishing sounds. Lexicology examines every feature of a word – including formation, spelling, origin, usage, and definition.
A morpheme is the smallest meaningful constituent of a linguistic expression. The field of linguistic study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology.
In linguistics, morphology is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary.
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Someone who engages in this study is called a linguist. See also the Outline of linguistics, the List of phonetics topics, the List of linguists, and the List of cognitive science topics. Articles related to linguistics include:

A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consensus among linguists on its definition and numerous attempts to find specific criteria of the concept remain controversial. Different standards have been proposed, depending on the theoretical background and descriptive context; these do not converge on a single definition. Some specific definitions of the term "word" are employed to convey its different meanings at different levels of description, for example based on phonological, grammatical or orthographic basis. Others suggest that the concept is simply a convention used in everyday situations.

Syntactic Structures is an influential work in linguistics by American linguist Noam Chomsky, originally published in 1957. It is an elaboration of his teacher Zellig Harris's model of transformational generative grammar. A short monograph of about a hundred pages, Chomsky's presentation is recognized as one of the most significant studies of the 20th century. It contains the now-famous sentence "Colorless green ideas sleep furiously", which Chomsky offered as an example of a grammatically correct sentence that has no discernible meaning. Thus, Chomsky argued for the independence of syntax from semantics.
Lexical diffusion is the hypothesis that a sound change is an abrupt change that spreads gradually across the words in a language to which it is applicable. It contrasts with the Neogrammarian view that a sound change results from phonetically-conditioned articulatory drift acting uniformly on all applicable words, which implies that sound changes are regular, with exceptions attributed to analogy and dialect borrowing.
Glossematics is a structuralist linguistic theory proposed by Louis Hjelmslev and Hans Jørgen Uldall although the two ultimately went separate ways each with their own approach. Hjelmslev’s theory, most notably, is an early mathematical methodology for the analysis of language which was subsequently incorporated into the analytical foundation of current models of functional—structural grammar such as Danish Functional Grammar, Functional Discourse Grammar and Systemic Functional Linguistics. Hjelmslev’s theory likewise remains fundamental for modern semiotics.
In historical linguistics, grammaticalization is a process of language change by which words representing objects and actions become grammatical markers. Thus it creates new function words from content words, rather than deriving them from existing bound, inflectional constructions. For example, the Old English verb willan 'to want', 'to wish' has become the Modern English auxiliary verb will, which expresses intention or simply futurity. Some concepts are often grammaticalized, while others, such as evidentiality, are not so much.
Odia grammar is the study of the morphological and syntactic structures, word order, case inflections, verb conjugation and other grammatical structures of Odia, an Indo-Aryan language spoken in South Asia.
Structural linguistics, or structuralism, in linguistics, denotes schools or theories in which language is conceived as a self-contained, self-regulating semiotic system whose elements are defined by their relationship to other elements within the system. It is derived from the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure and is part of the overall approach of structuralism. Saussure's Course in General Linguistics, published posthumously in 1916, stressed examining language as a dynamic system of interconnected units. Saussure is also known for introducing several basic dimensions of semiotic analysis that are still important today. Two of these are his key methods of syntagmatic and paradigmatic analysis, which define units syntactically and lexically, respectively, according to their contrast with the other units in the system.
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with the cognitive as well as the social aspects of language. It is considered an applied scientific field as well as an academic discipline within the humanities and social sciences; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science, or part of the humanities.
Morphemization is a term describing the process of creating a new morpheme using existing linguistic material. While one source cites "Eric B." as the first person who coined the term, another holds that the term had already been used by Shirley Silver, though the meaning is different from Eric's. Silver used the term for fused words, or for phrasal words like "La Brea Tar Pits" as a proper noun.
In linguistics and related fields, an emic unit is a type of abstract object. Kinds of emic units are generally denoted by terms with the suffix -eme, such as phoneme, grapheme, and morpheme. The term "emic unit" is defined by Nöth (1995) to mean "an invariant form obtained from the reduction of a class of variant forms to a limited number of abstract units". The variant forms are called etic units. This means that a given emic unit is considered to be a single underlying object that may have a number of different observable "surface" representations.
Distributionalism was a general theory of language and a discovery procedure for establishing elements and structures of language based on observed usage. It can be seen as an elaboration of structuralism but takes a more computational approach. Originally mostly applied to understanding phonological processes and phonotactics, distributional methods were also applied to work on lexical semantics and provide the basis for the distributional hypothesis for meaning. Current computational approaches to learn the semantics of words from text in the form of word embeddings using machine learning are based on distributional theory.
Rudolf P. Botha is a South African linguist. He is Emeritus Professor of General Linguistics at Stellenbosch University and Honorary Professor of Linguistics at Utrecht University. Botha is best known for his works on the philosophy of linguistics.