
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Ancient Greek and Roman literature and their original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics may also include as secondary subjects Greco-Roman philosophy, history, archaeology, anthropology, art, mythology, and society.
Digamma or wau is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. It originally stood for the sound but it has remained in use principally as a Greek numeral for 6. Whereas it was originally called waw or wau, its most common appellation in classical Greek is digamma; as a numeral, it was called episēmon during the Byzantine era and is now known as stigma after the Byzantine ligature combining σ-τ as ϛ.

An idiot, in modern use, is a stupid or foolish person.
A sophist was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BCE. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics and mathematics. They taught arete, "virtue" or "excellence", predominantly to young statesmen and nobility.

Polis means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word polis had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, today's πόλη is located within a χώρα (khôra), "country", which is a πατρίδα (patrida) or "native land" for its citizens. In ancient Greece, the polis was the native land; there was no other. It had a constitution and demanded the supreme loyalty of its citizens. χώρα was only the countryside, not a country. Ancient Greece was not a sovereign country, but was a territory occupied by Hellenes, people who claimed as their native language some dialect of Ancient Greek.

The Battle of Thermopylae was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it was one of the most prominent battles of both the second Persian invasion of Greece and the wider Greco-Persian Wars.

A tyrant, in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to repressive means. The original Greek term meant an absolute sovereign who came to power without constitutional right, yet the word had a neutral connotation during the Archaic and early Classical periods. However, Greek philosopher Plato saw tyrannos as a negative form of government, and on account of the decisive influence of philosophy on politics, deemed tyranny the "fourth and worst disorder of a state."
Tyrants lack "the very faculty that is the instrument of judgment"—reason. The tyrannical man is enslaved because the best part of him (reason) is enslaved, and likewise, the tyrannical state is enslaved, because it too lacks reason and order.
The English expression the hoi polloi was borrowed from Ancient Greek, where it means "the many" or, in the strictest sense, "the people". In English, it has been given a negative connotation to signify the common people. Synonyms for hoi polloi include "the plebs" (plebeians), "the rabble", "the masses", "the great unwashed", "the riffraff", and "the proles" (proletarians).

The Temple of Hephaestus or Hephaisteion, is a well-preserved Greek temple dedicated to Hephaestus; it remains standing largely intact today. It is a Doric peripteral temple, and is located at the north-west side of the Agora of Athens, on top of the Agoraios Kolonos hill. From the 7th century until 1834, it served as the Greek Orthodox church of Saint George Akamates. The building's condition has been maintained due to its history of varied use.

The Frogs is a comedy written by the Ancient Greek playwright Aristophanes. It was performed at the Lenaia, one of the Festivals of Dionysus in Athens, in 405 BC and received first place.

The Epistle to Diognetus is an example of Christian apologetics, writings defending Christianity against the charges of its critics. The Greek writer and recipient are not otherwise known. Estimates of dating based on the language and other textual evidence have ranged from AD 130, to the general era of Melito of Sardis, Athenagoras of Athens, and Tatian.
Rex Warner was an English classicist, writer, and translator. He is now probably best remembered for The Aerodrome (1941). Warner was described by V. S. Pritchett as "the only outstanding novelist of ideas whom the decade of ideas produced".

Barry Unsworth FRSL was an English writer known for his historical fiction. He published 17 novels, and was shortlisted for the Booker Prize three times, winning once for the 1992 novel Sacred Hunger.
Louis George Alexander was a British teacher and the author of numerous EFL course books, including New Concept English.

The Songs of Kings was a novel published in 2002 by Barry Unsworth that retells the story of Iphigenia at Aulis told by the Greek tragic poet Euripides.

The 300 Spartans is a 1962 CinemaScope epic historical drama film depicting the Battle of Thermopylae. It was directed by Rudolph Maté and stars Richard Egan, Ralph Richardson, David Farrar, Diane Baker, and Barry Coe. Produced with the cooperation of the Greek government, it was filmed in the village of Perachora in the Peloponnese.

The Parian Chronicle or Parian Marble is a Greek chronology, covering the years from 1582 BC to 299 BC, inscribed on a stele. Found on the island of Paros in two sections, and sold in Smyrna in the early 17th century to an agent for Thomas Howard, Earl of Arundel, this inscription was deciphered by John Selden and published among the Arundel Marbles, Marmora Arundelliana nos. 1–14, 59–119. The first of the sections published by Selden has subsequently disappeared. A further third fragment of this inscription, comprising the base of the stele and containing the end of the text, was found on Paros in 1897. It has entries from 336/35 to 299/98 BC.

The Academy, variously known as Plato's Academy, the Platonic Academy, and the Academic School, was founded at Athens by Plato circa 387 BC. Aristotle studied there for twenty years before founding his own school, the Lyceum. The Academy persisted throughout the Hellenistic period as a skeptical school, until coming to an end after the death of Philo of Larissa in 83 BC. The Platonic Academy was destroyed by the Roman dictator Sulla in 86 BC.

John 6 is the sixth chapter of the Gospel of John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It records Jesus' miracles of feeding the five thousand and walking on water, the Bread of Life Discourse, popular rejection of his teaching, and Peter's confession of faith. The final verses anticipate Jesus' betrayal by Judas Iscariot.
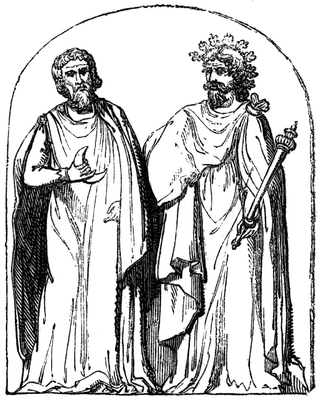
A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. While they were reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form. Their beliefs and practices are attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks.















