The Apostles' Creed, sometimes titled the Apostolic Creed or the Symbol of the Apostles, is a Christian creed or "symbol of faith".

The Council of Chalcedon was the fourth ecumenical council of the Christian Church. It was convoked by the Roman emperor Marcian. The council convened in the city of Chalcedon, Bithynia from 8 October to 1 November 451 AD. The council was attended by over 520 bishops or their representatives, making it the largest and best-documented of the first seven ecumenical councils. The principal purpose of the council was to re-assert the teachings of the ecumenical Council of Ephesus against the heresies of Eutyches and Nestorius. Such heresies attempted to dismantle and separate Christ's divine nature from his humanity (Nestorianism) and further, to limit Christ as solely divine in nature (Monophysitism).
Vexilla regis prodeunt is a Latin hymn in long metre by the Christian poet and saint Venantius Fortunatus, Bishop of Poitiers. It takes its title from its incipit.

The New Apostolic Church (NAC) is a Christian church that split from the Catholic Apostolic Church during an 1863 schism in Hamburg, Germany.

Once in Royal David's City is a Christmas carol originally written as a poem by Cecil Frances Alexander. The carol was first published in 1848 in her hymnbook Hymns for Little Children. A year later, the English organist Henry Gauntlett discovered the poem and set it to music.
The Chicago-Lambeth Quadrilateral, frequently referred to as the Lambeth Quadrilateral or the Lambeth-Chicago Quadrilateral, is a four-point articulation of Anglican identity, often cited as encapsulating the fundamentals of the Anglican Communion's doctrine and as a reference point for ecumenical discussion with other Christian denominations. The four points are:
- The Holy Scriptures, as containing all things necessary to salvation;
- The creeds, as the sufficient statement of Christian faith;
- The dominical sacraments of baptism and Holy Communion;
- The historic episcopate, locally adapted.
Anglican doctrine is the body of Christian teachings used to guide the religious and moral practices of Anglicans.

"Holy, Holy, Holy! Lord God Almighty!" is a Christian hymn written by the Anglican bishop Reginald Heber (1783–1826).

"Ye Watchers and Ye Holy Ones" is a popular Christian hymn with text by Athelstan Riley, first published in the English Hymnal (1906). It is sung to the German tune Lasst uns erfreuen (1623). Its uplifting melody and repeated "Alleluias" make this a favourite Anglo-Catholic hymn during the Easter season, the Feast of All Saints, and other times of great rejoicing.

Samuel John Stone was an English poet, hymnodist, and a priest in the Church of England.
The East–West Schism that occurred in 1054 represents one of the most significant events in the history of Christianity. It includes various events and processes that led to the schism and also those events and processes that occurred as a result of the schism. Eastern and Western Christians had a history of differences and disagreements, some dating back to the period of Early Christianity. At the very root of what later became the Great Schism were several questions of pneumatology and ecclesiology. The most important theological difference occurred over various questions regarding the procession of the Holy Spirit, and the use of the filioque clause in the Nicene Creed. One of the main ecclesiological issues was the question of papal supremacy. Other points of difference were related to various liturgical, ritual, and disciplinary customs and practices. Some political and cultural processes also contributed to the breakout of the schism.
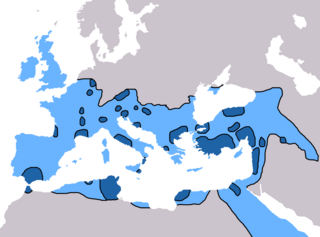
Christianity in the 4th century was dominated in its early stage by Constantine the Great and the First Council of Nicaea of 325, which was the beginning of the period of the First seven Ecumenical Councils (325–787), and in its late stage by the Edict of Thessalonica of 380, which made Nicene Christianity the state church of the Roman Empire.

Christianity in late antiquity traces Christianity during the Christian Roman Empire — the period from the rise of Christianity under Emperor Constantine, until the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The end-date of this period varies because the transition to the sub-Roman period occurred gradually and at different times in different areas. One may generally date late ancient Christianity as lasting to the late 6th century and the re-conquests under Justinian of the Byzantine Empire, though a more traditional end-date is 476, the year in which Odoacer deposed Romulus Augustus, traditionally considered the last western emperor.
The history of Eastern Orthodox Christian theology begins with the life of Jesus and the forming of the Christian Church. Major events include the Chalcedonian schism of 451 with the Oriental Orthodox miaphysites, the Iconoclast controversy of the 8th and 9th centuries, the Photian schism (863-867), the Great Schism between East and West, and the Hesychast controversy. The period after the end of the Second World War in 1945 saw a re-engagement with the Greek, and more recently Syriac Fathers that included a rediscovery of the theological works of St. Gregory Palamas, which has resulted in a renewal of Orthodox theology in the 20th and 21st centuries.

"Komm, Heiliger Geist, Herre Gott" is a Lutheran hymn for Pentecost, with words written by Martin Luther based on "Veni Sancte Spiritus, reple tuorum corda fidelium". The hymn in three stanzas was first published in 1524. For centuries the chorale has been the prominent hymn (Hauptlied) for Pentecost in German-speaking Lutheranism. Johann Sebastian Bach used it in several chorale preludes, cantatas and his motet Der Geist hilft unser Schwachheit auf, BWV 226.
Robert Hall Baynes was an Anglican priest, a hymnodist and a hymn writer. He was editor of the Lyra Anglicana, which was among the most influential hymnals of the Oxford Movement in the 1860s and 1870s, having a relatively broad selection of Anglican authors.

"Die güldne Sonne voll Freud und Wonne" is a Lutheran hymn by Paul Gerhardt. It is a morning hymn which was first published in 1666, with a four-part setting by Johann Georg Ebeling. Gerhardt created an unusual hymn metre for its 12 stanzas.

"There is a green hill far away" is a Christian hymn, originally written as a children's hymn but now usually sung for Passiontide. The words are by Cecil Frances Alexander, and the most popular tune by William Horsley.

"O Jesu Christe, wahres Licht" is a Lutheran hymn by the German Baroque poet, Lutheran minister and hymn-writer Johann Heermann. The text was first published in 1630 during the Thirty Years' War. It is a prayer for enlightenment of those who are ignorant, and of those who turned away. It was associated with a melody from Nürnberg, dating to 1676. The hymn is part of modern German hymnals, both Protestant and Catholic. It was translated to English as "O Christ, our true and only light".













