Related Research Articles
A tomahawk is a type of axe made and used by Native Americans.
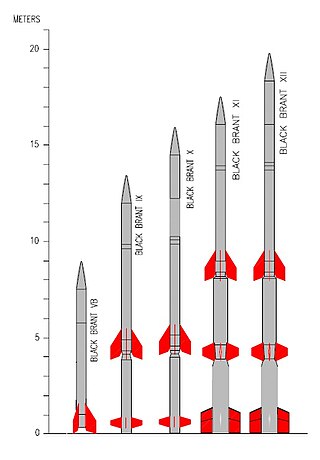
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.

The Luigi Broglio Malindi Space Center (LBMSC) located near Malindi, Kenya, is an Italian Space Agency (ASI) Spaceport. It was named after its founder and Italian space pioneer Luigi Broglio. Developed in the 1960s through a partnership between the Sapienza University of Rome's Aerospace Research Centre and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the BSC served as a spaceport for the launch of both Italian and international satellites (1967–1988). The center comprises a main offshore launch site, known as the San Marco platform, as well as two secondary control platforms and a communications ground station on the mainland.

Orion is the designation of a small American sounding rocket. The Orion has a length of 5.60 meters, a diameter of 0.35 m, a launch weight of 400 kg, a launch thrust of 7 kN and a ceiling of 85 kilometers. The Orion, built by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center's Wallops Flight Facility, is also used as an upper stage of sounding rockets, usually paired with a Terrier missile as the first stage, although Nike, Taurus and VS-30 rockets are also used.
The TE-416 Tomahawk is a sounding rocket developed by the American company Thiokol at the beginning of the 1960s for Sandia National Laboratories. Although the TE-416 Tomahawk can be launched alone, it was started predominantly as upper stage in connection with other rockets, for example with a Nike rocket as first stage. The TE-416 Tomahawk has a thrust of 9,500 lbf (42 kN) and a burn time of 9.5 seconds. The diameter of the TE-416 Tomahawk is 9 inches (23 cm) and the fin span is 36 in (91 cm).
Punta Lobos is a headland and was a launch site for sounding rockets in Peru at 12°30′S76°48′W. Between 1980 and 1990, various rockets of the type super Loki, Nike Orion, Taurus Orion and Taurus Tomahawk were launched there.
Taurus Tomahawk is a two-stage sounding rocket, consisting of a Taurus first stage derived from MGR-1 Honest John rocket and a TE-416 Tomahawk upper stage.
Nike Hydac is the designation of an American sounding rocket with two stages, based upon the Nike Ajax booster. The Nike Hydac was launched 87 times from many missile sites. Such sites were White Sands Missile Range, Poker Flat Research Range, Kwajalein Missile Range, Cassino Site - Rio Grande Airport, Brazil, and from North Truro Air Force Station in Massachusetts during Operation Have Horn in 1969.

The Poker Flat Research Range (PFRR) is a launch facility and rocket range for sounding rockets in the U.S. state of Alaska, located on a 5,132-acre (20.77 km2) site at Chatanika, about 30 miles (50 km) northeast of Fairbanks and 1.5 degrees south of the Arctic Circle. More than 1,700 launches have been conducted at the range to study the Earth's atmosphere and the interaction between the atmosphere and the space environment. Areas studied at PFRR include the aurora, plasma physics, the ozone layer, solar proton events, Earth's magnetic field, and ultraviolet radiation. Rockets launched at PFRR have attained an apogee of 930 miles (1,500 km).

Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) is an Indian rocket launching site established on 21 November 1963. Operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), it is located in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, which is near the southwestern tip of mainland India, very close to Earth's magnetic equator. It is currently used by ISRO for launching sounding rockets.

The Minotaur I, or just Minotaur is an American expendable launch system derived from the Minuteman II missile. It is used to launch small satellites for the US Government, and is a member of the Minotaur family of rockets produced by Orbital Sciences Corporation.

Sondrestrom Air Base, originally Bluie West-8, was a United States Air Force base in central Greenland. The site is located 60 mi (97 km) north of the Arctic Circle and 90 mi (140 km) from the northeast end of Kangerlussuaq Fjord. The base is approximately 11 mi (18 km) west-northwest of Ravneklippen and 80 mi (130 km) east of Sisimiut.

Antares, known during early development as Taurus II, is an American expendable medium-lift launch vehicle developed and built by Orbital Sciences Corporation with financial support from NASA under the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) program awarded in February 2008, alongside the company's automated cargo spacecraft, Cygnus. Like other launch vehicles developed by Orbital, Antares leveraged lower-cost, off-the-shelf parts and designs.

Launch Area 3 (LA-3) at the Wallops Flight Facility is a launch complex which was used, mostly by Scout rockets, between 1960 and 1985. Forty-one Scout launches occurred from the complex, making both orbital and suborbital. In addition, four Nike sounding rockets were launched from the complex in 1970.
The Cajun was an American sounding rocket developed during the 1950s. It was extensively used for scientific experiments by NASA and the United States military between 1956 and 1976.

The Nike Smoke was a sounding rocket, part of a research project on the behavior of the horizontal winds in the upper atmosphere, developed by NASA in the 1960s based on the Nike booster. The goal was to obtain more accurate data on the behavior of these winds in order to guide the design of new vehicles particularly the Saturn family of vehicles.
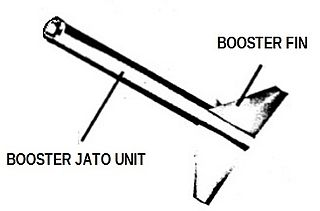
The Nike stage or Nike booster, a solid fuel rocket motor, was developed by Hercules Aerospace for use as the first stage of the Nike Ajax and Nike Hercules missiles as part of Project Nike.

The Exos, originally designated RM-86 and later PWN-4, was a sounding rocket developed by the University of Michigan and NACA for use by the United States Air Force.
Nike Yardbird was an American sounding rocket with two stages, based upon the Nike Hercules M5E1 booster and a Thiokol TE-289 Yardbird upper stage. Yardbird was an improved Thiokol XM-19 motor. The Nike Yardbird was launched 2 times from Wallops Island on Sphere Test aeronomy missions both of which were classified as failures. Information available does not state the reason for the mission failures but Astronautix lists the apogee of both missions as 10 km (6 mi) which is well below the goal of 120 km (70 mi).
References
- 1 2 "Taurus Nike Tomahawk". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on December 13, 2016. Retrieved 10 April 2022.