
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs as well as organism structure and function. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.

The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of biochemical reactions to release the energy stored in nutrients through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The chemical energy released is available under the form of ATP. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.

Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.
Pyruvic acid (IUPAC name: 2-oxopropanoic acid, also called acetoic acid) (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.

Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which contains energy. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into ATP, and then release waste products.
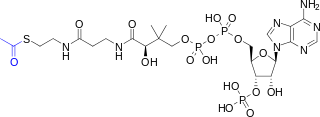
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production.

Anabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catabolism is the breaking-down aspect. Anabolism is usually synonymous with biosynthesis.
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise.

Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to treat a number of health conditions. Its effect is opposite to that of insulin, which lowers extracellular glucose. It is produced from proglucagon, encoded by the GCG gene.
Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of the biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic formation, breakdown, and interconversion of carbohydrates in living organisms.

Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) is a complex of three enzymes that converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. Acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration, and this complex links the glycolysis metabolic pathway to the citric acid cycle. Pyruvate decarboxylation is also known as the "pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction" because it also involves the oxidation of pyruvate.

Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.

Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes that occur in animals. It takes part in gluconeogenesis, the urea cycle, the glyoxylate cycle, amino acid synthesis, fatty acid synthesis and the citric acid cycle.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
Fatty acid metabolism consists of various metabolic processes involving or closely related to fatty acids, a family of molecules classified within the lipid macronutrient category. These processes can mainly be divided into (1) catabolic processes that generate energy and (2) anabolic processes where they serve as building blocks for other compounds.

Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) encoded by the gene PC is an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes the physiologically irreversible carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate (OAA).

Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase is an enzyme component of the multienzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is responsible for the pyruvate decarboxylation step that links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. This involves the transformation of pyruvate from glycolysis into acetyl-CoA which is then used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration.
Oxidative decarboxylation is a decarboxylation reaction caused by oxidation. Most are accompanied by α- Ketoglutarate α- Decarboxylation caused by dehydrogenation of hydroxyl carboxylic acids such as carbonyl carboxylic acid, malic acid, isocitric acid, etc.
In biochemistry, fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is converted into fatty acids is derived from carbohydrates via the glycolytic pathway. The glycolytic pathway also provides the glycerol with which three fatty acids can combine to form triglycerides, the final product of the lipogenic process. When only two fatty acids combine with glycerol and the third alcohol group is phosphorylated with a group such as phosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid is formed. Phospholipids form the bulk of the lipid bilayers that make up cell membranes and surrounds the organelles within the cells. In addition to cytosolic fatty acid synthesis, there is also mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (mtFASII), in which malonyl-CoA is formed from malonic acid with the help of malonyl-CoA synthetase (ACSF3), which then becomes the final product octanoyl-ACP (C8) via further intermediate steps.
Acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS) or Acetate—CoA ligase is an enzyme involved in metabolism of acetate. It is in the ligase class of enzymes, meaning that it catalyzes the formation of a new chemical bond between two large molecules.











