
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response.
Gene silencing is the regulation of gene expression in a cell to prevent the expression of a certain gene. Gene silencing can occur during either transcription or translation and is often used in research. In particular, methods used to silence genes are being increasingly used to produce therapeutics to combat cancer and other diseases, such as infectious diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.

Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA at first non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20-24 base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. It interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences by degrading mRNA after transcription, preventing translation.
Transfection is the process of deliberately introducing naked or purified nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. It may also refer to other methods and cell types, although other terms are often preferred: "transformation" is typically used to describe non-viral DNA transfer in bacteria and non-animal eukaryotic cells, including plant cells. In animal cells, transfection is the preferred term as transformation is also used to refer to progression to a cancerous state (carcinogenesis) in these cells. Transduction is often used to describe virus-mediated gene transfer into eukaryotic cells.
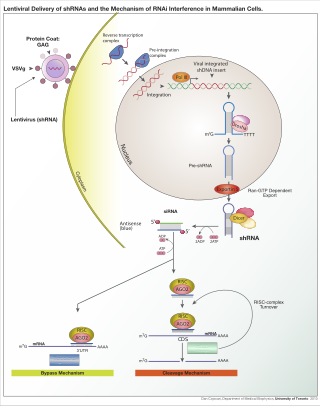
A short hairpin RNA or small hairpin RNA is an artificial RNA molecule with a tight hairpin turn that can be used to silence target gene expression via RNA interference (RNAi). Expression of shRNA in cells is typically accomplished by delivery of plasmids or through viral or bacterial vectors. shRNA is an advantageous mediator of RNAi in that it has a relatively low rate of degradation and turnover. However, it requires use of an expression vector, which has the potential to cause side effects in medicinal applications.
Targeted drug delivery, sometimes called smart drug delivery, is a method of delivering medication to a patient in a manner that increases the concentration of the medication in some parts of the body relative to others. This means of delivery is largely founded on nanomedicine, which plans to employ nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery in order to combat the downfalls of conventional drug delivery. These nanoparticles would be loaded with drugs and targeted to specific parts of the body where there is solely diseased tissue, thereby avoiding interaction with healthy tissue. The goal of a targeted drug delivery system is to prolong, localize, target and have a protected drug interaction with the diseased tissue. The conventional drug delivery system is the absorption of the drug across a biological membrane, whereas the targeted release system releases the drug in a dosage form. The advantages to the targeted release system is the reduction in the frequency of the dosages taken by the patient, having a more uniform effect of the drug, reduction of drug side-effects, and reduced fluctuation in circulating drug levels. The disadvantage of the system is high cost, which makes productivity more difficult, and the reduced ability to adjust the dosages.
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular intake and uptake of molecules ranging from nanosize particles to small chemical compounds to large fragments of DNA. The "cargo" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions.
Magnetofection is a transfection method that uses magnetic fields to concentrate particles containing vectors to target cells in the body. Magnetofection has been adapted to a variety of vectors, including nucleic acids, non-viral transfection systems, and viruses. This method offers advantages such as high transfection efficiency and biocompatibility which are balanced with limitations.

Hyperthermia therapy(or hyperthermia, or thermotherapy) is a type of medical treatment in which body tissue is exposed to temperatures above body temperature, in the region of 40–45 °C (104–113 °F). Hyperthermia is usually applied as an adjuvant to radiotherapy or chemotherapy, to which it works as a sensitizer, in an effort to treat cancer.
Reverse transfection is a technique for the transfer of genetic material into cells. As DNA is printed on a glass slide for the transfection process to occur before the addition of adherent cells, the order of addition of DNA and adherent cells is reverse that of conventional transfection. Hence, the word “reverse” is used.

Targeted drug delivery is one of many ways researchers seek to improve drug delivery systems' overall efficacy, safety, and delivery. Within this medical field is a special reversal form of drug delivery called chemotactic drug targeting. By using chemical agents to help guide a drug carrier to a specific location within the body, this innovative approach seeks to improve precision and control during the drug delivery process, decrease the risk of toxicity, and potentially lower the required medical dosage needed. The general components of the conjugates are designed as follows: (i) carrier – regularly possessing promoter effect also on internalization into the cell; (ii) chemotactically active ligands acting on the target cells; (iii) drug to be delivered in a selective way and (iv) spacer sequence which joins drug molecule to the carrier and due to it enzyme labile moiety makes possible the intracellular compartment specific release of the drug. Careful selection of chemotactic component of the ligand not only the chemoattractant character could be expended, however, chemorepellent ligands are also valuable as they are useful to keep away cell populations degrading the conjugate containing the drug. In a larger sense, chemotactic drug-targeting has the potential to improve cancer, inflammation, and arthritis treatment by taking advantage of the difference in environment between the target site and its surroundings. Therefore, this Wikipedia article aims to provide a brief overview of chemotactic drug targeting, the principles behind the approach, possible limitations and advantages, and its application to cancer and inflammation.

Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are nanoparticles composed of lipids. They are a novel pharmaceutical drug delivery system, and a novel pharmaceutical formulation. LNPs as a drug delivery vehicle were first approved in 2018 for the siRNA drug Onpattro. LNPs became more widely known in late 2020, as some COVID-19 vaccines that use RNA vaccine technology coat the fragile mRNA strands with PEGylated lipid nanoparticles as their delivery vehicle.

RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector may be developed and find utility as novel therapeutic agents.

Gene therapy utilizes the delivery of DNA into cells, which can be accomplished by several methods, summarized below. The two major classes of methods are those that use recombinant viruses and those that use naked DNA or DNA complexes.
Nanoparticles for drug delivery to the brain is a method for transporting drug molecules across the blood–brain barrier (BBB) using nanoparticles. These drugs cross the BBB and deliver pharmaceuticals to the brain for therapeutic treatment of neurological disorders. These disorders include Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, depression, and brain tumors. Part of the difficulty in finding cures for these central nervous system (CNS) disorders is that there is yet no truly efficient delivery method for drugs to cross the BBB. Antibiotics, antineoplastic agents, and a variety of CNS-active drugs, especially neuropeptides, are a few examples of molecules that cannot pass the BBB alone. With the aid of nanoparticle delivery systems, however, studies have shown that some drugs can now cross the BBB, and even exhibit lower toxicity and decrease adverse effects throughout the body. Toxicity is an important concept for pharmacology because high toxicity levels in the body could be detrimental to the patient by affecting other organs and disrupting their function. Further, the BBB is not the only physiological barrier for drug delivery to the brain. Other biological factors influence how drugs are transported throughout the body and how they target specific locations for action. Some of these pathophysiological factors include blood flow alterations, edema and increased intracranial pressure, metabolic perturbations, and altered gene expression and protein synthesis. Though there exist many obstacles that make developing a robust delivery system difficult, nanoparticles provide a promising mechanism for drug transport to the CNS.
Gold nanoparticles in chemotherapy and radiotherapy is the use of colloidal gold in therapeutic treatments, often for cancer or arthritis. Gold nanoparticle technology shows promise in the advancement of cancer treatments. Some of the properties that gold nanoparticles possess, such as small size, non-toxicity and non-immunogenicity make these molecules useful candidates for targeted drug delivery systems. With tumor-targeting delivery vectors becoming smaller, the ability to by-pass the natural barriers and obstacles of the body becomes more probable. To increase specificity and likelihood of drug delivery, tumor specific ligands may be grafted onto the particles along with the chemotherapeutic drug molecules, to allow these molecules to circulate throughout the tumor without being redistributed into the body.
Cancer treatments may vary depending on what type of cancer is being targeted, but one challenge remains in all of them: it is incredibly difficult to target without killing good cells. Cancer drugs and therapies all have very low selective toxicity. However, with the help of nanotechnology and RNA silencing, new and better treatments may be on the horizon for certain forms of cancer.
Cytokines are polypeptides or glycoproteins that help immune cells communicate to each other to induce proliferation, activation, differentiation, and inflammatory or anti-inflammatory signals in various cell types. Studies utilizing cytokines for antitumor therapies has increased significantly since 2000, and different cytokines provide unique antitumor activities. Cytokines hinder tumor cell development mostly through antiproliferative or proapoptotic pathways but can also interrupt development indirectly by eliciting immune cells to have cytotoxic effects against tumor cells. Even though there are FDA-approved cytokine therapies, there are two main challenges associated with cytokine delivery. The first is that cytokines have a short half-life, so frequent administration of high doses is required for therapeutic effect. The second is that systemic toxicity could occur if the cytokines delivered cause an intense immune response, known as a cytokine storm.
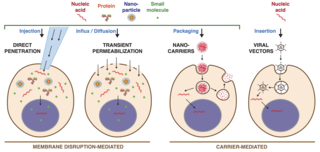
Intracellular delivery is the process of introducing external materials into living cells. Materials that are delivered into cells include nucleic acids, proteins, peptides, impermeable small molecules, synthetic nanomaterials, organelles, and micron-scale tracers, devices and objects. Such molecules and materials can be used to investigate cellular behavior, engineer cell operations or correct a pathological function.

Liangfang Zhang is a Chinese-American nanoengineer. He is the Chancellor Professor of Nanoengineering and Bioengineering and Director of Chemical Engineering at the University of California, San Diego. Zhang is a Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering, American Association for the Advancement of Science, and the National Academy of Inventors.









