
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, coughing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note that food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions.

Toxicodendron is a genus of flowering plants in the sumac family, Anacardiaceae. It contains trees, shrubs and woody vines, including poison ivy, poison oak, and the lacquer tree. All members of the genus produce the skin-irritating oil urushiol, which can cause a severe allergic reaction. The generic name is derived from the Greek words τοξικός (toxikos), meaning "poison," and δένδρον (dendron), meaning "tree". The best known members of the genus in North America are poison ivy (T. radicans), practically ubiquitous throughout most of eastern North America, and western poison oak, similarly ubiquitous throughout much of the western part of the continent.

Toxicodendron radicans, commonly known as eastern poison ivy or poison ivy, is an allergenic flowering plant that occurs in Asia and eastern North America. The species is well known for causing urushiol-induced contact dermatitis, an itchy, irritating, and sometimes painful rash, in most people who touch it. The rash is caused by urushiol, a clear liquid compound in the plant's sap. The species is variable in its appearance and habit, and despite its common name, it is not a true ivy (Hedera), but rather a member of the cashew and pistachio family (Anacardiaceae). T. radicans is commonly eaten by many animals and the seeds are consumed by birds, but poison ivy is most often thought of as an unwelcome weed. It is a different species from western poison ivy, T. rydbergii, which has similar effects.

A blister is a small pocket of body fluid within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid, either serum or plasma. However, blisters can be filled with blood or with pus.

Urushiol is an oily mixture of organic compounds with allergenic properties found in plants of the family Anacardiaceae, especially Toxicodendronspp., Comocladia spp. (maidenplums), Metopium spp. (poisonwood), and also in parts of the mango tree as well as the fruit of the cashew tree.
Haptens are small molecules that elicit an immune response only when attached to a large carrier such as a protein; the carrier may be one that also does not elicit an immune response by itself. The mechanisms of absence of immune response may vary and involve complex immunological interactions, but can include absent or insufficient co-stimulatory signals from antigen-presenting cells.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.

Toxicodendron diversilobum, commonly named Pacific poison oak or western poison oak, is a woody vine or shrub in the sumac family, Anacardiaceae.

Toxicodendron vernix, commonly known as poison sumac, or swamp-sumach, is a woody shrub or small tree growing to 9 metres (30 feet) tall. It was previously known as Rhus vernix. This plant is also known as thunderwood, particularly where it occurs in the southern United States.
Burow's solution is an aqueous solution of aluminium triacetate. It is available in the U.S. as an over-the-counter drug for topical administration, with brand names including Domeboro, Domeboro Otic, Star-Otic, and Borofair. The preparation has astringent and antibacterial properties and may be used to treat a number of skin conditions, including insect bites and stings, rashes caused by poison ivy and poison sumac, swelling, allergies, and bruises. However, its main use is for treatment of otitis, including otomycosis.

Fels-Naptha is an American brand of laundry soap manufactured by Summit Brands. The soap was originally created in 1893 by Fels and Company.
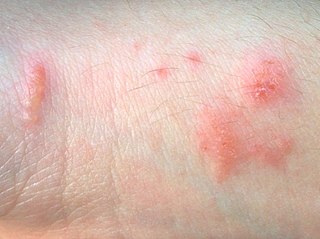
Urushiol-induced contact dermatitis is a type of allergic contact dermatitis caused by the oil urushiol found in various plants, most notably sumac family species of the genus Toxicodendron: poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, and the Chinese lacquer tree. The name is derived from the Japanese word for the sap of the Chinese lacquer tree, urushi. Other plants in the sumac family also contain urushiol, as do unrelated plants such as Ginkgo biloba.

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a form of contact dermatitis that is the manifestation of an allergic response caused by contact with a substance; the other type being irritant contact dermatitis (ICD).

Toxicodendron rydbergii, the western poison ivy or northern poison oak, is a species of Toxicodendron in the cashew family native to North America.

Toxicodendron pubescens, commonly known as Atlantic poison oak, or eastern poison oak, is an upright shrub that can grow to 1 metre (3 feet) tall. Its leaves are 15 centimetres (6 inches) long, alternate, with three leaflets on each. The leaflets are usually hairy and are variable in size and shape, but most often resemble white oak leaves; they usually turn yellow or orange in autumn. The fruit is small, round, and yellowish or greenish. It is not closely related to the true oaks in the beech family, instead being more closely related to sumacs. It is closely related to the other plants in the Toxicodendron genus, including poison ivy, poison sumac, and the lacquer tree.

Toxicodendron vernicifluum, also known by the common name Chinese lacquer tree, is an Asian tree species of genus Toxicodendron native to China and the Indian subcontinent, and cultivated in regions of China, Japan and Korea. Other common names include Japanese lacquer tree, Japanese sumac, and varnish tree. The trees are cultivated and tapped for their toxic sap, which is used as a highly durable lacquer to make Chinese, Japanese, and Korean lacquerware.

Tec Laboratories, Inc. is a manufacturer of over-the-counter pharmaceutical dermatological preparations. The company was founded in 1977 by a former Mead Johnson executive, chemical engineer Robert L. Smith, and is headquartered in Albany, Oregon. The company's products, including its flagship poison oak scrub, Tecnu, are sold in approximately 47,000 retail outlets which have sold over 53 million units, as of 2014.

Poison ivy is a type of allergenic plant in the genus Toxicodendron native to Asia and North America. Formerly considered a single species, Toxicodendron radicans, poison ivies are now generally treated as a complex of three separate species: Toxicodendron radicans, Toxicodendron rydbergii, and Toxicodendron orientale. They are well known for causing urushiol-induced contact dermatitis, an itchy, irritating, and sometimes painful rash, in most people who touch them. The rash is caused by urushiol, a clear liquid compound in the plant's sap. They are variable in appearance and habit, and despite its common name, it is not a "true" ivy (Hedera), but rather a member of the cashew and pistachio family (Anacardiaceae). T. radicans is commonly eaten by many animals, and the seeds are consumed by birds, but poison ivy is most often thought of as an unwelcome weed.

Aluminium diacetate, also known as basic aluminium acetate, is a white powder with the chemical formula C4H7AlO5. It is one of a number of aluminium acetates and can be prepared in a reaction of sodium aluminate (NaAlO2) with acetic acid.
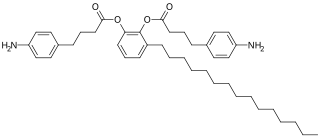
PDC-APB, or 3-pentadecyl-1,2-phenylene bis(4- butanoate), is a drug candidate under evaluation to determine if it might protect against contact dermatitis caused by urishiol from poison ivy, poison oak, and poison sumac.

















