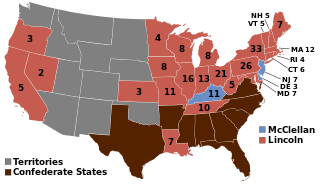
The 1864 United States presidential election was the 20th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1864. Near the end of the American Civil War, incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.

Samuel Medary was an American newspaper owner and politician.

In the 1860s, the Copperheads, also known as Peace Democrats, were a faction of Democrats in the Union who opposed the American Civil War and wanted an immediate peace settlement with the Confederates.

Clement Laird Vallandigham was an American lawyer and politician who served as the leader of the Copperhead faction of anti-war Democrats during the American Civil War.

During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States remaining after the secession of eleven Southern states to form the Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union, led by President Abraham Lincoln, is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it is also often used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government"; in this broader definitional meaning, the Union included 20 free states and five border states.

David Tod was an American politician and industrialist from the U.S. state of Ohio. As the 25th governor of Ohio, Tod gained recognition for his forceful and energetic leadership during the American Civil War.

The Knights of the Golden Circle (KGC) was a secret society founded in 1854 by American George W. L. Bickley, the objective of which was to create a new country, known as the Golden Circle, where slavery would be legal. The country would have been centered in Havana and would have consisted of the Southern United States and a "golden circle" of territories in Mexico, Central America, northern parts of South America, and Cuba, Haiti, Dominican Republic, and most other islands in the Caribbean, about 2,400 miles (3,900 km) in diameter.

Daniel Wolsey Voorhees was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States Senator from Indiana from 1877 to 1897. He was the leader of the Democratic Party and an anti-war Copperhead during the American Civil War.

Joel Parker was an American attorney and Democratic Party politician who served two non-consecutive terms as the 20th governor of New Jersey from 1863 to 1866 and 1872 to 1875. As a Democratic governor during the American Civil War, Parker was one of the leading critics of the Abraham Lincoln administration's domestic and military policy, though he was generally a supporter of the Union war effort. In 1868 and 1876, he was nominated for President of the United States as a favorite son by New Jersey's party delegation.

George Washington Lafayette Bickley was the founder of the Knights of the Golden Circle, a Civil War era secret society used to promote the interests of the Southern United States by preparing the way for annexation of a "golden circle" of territories in Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean which would be included into the United States as southern or slave states. Bickley was arrested by the United States government and it was during this time he wrote a letter to Abraham Lincoln expressing his distastes with Lincoln's handling of the government.
The 1864 Democratic National Convention was held at The Amphitheatre in Chicago, Illinois.

During the American Civil War, the State of Ohio played a key role in providing troops, military officers, and supplies to the Union army. Due to its central location in the Northern United States and burgeoning population, Ohio was both politically and logistically important to the war effort. Despite the state's boasting a number of very powerful Republican politicians, it was divided politically. Portions of Southern Ohio followed the Peace Democrats and openly opposed President Abraham Lincoln's policies. Ohio played an important part in the Underground Railroad prior to the war, and remained a haven for escaped and runaway slaves during the war years.
Popular opposition to the American Civil War, which lasted from 1861 to 1865, was widespread. Although there had been many attempts at compromise prior to the outbreak of war, there were those who felt it could still be ended peacefully or did not believe it should have occurred in the first place. Opposition took the form of both those in the North who believed the South had the right to be independent and those in the South who wanted neither war nor a Union advance into the newly declared Confederate States of America.

The American state of Virginia became a prominent part of the Confederacy when it joined during the American Civil War. As a Southern slave-holding state, Virginia held the state convention to deal with the secession crisis, and voted against secession on April 4, 1861. Opinion shifted after the Battle of Fort Sumter on April 12, and April 15, when U.S. President Abraham Lincoln called for troops from all states still in the Union to put down the rebellion. For all practical purposes, Virginia joined the Confederacy on April 17, though secession was not officially ratified until May 23. A Unionist government was established in Wheeling and the new state of West Virginia was created by an act of Congress from 50 counties of western Virginia, making it the only state to lose territory as a consequence of the war.

During the American Civil War, the Ohio River port city of Cincinnati, Ohio, played a key role as a major source of supplies and troops for the Union Army. It also served as the headquarters for much of the war for the Department of the Ohio, which was charged with the defense of the region, as well as directing the army's offensives into Kentucky and Tennessee.
Ex parte Vallandigham, 68 U.S. 243 (1864), is a United States Supreme Court case, involving a former congressman Clement Vallandigham of Ohio, who had violated an Army order against the public expression of sympathy for the Confederate States and their cause. Vallandigham was tried before a military tribunal by Major General Ambrose E. Burnside for treason after he delivered an incendiary speech at Mount Vernon; he then appealed the tribunal's verdict to the Supreme Court, arguing that he as a civilian could not be tried before a military tribunal.
The New Departure refers to the political strategy used by the Democratic Party in the United States after 1865 to distance itself from its pro-slavery and Copperhead history in an effort to broaden its political base, and focus on issues where it had more of an advantage, especially economic issues. The New Departure theory also argued that the Fourteenth Amendment and the Fifteenth Amendment had already given women suffrage, but that argument was rejected in state and federal courts.
War Democrats in American politics of the 1860s were members of the Democratic Party who supported the Union and rejected the policies of the Copperheads. The War Democrats demanded a more aggressive policy toward the Confederacy and supported the policies of Republican President Abraham Lincoln when the American Civil War broke out a few months after his victory in the 1860 presidential election.

During the American Civil War, the state of Illinois was a major source of troops for the Union Army, and of military supplies, food, and clothing. Situated near major rivers and railroads, Illinois became a major jumping off place early in the war for Ulysses S. Grant's efforts to seize control of the Mississippi and Tennessee rivers. Statewide, public support for the Union was high despite Copperhead sentiment.

In the 1864 U.S. presidential election, the Democrats nominated Union Army General George McClellan for U.S. President and Ohio U.S. Representative George Pendleton for U.S. Vice President. During the campaign, McClellan vowed to do a better job of prosecuting the Union Army effort in the American Civil War than incumbent U.S. President Abraham Lincoln did. Ultimately, the McClellan-Pendleton ticket lost to the National Union ticket of Abraham Lincoln and former U.S. Senator Andrew Johnson.













