
The economy of the Philippines is an emerging market, and considered as a newly industrialized country in the Asia-Pacific region. In 2024, the Philippine economy is estimated to be at ₱26.55 trillion, making it the world's 32nd largest by nominal GDP and 13th largest in Asia according to the International Monetary Fund.

The U.S. Economic Development Administration (EDA) is an agency in the United States Department of Commerce that provides grants and technical assistance to economically distressed communities in order to generate new employment, help retain existing jobs and stimulate industrial and commercial growth through a variety of investment programs. EDA works with boards and communities across the country on economic development strategies.

Lorna Regina "Loren" Bautista Legarda is a Filipina politician, environmentalist, cultural worker, and former journalist who is currently serving as a Senator and served as the president pro tempore of the Senate of the Philippines from 2022 to 2024. This also makes her the first woman to serve as Senate President Pro Tempore in the upper chamber's history. Before entering politics, she began her career as a news reporter until becoming a news anchor. She previously served three terms in the Senate from 1998 to 2004 and from 2007 to 2019. She is the longest-serving female Senator in the history of the Senate, and the only female in the Philippines to top two senatorial elections: 1998 and 2007. Legarda was also the House Deputy Speaker during her three-year stint as the representative of Antique from 2019 to 2022.

The Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas is the central bank of the Philippines. It was established on July 3, 1993, pursuant to the provision of Republic Act 7653 or the New Central Bank Act of 1993 as amended by Republic Act 11211 or the New Central Bank Act of 2019. The principal author was Senator Franklin Drilon. It was signed by President Rodrigo Duterte.

Edgardo Javier Angara was a Filipino lawyer and politician who served as Senate President from 1993 to 1995. Angara had the second longest tenure in the history of the Senate, serving four terms and a total of twenty-three years. As a legislator, Angara has championed numerous important laws and bills including the free high school law, the Senior Citizen discount law, and many more.

The Philippine Statistics Authority is the central statistical authority of the Philippine government that collects, compiles, analyzes, and publishes statistical information on economic, social, demographic, political affairs, and general affairs of the people of the Philippines, as well as enforcing the civil registration functions in the country.

Overseas Filipino Worker (OFW) is a term often used to refer to Filipino migrant workers, people with Filipino citizenship who reside in another country for a limited period of employment. The number of these workers was roughly 1.77 million between April and September 2020. Of these, female workers comprised a larger portion, making up 59.6 percent, or 1.06 million. However, this number declined to 405.62 thousand between 2019 and 2020.

The Department of Budget and Management is an executive body under the Office of the President of the Philippines. It is responsible for the sound and efficient use of government resources for national development and also as an instrument for the meeting of national socio-economic and political development goals.

The Department of Trade and Industry is the executive department of the Philippine government responsible for the advancement, promotion, governance, regulation, management and growth of industry and trade.

The National Book Development Board, abbreviated as NBDB, is an agency of the Philippine government under the Department of Education formed through Republic Act No. 8047 or the Book Publishing Industry Development Act, which was responsible for promoting the continuing development of the book-publishing industry in the Philippines, with the active participation of the private sector. NBDB's operational plans are: grassroots capacity-building initiatives, investment and trade promotion activities, public campaigns and institutionalized research and data gathering.

Science and technology in the Philippines describes scientific and technological progress made by the Philippines and analyses related policy issues. The main agency responsible for managing science and technology (S&T) is the Department of Science and Technology (DOST). There are also sectoral councils for Forestry, Agriculture and Aquaculture, the Metal Industry, Nuclear Research, Food and Nutrition, Health, Meteorology, Volcanology and Seismology.

The Mutual Defense Treaty between the Republic of the Philippines and the United States of America (MDT) was signed on August 30, 1951 by their representatives in Washington, D.C. The treaty has eight articles and requires both nations to support each other if another party attacks the Philippines or the United States.

Juan Edgardo "Sonny" Manalang Angara is a Filipino politician and lawyer currently serving as the 39th secretary of education since 2024. He previously served as a senator from 2013 to 2024 and as the representative of Aurora's lone district from 2004 to 2013. He is also the chairman of Samahang Basketbol ng Pilipinas, the governing body of basketball in the Philippines, since 2016. He is also a member of the Laban ng Demokratikong Pilipino party, where he currently serves as the chairman.

Sherwin Ting Gatchalian, known as Win Gatchalian, is a Filipino politician and businessman serving as a Senator since 2016. A member of the Nationalist People's Coalition (NPC), he previously served as the Representative of Valenzuela's 1st district from 2001 to 2004 and from 2013 to 2016. He was the Mayor of Valenzuela from 2004 to 2013.
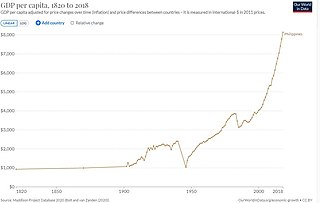
The economic history of the Philippines chronicles the long history of economic policies in the nation over the years.

The Magna Carta for Philippine Internet Freedom is an internet law bill filed in the Congress of the Philippines. The bill contains provisions promoting civil and political rights and Constitutional guarantees for Philippine internet users, such as freedom of expression, as well as provisions on information and communications technology (ICT) policy, ICT4D, internet governance, e-governance, cybersecurity, cyberwarfare, cyberterrorism, and cybercrime.

The Philippine Space Agency (PhilSA) is the national space agency of the Philippines.
The National Privacy Commission, or NPC, is an independent body created under Republic Act No. 10173 or the Data Privacy Act of 2012, mandated to administer and implement the provisions of the Act, and to monitor and ensure compliance of the country with international standards set for data protection. It is attached to the Philippines' Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) for purposes of policy coordination, but remains independent in the performance of its functions. The Commission safeguards the fundamental human right of every individual to privacy, particularly Information privacy while ensuring the free flow of information for innovation, growth, and national development.

The Philippine Competition Commission (PhCC) is an independent, quasi-judicial body formed to implement the Philippine Competition Act (Republic Act No. 10667). The PhCC aims to promote and maintain market competition within the Philippines by regulating anti-competition behavior. The main role of the PhCC is to promote economic efficiency within the Philippine economy, ensuring fair and healthy market competition.

The Tax Reform for Acceleration and Inclusion Law, officially designated as Republic Act No. 10963, is the initial package of the Comprehensive Tax Reform Program (CTRP) signed into law by President Rodrigo Duterte on December 19, 2017.



















