
The Piltdown Man was a paleoanthropological fraud in which bone fragments were presented as the fossilised remains of a previously unknown early human. Although there were doubts about its authenticity virtually from the beginning, the remains were still broadly accepted for many years, and the falsity of the hoax was only definitively demonstrated in 1953. An extensive scientific review in 2016 established that amateur archaeologist Charles Dawson was responsible for the fraudulent evidence.

An out-of-place artifact is an artifact of historical, archaeological, or paleontological interest to someone that is claimed to have been found in an unusual context, which someone claims to challenge conventional historical chronology by its presence in that context. Some people might think that those artifacts are too advanced for the technology known to have existed at the time, or that human presence existed at a time before humans are known to have existed. Other people might hypothesize about a contact between different cultures that is hard to account for with conventional historical understanding.

Lizard Island, also known as Jiigurru or Dyiigurra, is an island on the Great Barrier Reef in Queensland, Australia, 1,624-kilometre (1,009 mi) northwest of Brisbane. It is part of the Lizard Island Group that also includes Palfrey Island, and also part of the Lizard Island National Park. Lizard Island is within the locality of Lizard in the Cook Shire. The traditional owners of the Lizard Island group are the Aboriginal Australian clan known as the Dingaal people.

Archaeological forgery is the manufacture of supposedly ancient items that are sold to the antiquities market and may even end up in the collections of museums. It is related to art forgery.

The Bimini Road, sometimes called the Bimini Wall, is an underwater rock formation near the island of North Bimini in the Bimini chain of islands. The Road consists of a 0.8 km (0.50 mi)-long northeast-southwest linear feature composed of roughly rectangular limestone blocks. Various claims have been made for this feature being either a wall, road, pier, breakwater, or other man-made structure. However, credible evidence or arguments are lacking for such an origin.

Riversleigh World Heritage Area is Australia's most famous fossil location, recognised for the series of well preserved fossils deposited from the Late Oligocene to more recent geological periods. The fossiliferous limestone system is located near the Gregory River in the north-west of Queensland, an environment that was once a very wet rainforest that became more arid as the Gondwanan land masses separated and the Australian continent moved north. The approximately 100 square kilometres (39 sq mi) area has fossil remains of ancient mammals, birds, and reptiles of the Oligocene and Miocene ages, many of which were discovered and are only known from the Riversleigh area; the species that have occurred there are known as the Riversleigh fauna.

The Upper Paleolithic is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago, according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans, until the advent of the Neolithic Revolution and agriculture.

Mekosuchus is a genus of extinct Australasian mekosuchine crocodilian. Species of Mekosuchus were generally small-sized, terrestrial animals with short, blunt-snouted heads and strong limbs. Four species are currently recognized, M. inexpectatus, M. whitehunterensis, M. sanderi and M. kalpokasi, all known primarily from fragmentary remains.
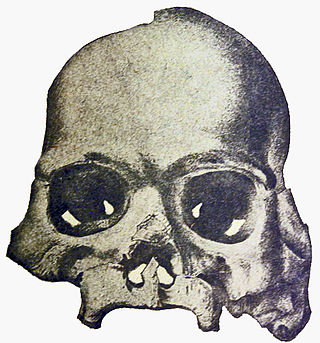
The Calaveras Skull was a human skull found in 1866 by miners in Calaveras County, California, which was presented as evidence that humans were in North America as early as during the Pliocene Epoch, and which was used to support the idea the humans, mastodons, and mammoths had coexisted. The skull was later revealed to be a hoax, although it is now known that humans, mastodons, and mammoths had indeed coexisted, but much more recently. Coincidentally, calaveras is the Spanish word for skulls.
Australian archaeology is a large sub-field in the discipline of archaeology. Archaeology in Australia takes four main forms: Aboriginal archaeology, historical archaeology, maritime archaeology and the archaeology of the contemporary past. Bridging these sub-disciplines is the important concept of cultural heritage management, which encompasses Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander sites, historical sites, and maritime sites.

Charles Dawson was a British amateur archaeologist who claimed to have made a number of archaeological and palaeontological discoveries that were later exposed as frauds. These forgeries included the Piltdown Man, a unique set of bones that he claimed to have found in 1912 in Sussex. Many technological methods such as fluorine testing indicate that this discovery was a hoax, and Dawson, the only one with the skill and knowledge to generate this forgery, was a major suspect.

Allora is a rural town and locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, the locality of Allora had a population of 1,205.
Devil's Lair is a single-chamber cave with a floor area of around 200 m2 (2,200 sq ft) that formed in a Quaternary dune limestone of the Leeuwin–Naturaliste Ridge, 5 km (3.1 mi) from the modern coastline of Western Australia. The stratigraphic sequence in the cave floor deposit consists of 660 cm (260 in) of sandy sediments, with more than 100 distinct layers, intercalated with flowstone and other indurated deposits. Excavations have been made in several areas of the cave floor. Since 1973, excavations have been concentrated in the middle of the cave, where 10 trenches have been dug. Archaeological evidence for intermittent human occupation extends down about 350 cm (140 in) to layer 30, with hearths, bone, and stone artefacts found throughout. The site provides evidence of human habitation of Southwest Australia 50,000 years before the present day.
The Lancefield Swamp is a rich fossil deposit from the Pleistocene epoch was discovered in the 19th century near Lancefield, Victoria, Australia.

Gabarnmung is an archaeological and rock art site in south-western Arnhem Land, in the Top End of Australia’s Northern Territory. Habitation of the site has been dated to at least 44,000 years ago, placing it among the oldest radiocarbon dated sites in Australia. The oldest rock art was produced more than 28,000 years ago, making it the oldest securely dated prehistoric art in Australia. The cave was still visited by members of the Jawoyn within living memory, possibly until as late as the 1950s, but its existence had been forgotten until its 2006 rediscovery.
The Keilor archaeological site was among the first places to demonstrate the antiquity of Aboriginal occupation of Australia when a cranium, unearthed in 1940, was found to be nearly 15,000 years old. Subsequent investigations of Pleistocene alluvial terraces revealed hearths about 31,000 years BP, making Keilor one of the earliest sites of human habitation in Australia. Remains of megafauna suggest a possible association with Aboriginal hunting.
Gibraltar 2, also known as Devil's Tower Child, represented five skull fragments of a male Neanderthal child discovered in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The discovery of the fossils at the Devil's Tower Mousterian rock shelter was made by archaeologist Dorothy Garrod in 1926. It represented the second excavation of a Neanderthal skull in Gibraltar, after Gibraltar 1, the second Neanderthal skull ever found. In the early twenty-first century, Gibraltar 2 underwent reconstruction.

Manot Cave is a cave in Western Galilee, Israel, discovered in 2008. It is notable for the discovery of a skull that belongs to a modern human, called Manot 1, which is estimated to be 54,700 years old. The partial skull was discovered at the beginning of the cave's exploration in 2008. Its significance was realised after detailed scientific analysis, and was first published in an online edition of Nature on 28 January 2015. This age implies that the specimen is the oldest known human outside Africa, and is evidence that modern humans lived side-by-side with Neanderthals. The cave is also noted for its "impressive archaeological record of flint and bone artefacts". Geologically, it is an "active stalactite cave".

Talgai Homestead is a heritage-listed homestead at Allora, Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by architect Richard George Suter for Queensland pastoralist and politician George Clark and was built in 1868. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 August 1992. It is also known as East Talgai Homestead to distinguish it from the West Talgai Homestead built by Clark's brother, Charles Clark. The homestead is now a private residence, owned by the Nioa family.

Tam Pa Ling is a cave in the Annamite Mountains in north-eastern Laos. It is situated at the top of Pa Hang Mountain, 1,170 m (3,840 ft) above sea level.
















