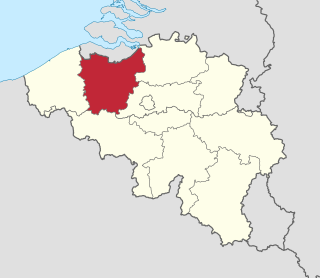
East Flanders is a province of Belgium. It borders the Dutch province of Zeeland and the Flemish province of Antwerp, Flemish Brabant, Hainaut and West Flanders. It has an area of 3,007 km2 (1,161 sq mi), divided into six administrative districts containing 60 municipalities, and a population of over 1.57 million as of January 2024. The capital is Ghent, home to the Ghent University and the Port of Ghent.

Geraardsbergen is a city and municipality located in the Denderstreek and in the Flemish Ardennes, the hilly southern part of the Belgian province of East Flanders. The municipality comprises the city of Geraardsbergen proper and the following towns:

De Standaard is a Flemish daily newspaper published in Belgium by Mediahuis. It was traditionally a Christian-Democratic paper, associated with the Christian-Democratic and Flemish Party, and in opposition to the Socialist Flemish daily De Morgen. In recent years De Standaard has renounced its original ideological ties.

Beersel Castle is a medieval castle located in Beersel, Flemish Brabant, Belgium. Originating in 1300 under the auspices of the Duchy of Brabant, the water castle's present configuration dates to 1357. It was twice sacked and was subject to significant restorations in 1491 and 1617. Its present condition owes much to a major restoration in 1928–39. Built largely of brick, a rare material for such buildings at the time, around a circular enceinte, its major feature is its three large towers. Nowadays, it is open to the public and is considered one of Belgium's best-preserved castles.
Nova Civitas was a Flemish think tank based on the principles of classic liberalism in combination with Anglo-Saxon conservatism. Nova Civitas claimed at its founding to be completely independent, although it was recognized and supported by the Flemish Liberal Party (VLD). The Founding Chairman of Nova Civitas, Boudewijn Bouckaert, was a long-time board member of the VLD.
According to their website, the basic principles of Nova Civitas were:
Isidoor Teirlinck was a Belgian writer. He is best known for his work on folklore.

Maurits Sabbe, born Maurice Charles Marie Guillaume Sabbe, was a Flemish man of letters and educator who became curator of the Plantin-Moretus Museum in Antwerp.

Johannes Franciscus Vonck, also known by the Francization Jean-François Vonck or the Netherlandization Jan-Frans Vonck, was a lawyer and one of the leaders of the Brabant Revolution from 1789–1790. This Revolution led to the founding of the United States of Belgium in January 1790. Vonck was the leader of the radical Vonckists faction of revolutionaries which were named after him. They were inspired by the French Revolution, pleaded for the abolition of the feudal government of the state based on privileges and were in favour of a more centralised government.

Flemish people or Flemings are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Flemish Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.

Brabantine Gothic, occasionally called Brabantian Gothic, is a significant variant of Gothic architecture that is typical for the Low Countries. It surfaced in the first half of the 14th century at St. Rumbold's Cathedral in the city of Mechelen.

Count Hieronymus Lauweryn or Jerome Laurinus of Watervliet was a courtier at the court of Philip the Handsome, to whom Lauweryn was treasurer. He was also a courtier at the courts of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, and of Margaret of Austria. Of common origins, the lordship of Watervliet was awarded to Hieronymus by Philip in 1507. He married twice His son Matthias Lauweryn, or Matthias Laurinus (d.1540), the second lord of Watervliet, was well known to Erasmus. He was responsible for the construction of the Church of Our Lady's Ascension in Watervliet.

Petegem-aan-de-Leie is a village in the Belgian province of East Flanders and a borough of Deinze. Petegem-aan-de-Leie is located on the south bank of the river Leie (Lys). The village today forms a single urban core with that of Deinze itself, which is located just across the river.

Flemish (Vlaams) is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch, Belgian Dutch, or Southern Dutch. Flemish is native to the region known as Flanders in northern Belgium; it is spoken by Flemings, the dominant ethnic group of the region. Outside of Belgium Flanders, it is also spoken to some extent in French Flanders and the Dutch Zeelandic Flanders.

The County of Flanders was one of the most powerful political entities in the medieval Low Countries, located on the North Sea coast of what is now Belgium. Unlike its neighbours, such as the counties of Brabant and Hainaut, it was within the territory of the Kingdom of France. The counts of Flanders held the most northerly part of the kingdom, and were among the original twelve peers of France. For centuries, the economic activity of the Flemish cities, such as Ghent, Bruges and Ypres, made Flanders one of the most affluent regions in Europe, and also gave them strong international connections to trading partners.

The Archdiocese of Mechelen–Brussels is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Belgium. It is the primatial see of Belgium and the centre of the ecclesiastical province governed by the Archbishop of Mechelen–Brussels, which covers the whole of Belgium. It was formed in 1559 and the bishop has a seat in two cathedrals, St. Rumbold's Cathedral in Mechelen and the Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula in Brussels. The current archbishop is Luc Terlinden, who was installed in September 2023.
Joost M. A. Caen is a Flemish independent artist and glass conservator since 1982. In his workshop, he creates contemporary stained-glass windows for churches and secular buildings. In 2003 he was one of the first stained-glass artists who incorporate solar cells into a glass creation. This work can be seen in the entrance hall of the District House at Deurne, Belgium. Caen also conserves stained-glass panels and windows, mainly for museums and collectors.

The Holy Cross Church is a church in the Belgian sub-municipality of Heusden. The church was built in 1844 on the site of an older church. It is dedicated to the Exaltation of the Holy Cross. The organ of the church was protected as a monument in 1980. It has a 1873 case designed by Auguste Van Assche.
Frans Van Dijk was a Belgian architect. He was an important representative of eclecticism in architecture.

Jozef Maria August Antoon (Jef) Van den Eynde was a prominent figure from Leuven's student life, an activist and member of the Council of Flanders during the First World War. After the war, he fled to the Netherlands, having received a 20-year sentence in absentia for collaboration.

Louis Van den Eynde was a Belgian painter. He was also a designer of ironwork, sgraffiti and posters.


















