
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids.
A hydrogen vehicle is a vehicle that uses hydrogen fuel for motive power. Hydrogen vehicles include hydrogen-fueled space rockets, as well as ships and aircraft. Power is generated by converting the chemical energy of hydrogen to mechanical energy, either by reacting hydrogen with oxygen in a fuel cell to power electric motors or, less commonly, by burning hydrogen in an internal combustion engine.

American Automobile Association is a federation of motor clubs throughout North America. AAA is a privately held not-for-profit national member association and service organization with over 60 million members in the United States and Canada. AAA provides services to its members, including roadside assistance and others. Its national headquarters are in Heathrow, Florida.

Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, which in turn may vary per application, and this spectrum of variance is often illustrated as a continuous energy profile. Non-transportation applications, such as industry, benefit from increased fuel efficiency, especially fossil fuel power plants or industries dealing with combustion, such as ammonia production during the Haber process.

The Toyota Prius is a car built by Toyota which has a hybrid drivetrain, combining an internal combustion engine with an electric motor. Initially offered as a four-door sedan, it has been produced only as a five-door liftback since 2003.
The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards are regulations in the United States, first enacted by the United States Congress in 1975, after the 1973–74 Arab Oil Embargo, to improve the average fuel economy of cars and light trucks produced for sale in the United States.

The Honda Insight is a hybrid electric vehicle that is manufactured and marketed by Honda. Its first generation was a two-door, two passenger liftback (1999–2006) and in its second generation was a four-door, five passenger liftback (2009–2014). In its third generation, it became a four-door sedan (2019–present). It was Honda's first model with Integrated Motor Assist system and the most fuel efficient gasoline-powered car available in the U.S. without plug-in capability — for the length of its production run.

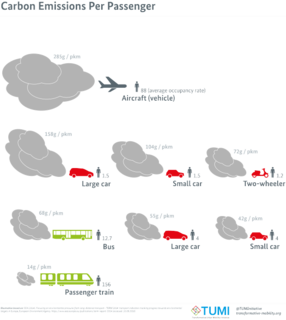
Sustainable transport refers to ways of transportation that are sustainable in terms of their social and environmental impacts. Components for evaluating sustainability include the particular vehicles used for road, water or air transport; the source of energy; and the infrastructure used to accommodate the transport. Transport operations and logistics as well as transit-oriented development are also involved in evaluation. Transportation sustainability is largely being measured by transportation system effectiveness and efficiency as well as the environmental and climate impacts of the system. Transport systems have significant impacts on the environment, accounting for between 20% and 25% of world energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions. The majority of the emissions, almost 97%, came from direct burning of fossil fuels. Greenhouse gas emissions from transport are increasing at a faster rate than any other energy using sector. Road transport is also a major contributor to local air pollution and smog.

A fuel cell vehicle (FCV) or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) is an electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell, sometimes in combination with a small battery or supercapacitor, to power its onboard electric motor. Fuel cells in vehicles generate electricity generally using oxygen from the air and compressed hydrogen. Most fuel cell vehicles are classified as zero-emissions vehicles that emit only water and heat. As compared with internal combustion vehicles, hydrogen vehicles centralize pollutants at the site of the hydrogen production, where hydrogen is typically derived from reformed natural gas. Transporting and storing hydrogen may also create pollutants.

A green vehicle, clean vehicle, eco-friendly vehicle or environmentally friendly vehicle is a road motor vehicle that produces less harmful impacts to the environment than comparable conventional internal combustion engine vehicles running on gasoline or diesel, or one that uses certain alternative fuels. Presently, in some countries the term is used for any vehicle complying or surpassing the more stringent European emission standards, or California's zero-emissions vehicle standards, or the low-carbon fuel standards enacted in several countries.

A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery pack can be recharged by plugging a charging cable into an external electric power source, in addition to internally by its on-board internal combustion engine-powered generator. Most PHEVs are passenger cars, but there are also PHEV versions of commercial vehicles and vans, utility trucks, buses, trains, motorcycles, mopeds, and even military vehicles.

A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that combines a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional vehicle or better performance. There is a variety of HEV types and the degree to which each function as an electric vehicle (EV) also varies. The most common form of HEV is the hybrid electric car, although hybrid electric trucks, buses, boats and aircraft also exist.

An alternative fuel vehicle is a motor vehicle that runs on alternative fuel rather than traditional petroleum fuels. The term also refers to any technology powering an engine that does not solely involve petroleum. Because of a combination of factors, such as environmental concerns, high oil-prices and the potential for peak oil, development of cleaner alternative fuels and advanced power systems for vehicles has become a high priority for many governments and vehicle manufacturers around the world.

The restyled North American second generation Ford Focus was sold by Ford as either a two-door coupe and 4-door sedan — the hatchbacks and wagon were discontinued.
Energy-efficient driving techniques are used by drivers who wish to reduce their fuel consumption, and thus maximize fuel efficiency. The use of these techniques is called "hypermiling".
The automotive industry crisis of 2008–2010 formed part of the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and the resulting Great Recession. The crisis affected European and Asian automobile manufacturers, but it was primarily felt in the American automobile manufacturing industry. The downturn also affected Canada by virtue of the Automotive Products Trade Agreement.

The Car Allowance Rebate System (CARS), colloquially known as "cash for clunkers", was a $3 billion U.S. federal scrappage program intended to provide economic incentives to U.S. residents to purchase a new, more fuel-efficient vehicle when trading in a less fuel-efficient vehicle. The program was promoted as a post-recession stimulus program to boost auto sales while putting more fuel-efficient vehicles on the roadways.

Environment America is a federation of state-based environmental advocacy organizations in the United States. The organization researches and advocates for environmental policies through lobbying, litigation, and the mobilization of public support. Environment America advocates new laws and policies to address climate change, air pollution and water pollution, and is a proponent of clean energy. It opposes offshore drilling.

TDI is Volkswagen Group's term for its current common rail direct injection turbodiesel engine range that have an intercooler in addition to the turbo compressor.

An automotive city or auto city is a city that facilitates and encourages the movement of people via private transportation, through 'physical planning', e.g., built environment innovations and 'soft programming' e.g., social policy surrounding city street usage.















