The Canadian Caver is a semiannual publication that documents the activities of Canadian cavers exploring caves within Canada and overseas.

To publish is to make content available to the general public. While specific use of the term may vary among countries, it is usually applied to text, images, or other audio-visual content, including paper. The word publication means the act of publishing, and also refers to any printed copies.

A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word cave can also refer to much smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, though strictly speaking a cave is exogene, meaning it is deeper than its opening is wide, and a rock shelter is endogene.

Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres, making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Canada's southern border with the United States is the world's longest bi-national land border. Its capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. As a whole, Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land area being dominated by forest and tundra. Consequently, its population is highly urbanized, with over 80 percent of its inhabitants concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, many near the southern border. Canada's climate varies widely across its vast area, ranging from arctic weather in the north, to hot summers in the southern regions, with four distinct seasons.
The Canadian Caver was created by members of the McMaster University Climbing and Caving Club from McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario to document cave explorations throughout North America at a time when Canada's fledgeling caving clubs had no club newsletters. [1] The first issue was produced in December 1969 and included articles on cave exploration in Alberta, Mexico, West Virginia and Georgia, and climbing in the Bugaboos of British Columbia. [2]

McMaster University is a public research university in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. The main McMaster campus is on 121 hectares of land near the residential neighbourhoods of Ainslie Wood and Westdale, adjacent to the Royal Botanical Gardens. It operates six academic faculties: the DeGroote School of Business, Engineering, Health Sciences, Humanities, Social Science, and Science. It is a member of the U15, a group of research-intensive universities in Canada.

Hamilton is a port city in the Canadian province of Ontario. An industrialized city in the Golden Horseshoe at the west end of Lake Ontario, Hamilton has a population of 536,917, and a metropolitan population of 747,545. The city is located about 60 km southwest of Toronto, with which the Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area (GTHA) is formed.

North America is a continent entirely within the Northern Hemisphere and almost all within the Western Hemisphere; it is also considered by some to be a northern subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean, and to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea.
By 1974 caving clubs in western Canada had achieved a level of maturity and stability (aided by the emigration of MUCCC cavers) that allowed the production and editorship of The Canadian Caver to move to Edmonton, Alberta, where it remained for several years. In 1978 cavers from Vancouver Island produced an issue, which introduced the concept of a roving production/editorship that persists to the present day.

Vancouver Island is in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is 460 kilometres (290 mi) in length, 100 kilometres (62 mi) in width at its widest point, and 32,134 km2 (12,407 sq mi) in area. It is the largest island on the West Coast of North America.
The advent of computers and inexpensive printing in the mid-1980s meant that Canada's principal caving clubs began to document cave explorations in their own newsletters, which presented a challenge of relevancy to The Canadian Caver. Rather than being the sole archive of cave surveys and histories of cave explorations, The Canadian Caver now provides a semiannual synopsis of the more significant cave explorations by Canadians at home and abroad.
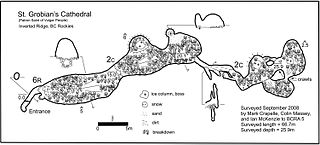
A cave survey is a map of all or part of a cave system, which may be produced to meet differing standards of accuracy depending on the cave conditions and equipment available underground. Cave surveying and cartography, i.e. the creation of an accurate, detailed map, is one of the most common technical activities undertaken within a cave and is a fundamental part of speleology. Surveys can be used to compare caves to each other by length, depth and volume, may reveal clues on speleogenesis, provide a spatial reference for other areas of scientific study and assist visitors with route-finding.
The Canadian Caver is possibly unique within the world in providing a national voice for cavers in a country that has no national caving organization. The Canadian Caver itself has no formal organization, no public funding, no fixed format, no long-range planning and no permanent editors.