
A proximity fuze is a fuze that detonates an explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such as planes, missiles, ships at sea, and ground forces. They provide a more sophisticated trigger mechanism than the common contact fuze or timed fuze. It is estimated that it increases the lethality by 5 to 10 times, compared to these other fuzes.

An anti-tank mine is a type of land mine designed to damage or destroy vehicles including tanks and armored fighting vehicles.

The Tellermine 35 (T.Mi.35) was a German metal-cased anti-tank mine used extensively during the Second World War. The mine's case is made of sheet steel, and has a slightly convex pressure plate on the top surface with a central fuze well. Two secondary fuze wells are located on the side and bottom of the mine for anti-handling devices.

The M1 mortar is an American 81 millimeter caliber mortar. It was based on the French Brandt mortar. The M1 mortar was used from before World War II until the 1950s when it was replaced by the lighter and longer ranged M29 mortar.

The Tellermine 42 (T.Mi.42) was a German metal-cased anti-tank blast mine used during the Second World War. The mine was a development of the Tellermine 35 with improved resistance to blast. It was followed by the simplified Tellermine 43.

The Tellermine 43 was a German circular steel cased anti-tank blast mine used during the Second World War. It was a simplified version of the Tellermine 42, which enabled simpler production techniques. Between March 1943 and the end of World War II, over 3.6 million Tellermine 43s were produced by Germany. Copies of the mine were produced by several countries including Denmark (M/47), France and Yugoslavia (TMM-1).
The PP Mi-D mine is a Czechoslovakian copy of the German Second World War Schu-mine 42 anti-personnel mine.

The TM-57 mine is a large, circular Soviet metal-cased blast anti-tank mine. It can either be triggered by a pressure or a tilt-rod fuze. A development of the TM-46 mine, it is found in Africa, the Middle East, and South East Asia.

The TM-46 mine is a large, circular, metal-cased Soviet anti-tank mine. It uses either a pressure fuze or tilt-rod, which is screwed into the top. Anti-tank mines with this type of fuze were capable of inflicting much more damage to armored vehicles. The TMN-46 is a variant of the mine fitted with a secondary fuze well on the bottom which is slightly off-set from the centre of the mine. This secondary fuze well can be fitted with a pull-fuze which functions as an anti-handling device. The mine was used by the North Vietnamese forces during the Vietnam War, and is found in many countries in Africa, the Middle East and South East Asia.
The TMM-1 is a circular, metal-cased, Yugoslavian anti-tank blast mine. It is a direct copy of the German Tellermine 43. The mine has a central fuze well that is covered by a screw on pressure plate. Two secondary fuze well are fitted to the side and bottom of the mine allowing the installation of anti-handling devices. The mine is found in Bosnia, Croatia, and Serbia.

A minimum metal mine is a land mine that is designed to use the smallest amount of metal possible in its construction. Typically, the only metal components are located inside the fuze mechanism which triggers detonation. Both minimum metal anti-tank and anti-personnel mines exist. Some designs contain virtually no metal at all, e.g., less than a gram. This is achieved by encasing the explosive charge in a plastic, wooden, or glass body, with metallic components limited to the few small parts in the fuze which can not easily be made from other materials, such as the spring, striker tip, and shear pin. Minimum metal mines are extremely difficult to detect using conventional metal mine detectors and usually require modern techniques, such as robotic Multi Period Sensing (MPS) equipment, to identify, but it is still extremely difficult to find non-metallic mines. These techniques are usually restricted to well-funded international mine clearing organizations and major militaries, making minimum metal mines especially pernicious where they are encountered.

The Teller mine was a German-made antitank mine common in World War II. With explosives sealed inside a sheet metal casing and fitted with a pressure-actuated fuze, Teller mines had a built-in carrying handle on the side. As the name suggests the mines were plate-shaped.

An anti-handling device is an attachment to or an integral part of a landmine or other munition such as some fuze types found in general-purpose air-dropped bombs, cluster bombs and sea mines. It is designed to prevent tampering or disabling, or to target bomb disposal personnel. When the protected device is disturbed, it detonates, killing or injuring anyone within the blast area. There is a strong functional overlap of booby traps and anti-handling devices.
The TM-44 was a circular metal-cased Soviet anti-tank landmine used during the Second World War. The mine's case consisted of a short cylinder with the entire top surface being used as a pressure plate. The mine was normally painted olive drab and was broadly similar to the earlier, smaller, TM-41 mine.

The Topfmines were a series of German circular minimum metal anti-tank blast mines that entered service with the German army in 1944, during the Second World War.
In military munitions, a fuze is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams.

An artillery fuze or fuse is the type of munition fuze used with artillery munitions, typically projectiles fired by guns, howitzers and mortars. A fuze is a device that initiates an explosive function in a munition, most commonly causing it to detonate or release its contents, when its activation conditions are met. This action typically occurs a preset time after firing, or on physical contact with or detected proximity to the ground, a structure or other target. Fuze, a variant of fuse, is the official NATO spelling.

The Holzmine 42 was an anti-tank mine that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
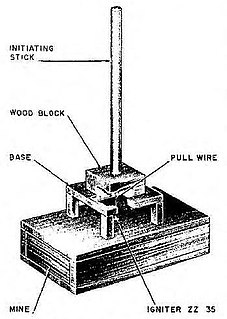
The B-Stabmine (Behelfs-Stabmine) or Makeshift Stickmine in English was an anti-tank mine that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.














