
Government Medical College, Kozhikode, also known as Calicut Medical College, is a public medical college in Kozhikode, in the Indian state of Kerala.
The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center is a public academic health science center in Dallas, Texas. With approximately 23,000 employees, more than 3,000 full-time faculty, and nearly 4 million outpatient visits per year, UT Southwestern is the largest medical school in the University of Texas System and the State of Texas.
The Texas A&M Institute of Biosciences and Technology (IBT), a component of Texas A&M Health, and The Texas A&M University System, is located in the world's largest medical center, the Texas Medical Center, in Houston, Texas. The institute provides a bridge between Texas A&M University System scientists and other institutions' researchers working in the Texas Medical Center and the biomedical and biotechnology research community in Houston. It emphasizes collaboration between member scientists and others working in all the fields of the biosciences and biotechnology. IBT encourages its scientists to transfer discoveries made in their laboratories to the clinic and marketplace.

Mario Ramberg Capecchi is an Italian-born molecular geneticist and a co-awardee of the 2007 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for discovering a method to create mice in which a specific gene is turned off, known as knockout mice. He shared the prize with Martin Evans and Oliver Smithies. He is currently Distinguished Professor of Human Genetics and Biology at the University of Utah School of Medicine.

Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) is the second largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School and the largest hospital in the Longwood Medical Area in Boston, Massachusetts. Along with Massachusetts General Hospital, it is one of the two founding members of Mass General Brigham, the largest healthcare provider in Massachusetts. Robert Higgins, MD, MSHA serves as the hospital's current president.

Sir Martin John EvansFLSW is an English biologist who, with Matthew Kaufman, was the first to culture mice embryonic stem cells and cultivate them in a laboratory in 1981. He is also known, along with Mario Capecchi and Oliver Smithies, for his work in the development of the knockout mouse and the related technology of gene targeting, a method of using embryonic stem cells to create specific gene modifications in mice. In 2007, the three shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in recognition of their discovery and contribution to the efforts to develop new treatments for illnesses in humans.

A health or medical library is designed to assist physicians, health professionals, students, patients, consumers, medical researchers, and information specialists in finding health and scientific information to improve, update, assess, or evaluate health care. Medical libraries are typically found in hospitals, medical schools, private industry, and in medical or health associations. A typical health or medical library has access to MEDLINE, a range of electronic resources, print and digital journal collections, and print reference books. The influence of open access (OA) and free searching via Google and PubMed has a major impact on the way medical libraries operate.

The Jackson Laboratory is an independent, non-profit biomedical research institution which was founded by Clarence Cook Little in 1929. It employs over 3,000 employees in Bar Harbor, Maine; Sacramento, California; Farmington, Connecticut; Shanghai, China; and Yokohama, Japan. The institution is a National Cancer Institute-designated Cancer Center and has NIH Centers of Excellence in aging and systems genetics. The stated mission of The Jackson Laboratory is "to discover the genetic basis for preventing, treating and curing human diseases, and to enable research and education for the global biomedical community."

Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine (UMMSM) is the University of Miami's graduate medical school in Miami, Florida. Founded in 1952, it is the oldest medical school in the state of Florida.
Public health genomics is the use of genomics information to benefit public health. This is visualized as more effective preventive care and disease treatments with better specificity, tailored to the genetic makeup of each patient. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S.), Public Health genomics is an emerging field of study that assesses the impact of genes and their interaction with behavior, diet and the environment on the population's health.
Vamsi K. Mootha is an Indian-born American physician–scientist and computational biologist. He is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Professor of Systems Biology and Medicine at Harvard Medical School, Investigator in the Department of Molecular Biology at Massachusetts General Hospital. He is also an Institute Member of the Broad Institute.

Ralph Lawrence Brinster is an American geneticist, National Medal of Science laureate, and Richard King Mellon Professor of Reproductive Physiology at the School of Veterinary Medicine, University of Pennsylvania.
The International Knockout Mouse Consortium (IKMC) is a scientific endeavour to produce a collection of mouse embryonic stem cell lines that together lack every gene in the genome, and then to distribute the cells to scientific researchers to create knockout mice to study. Many of the targeted alleles are designed so that they can generate both complete and conditional gene knockout mice. The IKMC was initiated on March 15, 2007, at a meeting in Brussels. By 2011, Nature reported that approximately 17,000 different genes have already been disabled by the consortium, "leaving only around 3,000 more to go".

Genetically modified mammals are mammals that have been genetically engineered. They are an important category of genetically modified organisms. The majority of research involving genetically modified mammals involves mice with attempts to produce knockout animals in other mammalian species limited by the inability to derive and stably culture embryonic stem cells.
A knockout mouse, or knock-out mouse, is a genetically modified mouse in which researchers have inactivated, or "knocked out", an existing gene by replacing it or disrupting it with an artificial piece of DNA. They are important animal models for studying the role of genes which have been sequenced but whose functions have not been determined. By causing a specific gene to be inactive in the mouse, and observing any differences from normal behaviour or physiology, researchers can infer its probable function.

Allan Bradley FRS is a British geneticist at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute.
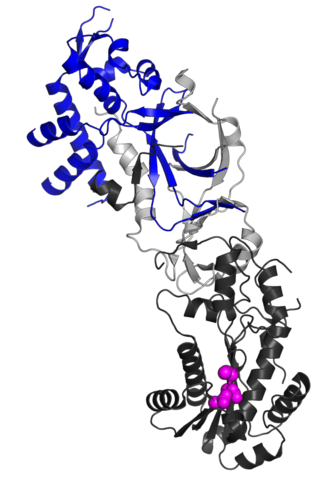
Ribonuclease H2, subunit B is a protein in humans is encoded by the RNASEH2B gene. RNase H2 is composed of a single catalytic subunit (A) and two non-catalytic subunits, and degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. The non-catalytic B subunit of RNase H2 is thought to play a role in DNA replication.

The Wellcome Centre for Human Genetics is a human genetics research centre of the Nuffield Department of Medicine in the Medical Sciences Division, University of Oxford, funded by the Wellcome Trust among others.
The Icahn Genomics Institute is a biomedical and genomics research institute within the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. Its aim is to establish a new generation of medicines that can better treat diseases afflicting the world, including cancer, heart disease and infectious pathogens. To do this, the institute’s doctors and scientists are developing and employing new types of treatments that utilize DNA and RNA based therapies, such as CRISPR, siRNA, RNA vaccines, and CAR T cells, and searching for novel drug targets through the use of functional genomics and data science. The institute is led by Brian Brown, a leading expert in gene therapy, genetic engineering, and molecular immunology.











