Related Research Articles

Gastroenterology is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the GI tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which include the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes GI doctors. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcer disease, gallbladder and biliary tract disease, hepatitis, pancreatitis, colitis, colon polyps and cancer, nutritional problems, and many more.

Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain, and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases.
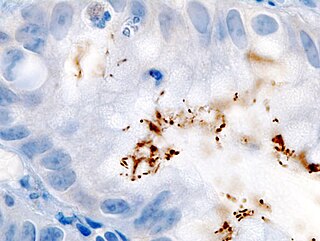
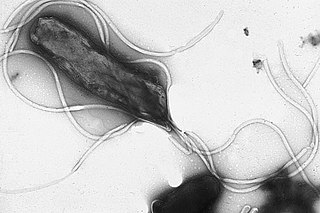
Helicobacter pylori, previously known as Campylobacter pylori, is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. H. pylori has been associated with cancer of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye, and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach.

Barry James Marshall is an Australian physician, Nobel Prize Laureate in Physiology or Medicine, Professor of Clinical Microbiology and Co-Director of the Marshall Centre at the University of Western Australia. Marshall and Robin Warren showed that the bacterium Helicobacter pylori plays a major role in causing many peptic ulcers, challenging decades of medical doctrine holding that ulcers were caused primarily by stress, spicy foods, and too much acid. This discovery has allowed for a breakthrough in understanding a causative link between Helicobacter pylori infection and stomach cancer.

Tomica Milosavljević is a Serbian doctor and politician. He served as Minister of Health in the Government of Serbia under four Prime Ministers with the total span of seven years. He is also employed as a full professor at the University of Belgrade and works in the Clinical Centre of Serbia in Belgrade.

John Robin Warren is an Australian pathologist, Nobel Laureate and researcher who is credited with the 1979 re-discovery of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, together with Barry Marshall. The duo proved to the medical community that the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is the cause of most peptic ulcers.
Walery Jaworski was a Polish physician and gastroenterologist. He is considered one of the pioneers of gastroenterology in Poland. He is also known for making one of the first observations of Helicobacter pylori in 1899.

Martin J. Blaser is the director of the Center for Advanced Biotechnology and Medicine at Rutgers (NJ) Biomedical and Health Sciences and the Henry Rutgers Chair of the Human Microbiome and Professor of Medicine and Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at the Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School in New Jersey.
Thomas J. Borody is an Australian gastroenterologist.
This is a timeline of the events relating to the discovery that peptic ulcer disease and some cancers are caused by H. pylori. In 2005, Barry Marshall and Robin Warren were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery that peptic ulcer disease (PUD) was primarily caused by Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium with affinity for acidic environments, such as the stomach. As a result, PUD that is associated with H. pylori is currently treated with antibiotics used to eradicate the infection. For decades prior to their discovery, it was widely believed that PUD was caused by excess acid in the stomach. During this time, acid control was the primary method of treatment for PUD, to only partial success. Among other effects, it is now known that acid suppression alters the stomach milieu to make it less amenable to H. pylori infection.
The British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) is a British professional organisation of gastroenterologists, surgeons, pathologists, radiologists, scientists, nurses, dietitians and others amongst its members, which number over 3,000. It was founded in 1937, and is a registered charity. Its offices are in Regent's Park, London.
Helicobacter pylori eradication protocols is a standard name for all treatment protocols for peptic ulcers and gastritis in the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. The primary goal of the treatment is not only temporary relief of symptoms but also total elimination of H. pylori infection. Patients with active duodenal or gastric ulcers and those with a prior ulcer history should be tested for H. pylori. Appropriate therapy should be given for eradication. Patients with MALT lymphoma should also be tested and treated for H. pylori since eradication of this infection can induce remission in many patients when the tumor is limited to the stomach. Several consensus conferences, including the Maastricht Consensus Report, recommend testing and treating several other groups of patients but there is limited evidence of benefit. This includes patients diagnosed with gastric adenocarcinoma, patients found to have atrophic gastritis or intestinal metaplasia, as well as first-degree relatives of patients with gastric adenocarcinoma since the relatives themselves are at increased risk of gastric cancer partly due to the intrafamilial transmission of H. pylori. To date, it remains controversial whether to test and treat all patients with functional dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, or other non-GI disorders as well as asymptomatic individuals.
Michael J. G. Farthing is British emeritus professor at the University of Sussex, where he was previously its vice-chancellor (2007–2016). His early academic career was in medicine, specialising in gastroenterology.

The World Gastroenterology Organisation (WGO) is an international federation of over 100 national GI societies and 4 regional associations of gastroenterology representing over 50,000 individual members.

Joseph Sung Jao-yiu is a Hong Kong physician and gastroenterologist, and the current Dean of Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at the Nanyang Technological University (NTU), also serving as the Senior Vice President of NTU. Previously, he was the Vice-Chancellor and President of the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK).
Nicholas "Nick" Talley FRACP, FAFPHM, FRCP (Lond), FRCP (Edin), FACP, FACG, AGAF, FAHMS is an Australian gastroenterologist, epidemiologist, researcher, and clinical educator.

Dame Parveen June Kumar is a British doctor who is currently Professor of Medicine and Education at Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry. She worked in the NHS for over 40 years as a consultant gastroenterologist and physician at Barts and the London Hospitals and the Homerton University Hospital. She was the President of the British Medical Association in 2006, of the Royal Society of Medicine from 2010 to 2012, of the Medical Women's Federation from 2016 to 2018 and of the Royal Medical Benevolent Fund from 2013 to 2020. She was also Vice President of the Royal College of Physicians from 2003 to 2005. In addition, she was a founding non-executive director of the National Institute of Clinical Excellence, chaired the Medicines Commission UK until 2005, and also chaired the BUPA Foundation Charity for Research until 2013.
David Hershel Alpers is a gastroenterologist, researcher, professor, and former president of the American Gastroenterological Association (1990–1991).
Natesan Rangabashyam (1936–2013), popularly known NR, was an Indian surgical gastroenterologist and medical academic, known for his pioneering efforts in the fields of surgical gastroenterology and proctology in India. He was known to have established the department of Surgical Gastroenterology at Madras Medical College and introduced the first MCh course in Surgical Gastroenterology in India. A former honorary surgeon to the President of India, he received B. C. Roy Award, the highest Indian award in the medical category, twice. The Government of India awarded him the third highest civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan, in 2002, for his contributions to medical science.
Alan Desmond is an Irish consultant gastroenterologist and writer known for his advocacy of plant-based nutrition.
References
- 1 2 "Tributes paid to Associate Professor Terry Bolin" . Retrieved 2023-07-07.
- 1 2 3 4 "Home". The Gut Foundation. Retrieved 2023-07-07.
- ↑ "Professor Barry Marshall, gastroenterologist | Australian Academy of Science". www.science.org.au. Retrieved 2023-07-07.
- ↑ "MEDAL (OAM) OF THE ORDER OF AUSTRALIA IN THE GENERAL DIVISION" (PDF). The Governor-General of the Commonwealth of Australia. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)