
Hypothetical types of biochemistry are forms of biochemistry agreed to be scientifically viable but not proven to exist at this time. The kinds of living organisms currently known on Earth all use carbon compounds for basic structural and metabolic functions, water as a solvent, and DNA or RNA to define and control their form. If life exists on other planets or moons it may be chemically similar, though it is also possible that there are organisms with quite different chemistries – for instance, involving other classes of carbon compounds, compounds of another element, or another solvent in place of water.

Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the second-largest in the Solar System, larger than any of the dwarf planets of the Solar System. It is the only moon known to have an atmosphere denser than the Earth's, and is the only known object in space other than Earth on which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found.
A propellant is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or another motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the engine that expels the propellant is called a reaction engine. Although technically a propellant is the reaction mass used to create thrust, the term "propellant" is often used to describe a substance which contains both the reaction mass and the fuel that holds the energy used to accelerate the reaction mass. For example, the term "propellant" is often used in chemical rocket design to describe a combined fuel/propellant, although the propellants should not be confused with the fuel that is used by an engine to produce the energy that expels the propellant. Even though the byproducts of substances used as fuel are also often used as a reaction mass to create the thrust, such as with a chemical rocket engine, propellant and fuel are two distinct concepts.

Tholins are a wide variety of organic compounds formed by solar ultraviolet or cosmic ray irradiation of simple carbon-containing compounds such as carbon dioxide, methane or ethane, often in combination with nitrogen or water. Tholins are disordered polymer-like materials made of repeating chains of linked subunits and complex combinations of functional groups, typically nitriles and hydrocarbons, and their degraded forms such as amines and phenyls. Tholins do not form naturally on modern-day Earth, but they are found in great abundance on the surfaces of icy bodies in the outer Solar System, and as reddish aerosols in the atmospheres of outer Solar System planets and moons.

Halomethane compounds are derivatives of methane with one or more of the hydrogen atoms replaced with halogen atoms. Halomethanes are both naturally occurring, especially in marine environments, and human-made, most notably as refrigerants, solvents, propellants, and fumigants. Many, including the chlorofluorocarbons, have attracted wide attention because they become active when exposed to ultraviolet light found at high altitudes and destroy the Earth's protective ozone layer.
"The Dying Night" is a science fiction short story by American writer Isaac Asimov. The story first appeared in the July 1956 issue of The Magazine of Fantasy & Science Fiction, and was reprinted in the collections Nine Tomorrows (1959), Asimov's Mysteries (1968), and The Best of Isaac Asimov (1973). "The Dying Night" is Asimov's third Wendell Urth story.

The Death Dealers is a 1958 mystery novel by American writer Isaac Asimov. It is about a university professor whose research student dies while conducting an experiment. The professor attempts to determine if the death was accident, suicide or murder.
Asimov's Mysteries, published in 1968, is a collection of 14 short stories by American writer Isaac Asimov, almost all of them science fiction mysteries. The stories were all originally published in magazines between 1954 and 1967, except for "Marooned off Vesta", Asimov's first published story, which first appeared in 1939.
"The Singing Bell" is a science fiction mystery short story by American writer Isaac Asimov, which first appeared in the January 1955 issue of The Magazine of Fantasy and Science Fiction and was reprinted in the 1968 collection Asimov's Mysteries. "The Singing Bell" was the first of Asimov's Wendell Urth stories.

Saturn's largest moon Titan is one of several candidates for possible future colonization of the outer Solar System, though protection against extreme cold is a major consideration.

The atmosphere of Mars is the layer of gases surrounding Mars. It is primarily composed of carbon dioxide (95%), molecular nitrogen (2.85%), and argon (2%). It also contains trace levels of water vapor, oxygen, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and noble gases. The atmosphere of Mars is much thinner and colder than Earth's having a max density 20g/m3 with a temperature generally below zero down to -60 Celsius. The average surface pressure is about 610 pascals (0.088 psi) which is less than 1% of the Earth's value.
The study of extraterrestrial atmospheres is an active field of research, both as an aspect of astronomy and to gain insight into Earth's atmosphere. In addition to Earth, many of the other astronomical objects in the Solar System have atmospheres. These include all the gas giants, as well as Mars, Venus and Titan. Several moons and other bodies also have atmospheres, as do comets and the Sun. There is evidence that extrasolar planets can have an atmosphere. Comparisons of these atmospheres to one another and to Earth's atmosphere broaden our basic understanding of atmospheric processes such as the greenhouse effect, aerosol and cloud physics, and atmospheric chemistry and dynamics.

Whether there is life on Titan, the largest moon of Saturn, is currently an open question and a topic of scientific assessment and research. Titan is far colder than Earth, but of all the places in the Solar System, Titan is the only place besides Earth known to have liquids in the form of rivers, lakes, and seas on its surface. Its thick atmosphere is chemically active and rich in carbon compounds. On the surface there are small and large bodies of both liquid methane and ethane, and it is likely that there is a layer of liquid water under its ice shell. Some scientists speculate that these liquid mixes may provide prebiotic chemistry for living cells different from those on Earth.

The atmosphere of Titan is the dense layer of gases surrounding Titan, the largest moon of Saturn. Titan is the only natural satellite in the Solar System with an atmosphere that is denser than the atmosphere of Earth and is one of two moons with an atmosphere significant enough to drive weather. Titan's lower atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (94.2%), methane (5.65%), and hydrogen (0.099%). There are trace amounts of other hydrocarbons, such as ethane, diacetylene, methylacetylene, acetylene, propane, PAHs and of other gases, such as cyanoacetylene, hydrogen cyanide, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, cyanogen, acetonitrile, argon and helium. The isotopic study of nitrogen isotopes ratio also suggests acetonitrile may be present in quantities exceeding hydrogen cyanide and cyanoacetylene. The surface pressure is about 50% higher than on Earth at 1.5 bars which is near the triple point of methane and allows there to be gaseous methane in the atmosphere and liquid methane on the surface. The orange color as seen from space is produced by other more complex chemicals in small quantities, possibly tholins, tar-like organic precipitates.

Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4. It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is hard because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure.

The Best Mysteries of Isaac Asimov is a collection of mystery short stories by American author Isaac Asimov. It was first published in hardcover by Doubleday in 1986, and in paperback by the Fawcett Crest imprint of Ballantine Books in September 1987.

The Key is a science fiction mystery novelette by American writer Isaac Asimov. It is one of the stories featuring the reclusive scientist Wendell Urth. It first appeared in The Magazine of Fantasy & Science Fiction in October 1966, and was reprinted in the anthologies Asimov's Mysteries (1968) and The Best Mysteries of Isaac Asimov (1986).

Chemical cycling describes systems of repeated circulation of chemicals between other compounds, states and materials, and back to their original state, that occurs in space, and on many objects in space including the Earth. Active chemical cycling is known to occur in stars, many planets and natural satellites.
Depending on the counting convention used, and including all titles, charts, and edited collections, there may be currently over 500 books in Isaac Asimov's bibliography—as well as his individual short stories, individual essays, and criticism. For his 100th, 200th, and 300th books, Asimov published Opus 100 (1969), Opus 200 (1979), and Opus 300 (1984), celebrating his writing.
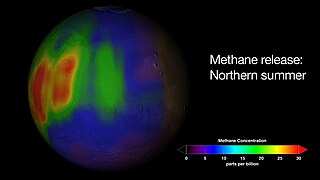
The reported presence of methane in the atmosphere of Mars is of interest to many geologists and astrobiologists, as methane may indicate the presence of microbial life on Mars, or a geochemical process such as volcanism or hydrothermal activity.















